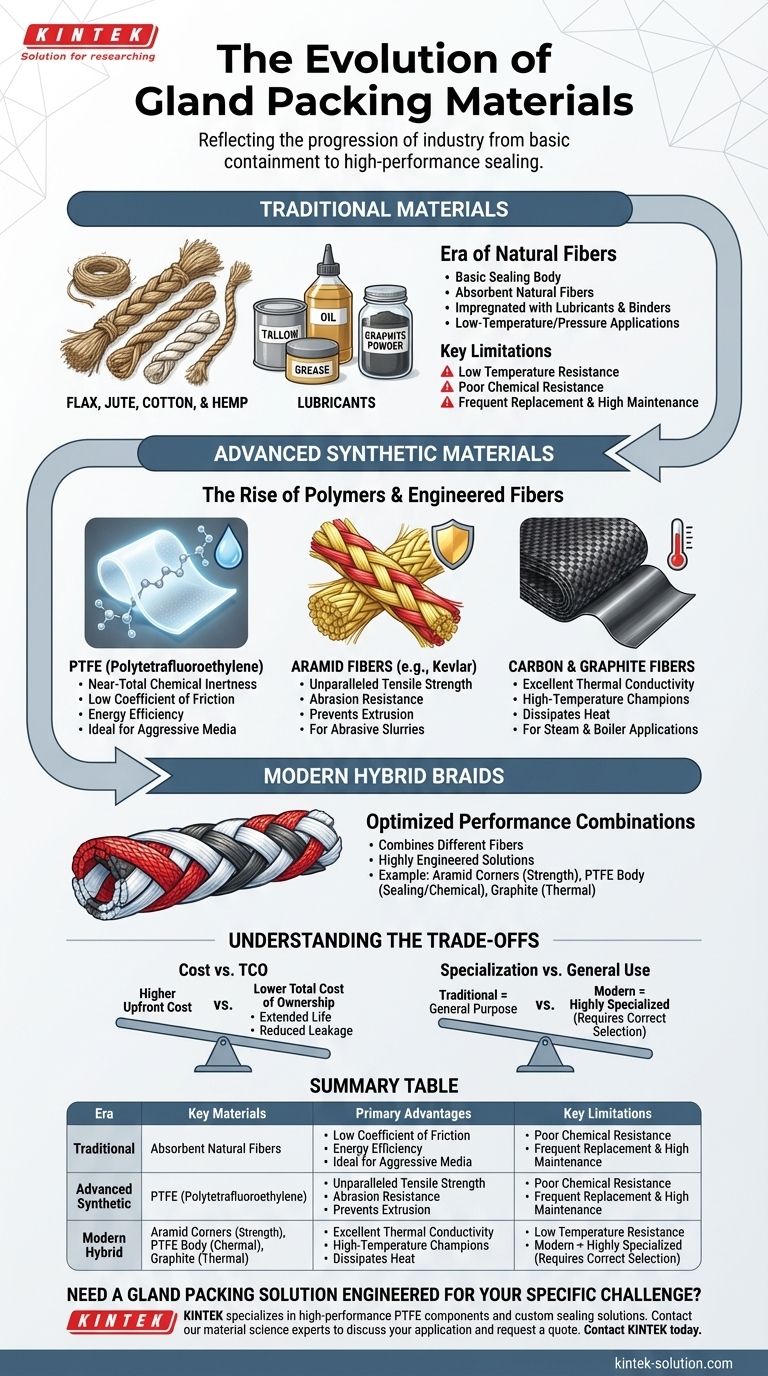
The evolution of gland packing materials reflects the evolution of industry itself, moving from basic natural fibers to highly engineered synthetic compounds. This progression was driven by a constant demand for seals that could withstand higher temperatures, more aggressive chemicals, and greater mechanical stress while reducing maintenance and leakage.
The core evolution of gland packing is a shift from simple containment using traditional, lubricated fibers to high-performance sealing using specialized synthetic materials engineered for specific industrial challenges.

The Era of Traditional Materials
Early gland packing was focused on a single task: physically blocking a leak path. The materials were readily available and sufficient for the low-temperature, low-pressure applications of the time.
The Foundation: Natural Fibers
The first packing materials were organic. Flax, jute, cotton, and hemp were braided into ropes, providing a basic but effective sealing body.
These materials were absorbent, which was a key feature. They were designed to soak up lubricants that were essential for their function.
The Role of Lubricants and Binders
Natural fibers alone are not effective seals. They were impregnated with lubricants like tallow, grease, or oil to reduce friction on the rotating shaft and help fill microscopic leak paths.
Later, graphite powder was added as a dry lubricant, which significantly improved temperature resistance and reduced friction compared to grease alone.
Inherent Limitations
Traditional materials have clear operational ceilings. They cannot withstand high temperatures, breaking down and charring easily.
They also offer very poor resistance to a wide range of chemicals, particularly aggressive acids and caustics. This forced frequent replacement and created significant operational risk.
The Shift to Advanced Synthetic Materials
As industrial processes advanced, the limitations of natural fibers became a critical point of failure. The development of synthetic polymers created a new class of sealing materials designed for performance and reliability.
The Rise of PTFE
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) was a revolutionary development. Its near-total chemical inertness made it the ideal solution for sealing aggressive media that would destroy natural fibers.
Its exceptionally low coefficient of friction also meant that pumps required less energy and generated less heat at the stuffing box, increasing the longevity of both the packing and the equipment shaft.
The Strength of Aramid Fibers
For applications involving abrasive media like slurries, a material with high mechanical strength was needed. Aramid fibers (such as Kevlar) provided unparalleled tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
This prevented the packing from being extruded out of the stuffing box under high pressure and resisted being worn away by abrasive particles in the process fluid.
The High-Temperature Champions: Carbon and Graphite
To handle high-temperature applications like steam valves and boiler feed pumps, materials that would not burn or degrade were required. Flexible graphite and carbon fibers filled this need perfectly.
These materials offer excellent thermal conductivity to dissipate heat away from the shaft and can maintain their integrity and sealing force at temperatures far beyond the limits of any other material.
The Power of Hybrid Braids
The most modern evolution is the combination of materials. Hybrid packings use different fibers in a single braid to optimize performance for specific challenges.
A common example is a packing with strong aramid corners to prevent extrusion, a PTFE body for excellent sealing and chemical resistance, and a graphite lubricant for thermal management. This represents a highly engineered, application-specific solution.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a modern material is not always a simple upgrade. The transition from traditional to synthetic packing introduces new considerations that must be balanced.
Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
Advanced synthetic packings have a significantly higher upfront purchase price than traditional materials.
However, their extended service life, reduced product leakage, and lower maintenance requirements often result in a lower total cost of ownership over the equipment's lifecycle.
Specialization vs. General Use
Traditional vegetable fiber packings were often seen as a general-purpose, "one-size-fits-most" solution for basic water or oil service.
Modern materials are highly specialized. Using a packing designed for chemicals in an abrasive slurry application (or vice-versa) will lead to premature failure. Correct material selection is critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The goal is to match the material's capabilities to the operational demands of the equipment.
- If your primary focus is general water service at low pressures and temperatures: A traditional, well-lubricated natural fiber packing can remain a cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals: PTFE-based packings provide the necessary chemical inertness and low-friction performance.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature steam or thermal fluids: Flexible graphite or carbon fiber packings are the only reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is abrasive slurries or high-pressure applications: Aramid fiber or hybrid packings deliver the essential strength and wear resistance.
Ultimately, modern gland packing provides a precise engineering solution to a specific sealing problem.
Summary Table:
| Era | Key Materials | Primary Advantages | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Flax, Jute, Cotton, Hemp | Low cost, suitable for basic water/oil service | Low temperature & chemical resistance, high maintenance |
| Advanced Synthetic | PTFE, Aramid Fibers, Graphite/Carbon | High chemical resistance, abrasion resistance, high-temperature capability | Higher initial cost, requires specific application knowledge |
| Modern Hybrid | Combinations (e.g., Aramid/PTFE/Graphite) | Optimized performance for specific challenges (e.g., abrasion + chemicals) | Most specialized, highest cost |
Need a Gland Packing Solution Engineered for Your Specific Challenge?
Choosing the right material is critical for performance and cost-efficiency. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals and packings, for the most demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We combine precision production with custom fabrication expertise—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to deliver a sealing solution that meets your exact operational requirements.
Let our material science experts help you select or design the optimal packing for your equipment. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and request a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the composition of graphite packing? The Science Behind a High-Performance Seal
- Why are fillers added to PTFE compounds? Enhance Wear, Strength, and Performance
- What are some common PTFE-based sealing components and their functions? Discover High-Performance Sealing Solutions
- What safety features do PTFE lined butterfly valves offer? Ensure Leak-Free Containment of Hazardous Media
- What are O-rings and why are they commonly used? A Guide to Simple, Reliable Sealing
- What industries benefit from using PTFE gaskets in ball valves? Ensure Purity & Reliability in Critical Processes
- What considerations are important when designing Teflon machined parts? Avoid Failure with Smart PTFE Design
- What are some examples of ePTFE applications in aerospace and automotive industries? Critical Components for Extreme Environments



















