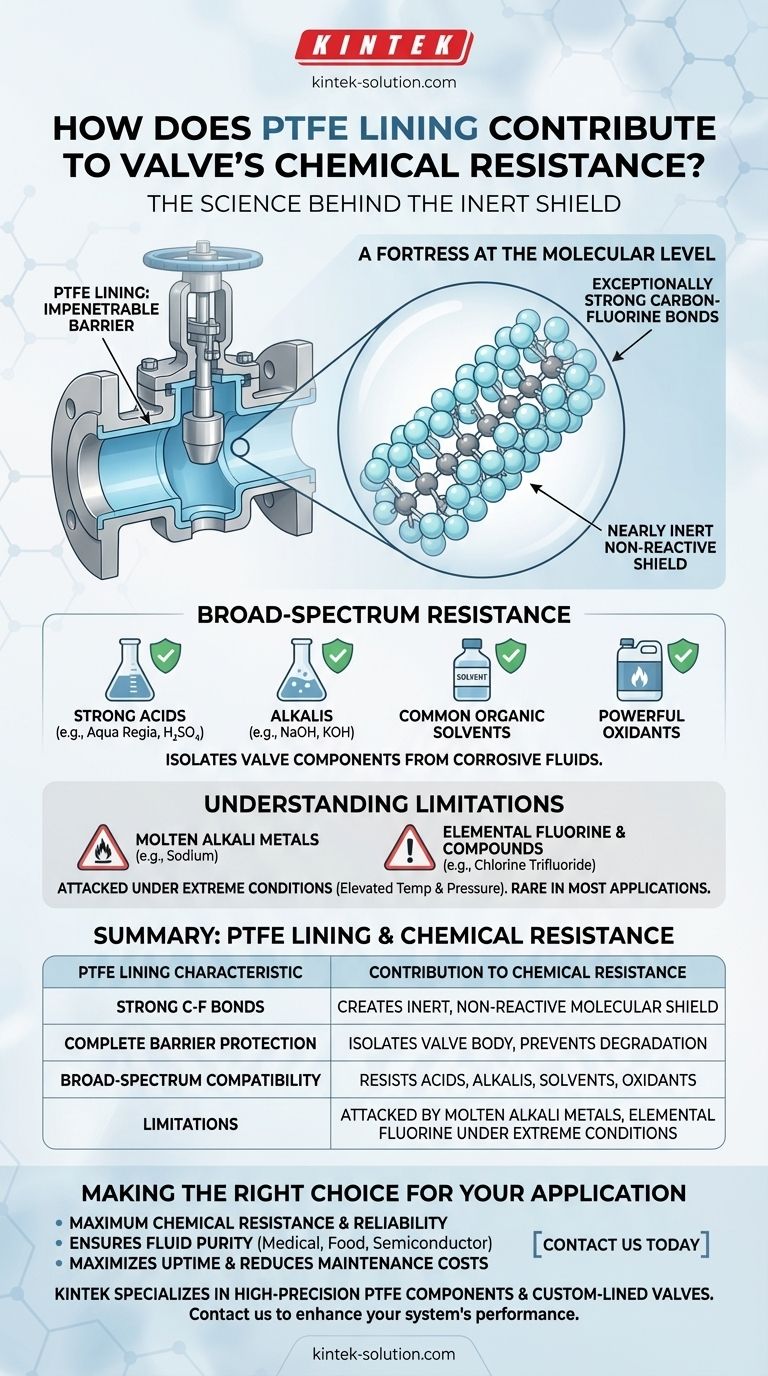
At its core, the PTFE lining provides chemical resistance because it is one of the most chemically inert substances known. Its stable molecular structure creates a non-reactive barrier that effectively isolates the valve's core components from virtually all corrosive fluids, including strong acids, alkalis, solvents, and powerful oxidants.
The exceptional strength of the carbon-fluorine bond in Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) makes the material almost completely non-reactive. This inertness creates a protective shield, preventing harsh chemicals from ever contacting and corroding the underlying valve body.

The Science Behind PTFE's Chemical Shield
To understand why PTFE is so effective, we must look at its molecular structure. It's not just a coating; it's a fundamental chemical defense.
A Fortress at the Molecular Level
The PTFE molecule consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by fluorine atoms.
The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable.
This creates a tight, protective "sheath" of fluorine atoms that shields the vulnerable carbon backbone from chemical attack, making the entire molecule nearly inert.
An Impenetrable Barrier for the Valve
This non-reactive lining acts as a complete barrier between the process fluid and the valve's structural materials (typically metal).
It protects the valve from corrosion and chemical damage that would otherwise degrade its integrity and cause it to fail.
Broad-Spectrum Resistance
This molecular stability gives PTFE its remarkable resistance to an incredibly wide range of aggressive media.
It can withstand exposure to aqua regia, all common organic solvents, strong acids, strong bases, and powerful oxidizing agents without degrading.
Understanding the Limitations
While its resistance is exceptional, it's crucial to recognize that "nearly inert" is not the same as "absolutely inert." For a technical professional, knowing the boundaries is as important as knowing the capabilities.
Near-Universal, But Not Absolute
PTFE’s primary weakness is against a very specific class of chemicals.
It can be attacked by molten alkali metals (like sodium), elemental fluorine, and certain fluorine compounds like chlorine trifluoride.
The Role of Extreme Conditions
These reactions typically only occur under conditions of elevated temperature and pressure.
For the vast majority of industrial and medical applications, these exceptions are not a concern, and PTFE remains the superior choice for chemical compatibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a PTFE-lined valve is a strategic decision based on the demands of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive or mixed chemical streams: PTFE's broad-spectrum resistance offers the highest level of security and reliability.
- If your primary focus is maintaining fluid purity (medical, food, or semiconductor): PTFE's inert nature ensures it will not react with or leach into the process medium, preventing contamination.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime and reducing maintenance costs: PTFE's durability against chemical attack directly translates to longer valve life and less frequent, costly downtime.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE lining is an investment in stability, ensuring the integrity of your system against the most demanding chemical environments.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Lining Characteristic | Contribution to Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|
| Strong Carbon-Fluorine Bonds | Creates a nearly inert, non-reactive molecular shield. |
| Complete Barrier Protection | Isolates valve body from corrosive fluids, preventing degradation. |
| Broad-Spectrum Compatibility | Resists strong acids, alkalis, solvents, and oxidants. |
| Limitations | Can be attacked by molten alkali metals and elemental fluorine under extreme conditions. |
Need a valve that can handle your most aggressive chemical processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom-lined valves, seals, and liners. Our expertise ensures your equipment delivers maximum chemical resistance, purity, and uptime for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision to meet your exact specifications.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how our PTFE solutions can enhance your system's reliability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications



















