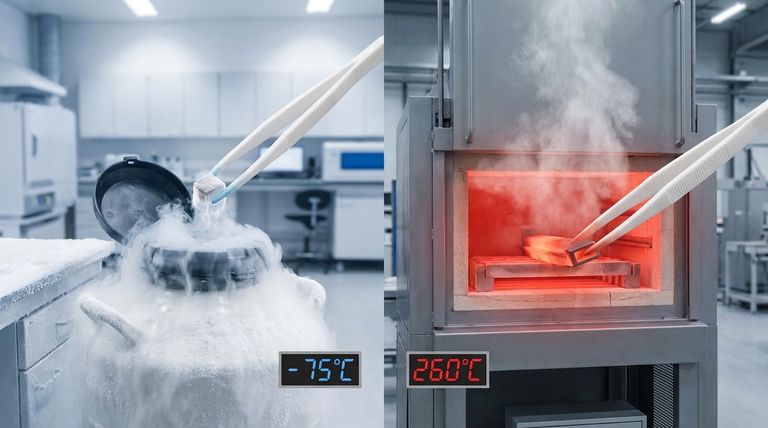
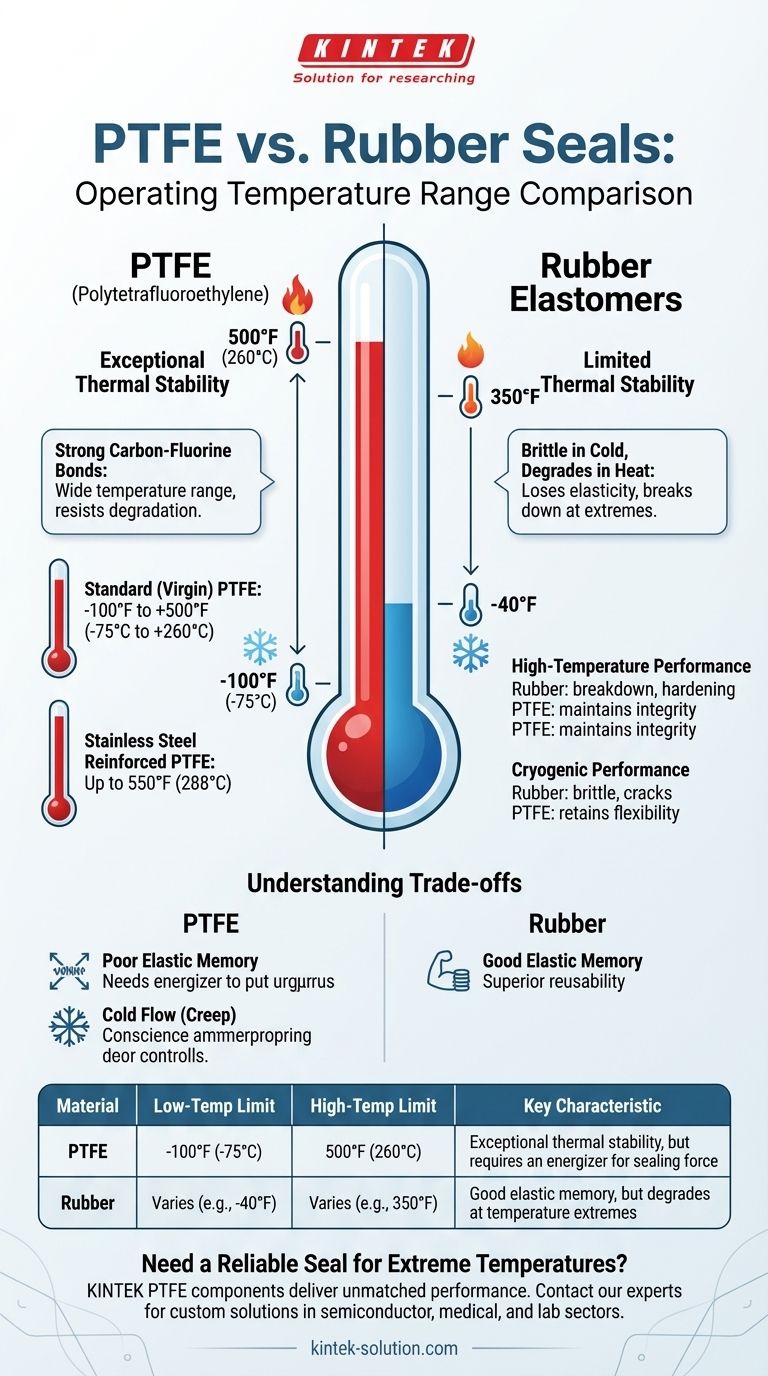
Simply put, PTFE operates in a vastly wider temperature range than rubber. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) seals can reliably function from cryogenic lows of around -100°F (-75°C) up to high temperatures of 500°F (260°C). This thermal stability far exceeds the capabilities of most common rubber elastomers, which become brittle in the cold and degrade quickly in high heat.
The core difference lies in their chemical structure. PTFE's strong carbon-fluorine bonds give it exceptional thermal stability, making it the default choice for applications involving extreme temperatures where rubber seals would fail catastrophically.

Why PTFE Excels at Temperature Extremes
The performance difference between PTFE and rubber is not incremental; it is a fundamental consequence of their molecular makeup. Understanding this helps clarify why material selection is so critical.
High-Temperature Performance
At elevated temperatures, rubber compounds begin to break down. They can lose their elasticity, become permanently hardened, or even revert to a soft, gummy state, destroying their ability to maintain a seal.
PTFE, by contrast, maintains its structural integrity and sealing properties well into temperatures that would incinerate most elastomers. This makes it essential for high-temperature industrial processes and engine components.
Cryogenic and Low-Temperature Performance
As temperatures drop, rubber elastomers lose their flexibility and become hard and brittle. A brittle seal will crack under pressure or vibration, leading to immediate leaks.
PTFE retains a significant degree of its flexibility even at cryogenic temperatures. This unique property makes it indispensable for applications in aerospace, deep space environments, and liquefied gas systems.
A Closer Look at PTFE Temperature Ranges
While PTFE's overall temperature range is impressive, specific grades and formulations can have slightly different ratings. The exact limits depend on the use of fillers and reinforcements.
Standard (Virgin) PTFE
The generally accepted operating range for standard, unfilled PTFE is approximately -100°F to +500°F (-75°C to +260°C). This range covers the vast majority of extreme-temperature sealing needs.
The Role of Fillers and Reinforcements
Adding materials like carbon, glass, or stainless steel can modify PTFE's properties. For instance, stainless steel reinforced PTFE can extend the upper service limit to 550°F (288°C).
These fillers not only adjust the temperature range but also improve other characteristics like wear resistance and resistance to creep (cold flow).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its thermal advantages, PTFE is not a universal replacement for rubber. Its unique properties introduce critical design trade-offs that must be considered.
Lack of Elastic Memory
The most significant difference is that PTFE is not a true elastomer. Unlike rubber, it does not spring back to its original shape after being compressed. It has poor elastic memory.
Because of this, PTFE seals often require a separate energizer, such as a metal spring or a rubber O-ring, to provide the constant force needed to maintain a seal.
The Issue of Cold Flow (Creep)
Under sustained pressure, especially at higher temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform over time. This phenomenon, known as creep or cold flow, can compromise the long-term integrity of a seal if not accounted for in the design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal material is a function of your system's specific operating conditions. Balancing performance, design complexity, and cost is key.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability: PTFE is the definitive and often only viable choice for applications operating below -60°F or above 350°F.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost seal in a moderate temperature range: A standard rubber elastomer is typically the more practical and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is reusability and elastic sealing: Rubber's ability to rebound after compression makes it far superior for applications that require repeated sealing cycles without a mechanical energizer.
Ultimately, choosing the right material means matching its inherent properties to the specific thermal and mechanical demands of your design.
Summary Table:
| Material | Low-Temperature Limit | High-Temperature Limit | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | -100°F (-75°C) | 500°F (260°C) | Exceptional thermal stability, but requires an energizer for sealing force |
| Rubber | Varies (e.g., -40°F) | Varies (e.g., 350°F) | Good elastic memory, but degrades at temperature extremes |
Need a Reliable Seal for Extreme Temperatures?
Your application's thermal demands are critical. While rubber seals fail under extreme heat or cryogenic cold, PTFE components from KINTEK deliver unmatched performance from -100°F to 500°F (-75°C to 260°C) and beyond.
We specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a custom prototype or high-volume production, our expertise ensures a solution that guarantees integrity and performance under your specific operating conditions.
Let's engineer the perfect seal for your application. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems



















