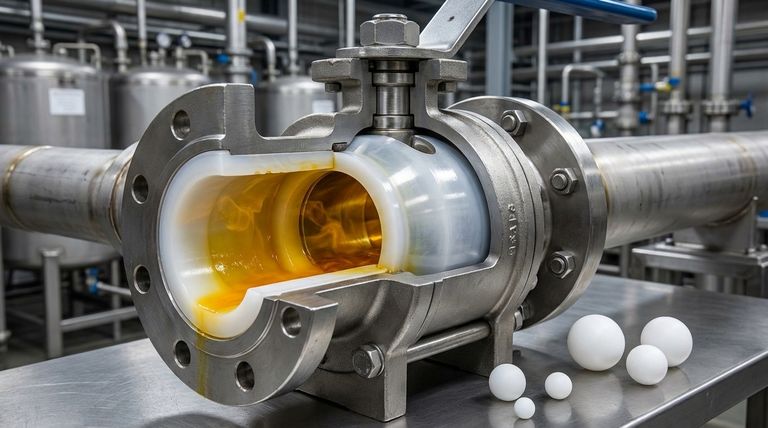
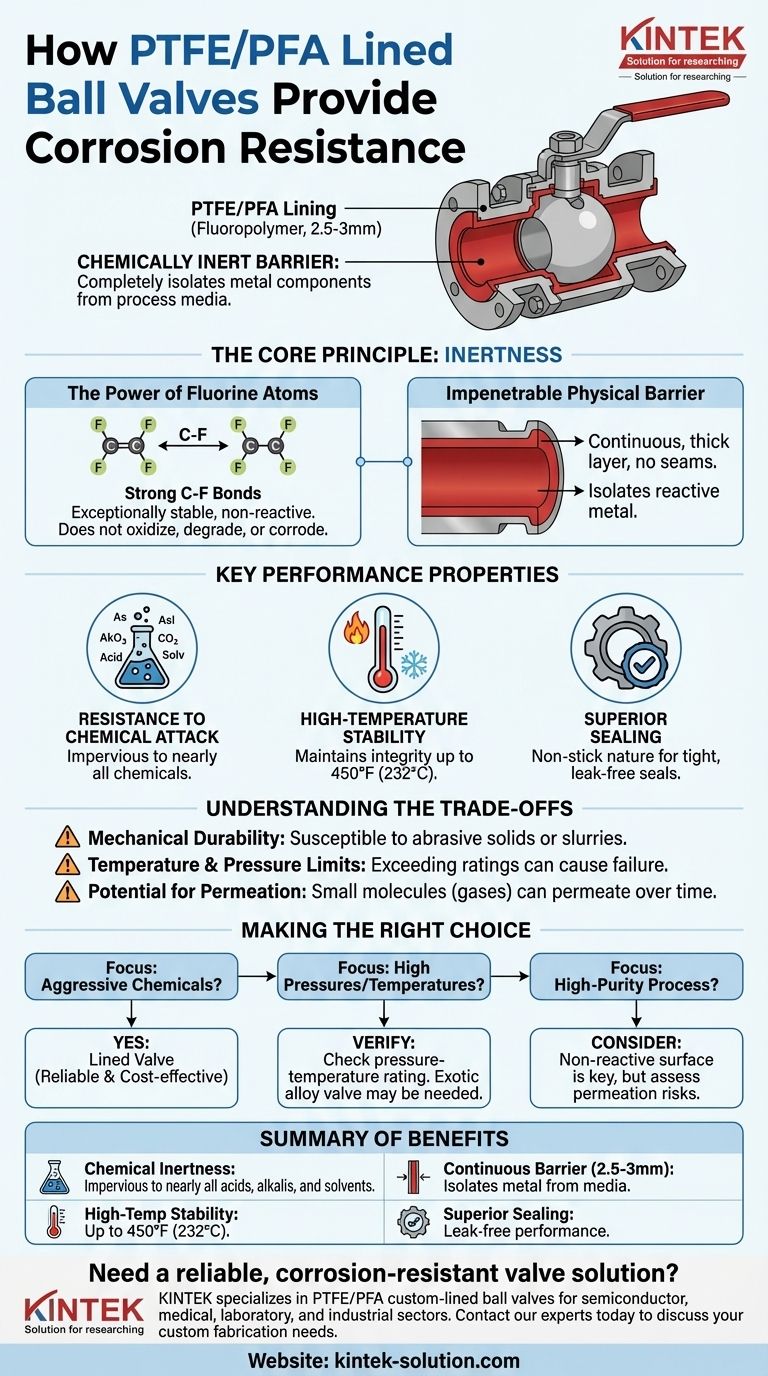
A PTFE/PFA lining provides corrosion resistance by creating a chemically inert barrier that completely isolates the valve's metal components from the process media. This fluoropolymer lining, typically 2.5-3mm thick, is molded to the interior of the valve body and the exterior of the ball, preventing aggressive substances like acids, alkalis, and salts from ever making physical contact with the structural metal.
The core principle of a lined valve is to leverage the best properties of two different materials. The outer metal body provides mechanical strength and pressure containment, while the inner fluoropolymer lining provides near-universal immunity to chemical attack, a task for which most metals are unsuited.

The Core Principle of Chemical Inertness
The effectiveness of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) and PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) linings stems from their unique molecular structure. This structure is what grants them their exceptional resistance to corrosion.
The Power of Fluorine Atoms
PTFE and PFA are fluoroplastics, a class of polymers containing strong carbon-fluorine bonds. These bonds are exceptionally stable and non-reactive.
This molecular stability means the lining material itself does not participate in chemical reactions. It will not oxidize, degrade, or corrode when exposed to even the most aggressive process fluids.
An Impenetrable Physical Barrier
The lining is applied as a continuous, thick layer (typically 2.5-3mm) without seams or joints inside the wetted areas of the valve.
This thickness ensures a robust physical shield. It isolates the reactive metal casting of the valve from the corrosive media, effectively making the internal character of the valve entirely that of the fluoropolymer.
Key Properties That Ensure Performance
Beyond simple inertness, several other characteristics of PTFE and PFA make them ideal for creating a reliable, long-lasting barrier against corrosion.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
The lining is impervious to a wide range of chemicals, including nearly all acids, alkalis, and solvents. Unlike exotic metal alloys that have specific resistances, fluoropolymers offer a much broader range of chemical compatibility.
High-Temperature Stability
PTFE linings can maintain their integrity and plasticity at continuous operating temperatures up to 450°F (232°C). This allows them to be used in heated chemical processes where other materials might fail.
Superior Sealing Capabilities
The same properties that make PTFE and PFA excellent lining materials also make them superior for gaskets and seals. Their non-stick nature and ability to conform under pressure create a tight, leak-free seal between valve components, preventing fugitive emissions of corrosive media.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, lined valves are an engineered solution with specific limitations that must be respected for safe and reliable operation.
Mechanical Durability
Fluoropolymer linings are softer than metal. They can be susceptible to damage from abrasive solids or slurries in the process media, which could scratch or erode the lining and expose the underlying metal.
Temperature and Pressure Limits
Every lined valve has a specific pressure-temperature rating curve. Exceeding these limits can cause the lining to deform or lose its seal, leading to catastrophic failure. While their temperature range is good, they cannot match the operational envelope of solid high-alloy valves.
Potential for Permeation
While the lining is a solid barrier, extremely small molecules (like certain gases such as chlorine or hydrogen) can sometimes slowly permeate through the polymer over a long period. This is a critical consideration in very specific high-purity or hazardous gas applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve requires matching its capabilities to your specific operational goal.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals like strong acids or alkalis: A lined valve is often the most reliable and cost-effective solution available.
- If your primary focus is managing high pressures or temperatures: You must verify that the valve's pressure-temperature rating meets your operational demands, as a solid exotic alloy valve may be required.
- If your primary focus is avoiding contamination in a high-purity process: The non-reactive surface of PTFE/PFA is a significant advantage, but you must consider any potential for media permeation.
By understanding how a fluoropolymer lining provides protection, you can confidently specify the right valve to ensure long-term operational integrity and safety.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Impervious to nearly all acids, alkalis, and solvents. |
| Continuous Barrier (2.5-3mm) | Isolates metal components completely from process media. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains integrity at continuous temperatures up to 450°F (232°C). |
| Superior Sealing | Non-stick nature ensures leak-free performance and prevents fugitive emissions. |
Need a reliable, corrosion-resistant valve solution for your critical process?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE and PFA components, including custom-lined ball valves for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure your equipment is protected from aggressive chemicals, enhancing operational integrity and safety.
Contact our experts today to discuss your custom fabrication needs, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the PH range and temperature tolerance of pure PTFE gaskets? Master Extreme Chemical and Thermal Sealing
- What are the advantages of Teflon in industrial applications? Boost Durability and Efficiency
- What does the leakage rate indicate about PTFE gaskets? Understanding the Sealing Performance Trade-off
- What advantages do PTFE slide bearings offer in terms of corrosion and heat loss? Boost System Longevity & Efficiency
- How do PTFE slide bearings compare in load capacity to traditional bearings? Superior Support for High-Load, Low-Speed Applications
- What is the development history of PTFE O-ring seals? From Simple Shapes to High-Performance Seals
- Why is ePTFE suitable for aerospace applications? Achieve Lightweight Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- How can virgin PTFE be prepared for bonding? Achieve a Permanent, High-Strength Bond



















