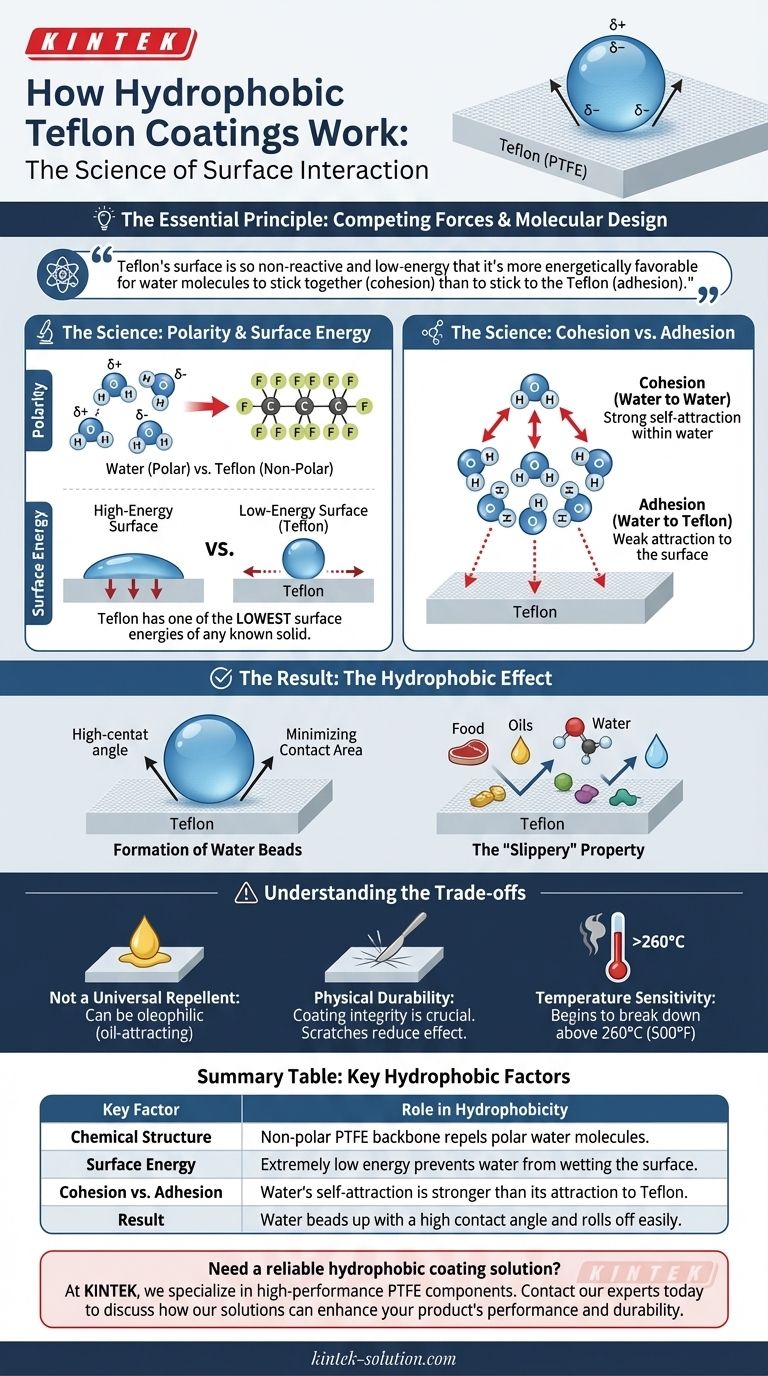
At its core, the hydrophobic property of Teflon coatings works by creating a surface to which water molecules are less attracted than they are to themselves. This is achieved through a combination of its non-polar chemical structure and its exceptionally low surface energy, forcing water to bead up and roll off rather than spreading out.
The essential principle is one of competing forces. Teflon’s surface is so non-reactive and low-energy that it's more energetically favorable for water molecules to stick together (cohesion) than it is for them to stick to the Teflon (adhesion).
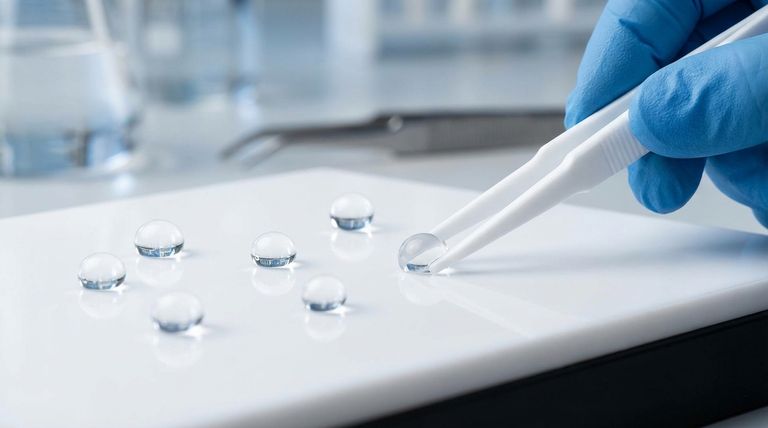

The Science of Surface Interaction
To truly understand why Teflon repels water so effectively, we need to look at the interactions happening at the molecular level. It's a tale of polarity, energy, and competing forces.
Polarity: The Root of Attraction
Water (H₂O) is a polar molecule. It has a slight positive charge on the hydrogen side and a slight negative charge on the oxygen side, much like a tiny magnet. This polarity is why water molecules are so attracted to each other.
Teflon, or Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a non-polar molecule. Its structure, featuring a carbon backbone shielded by fluorine atoms, creates an electrically balanced and neutral surface.
Because polar and non-polar substances do not readily mix, the polar water molecules are actively repelled by the non-polar Teflon surface.
Surface Energy Explained
Every solid has a certain amount of "surface energy." Think of it as the excess energy present on the surface of a material compared to its interior.
High-energy surfaces are unstable and actively try to be covered, or "wetted," by liquids to lower their energy state. In contrast, Teflon has one of the lowest surface energies of any known solid.
This low-energy state means the Teflon surface is very stable and has almost no incentive to bond with the water molecules that come into contact with it.
Cohesion vs. Adhesion
This brings us to the final two critical forces:
- Cohesion: The force of attraction between molecules of the same substance (e.g., water sticking to water).
- Adhesion: The force of attraction between molecules of different substances (e.g., water trying to stick to Teflon).
On a Teflon-coated surface, the cohesive forces within the water are significantly stronger than the adhesive forces between the water and the Teflon.
How This Creates the Non-Stick Effect
The interplay of these properties results in the visible hydrophobic behavior we associate with Teflon.
The Formation of Water Beads
Because water's self-attraction (cohesion) is so much stronger than its attraction to the low-energy surface (adhesion), the water minimizes its contact with the Teflon.
The most efficient way for a liquid to minimize surface area is to form a sphere. This is why water pulls itself into distinct beads with a high contact angle instead of spreading out in a thin film.
The "Slippery" Property
This same mechanism is what makes Teflon an excellent non-stick coating for cookware. Food, which contains water, oils, and other polar and non-polar molecules, simply cannot find a strong enough adhesive force to latch onto the low-energy surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its hydrophobicity is exceptional, it's important to recognize the limitations of Teflon coatings.
Not a Universal Repellent
Teflon is hydrophobic (water-repelling) but can be oleophilic (oil-attracting). Certain oils and other non-polar liquids have even lower surface tension than water and can "wet" a Teflon surface.
Physical Durability
The non-stick properties are entirely dependent on the integrity of the coating. Scratches from metal utensils or abrasive cleaning pads can damage the surface, creating higher-energy spots where water and food can begin to adhere.
Temperature Sensitivity
At extremely high temperatures (generally above 500°F or 260°C), the PTFE polymer can begin to break down. This not only degrades its hydrophobic properties but can also release potentially harmful fumes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this science allows you to predict how different surfaces will interact with liquids.
- If your primary focus is maximum water repellency: You need a material with an extremely low surface energy and a non-polar structure, just like Teflon.
- If your primary focus is creating a strong adhesive bond (like with glue): You need the opposite—a high-energy surface that promotes wetting and allows adhesive forces to dominate.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a Teflon-coated item: Always use non-abrasive tools and moderate heat to preserve the integrity of its uniquely low-energy surface.
Ultimately, Teflon's remarkable water-repellency is a direct result of its molecular-level design to minimize surface interaction.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Hydrophobicity |
|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Non-polar PTFE backbone repels polar water molecules. |
| Surface Energy | Extremely low energy prevents water from wetting the surface. |
| Cohesion vs. Adhesion | Water's self-attraction is stronger than its attraction to Teflon. |
| Result | Water beads up with a high contact angle and rolls off easily. |
Need a reliable hydrophobic coating solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components like seals, liners, and custom labware. Our precision-engineered Teflon coatings offer the exceptional water repellency and non-stick properties detailed in this article, making them ideal for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get a solution tailored to your specific needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















