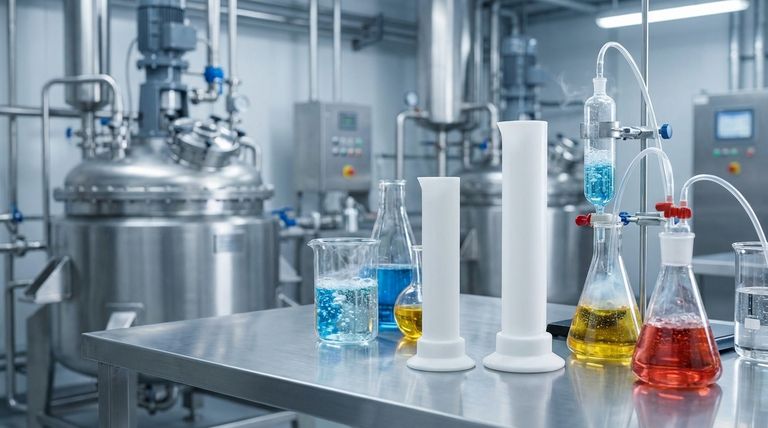
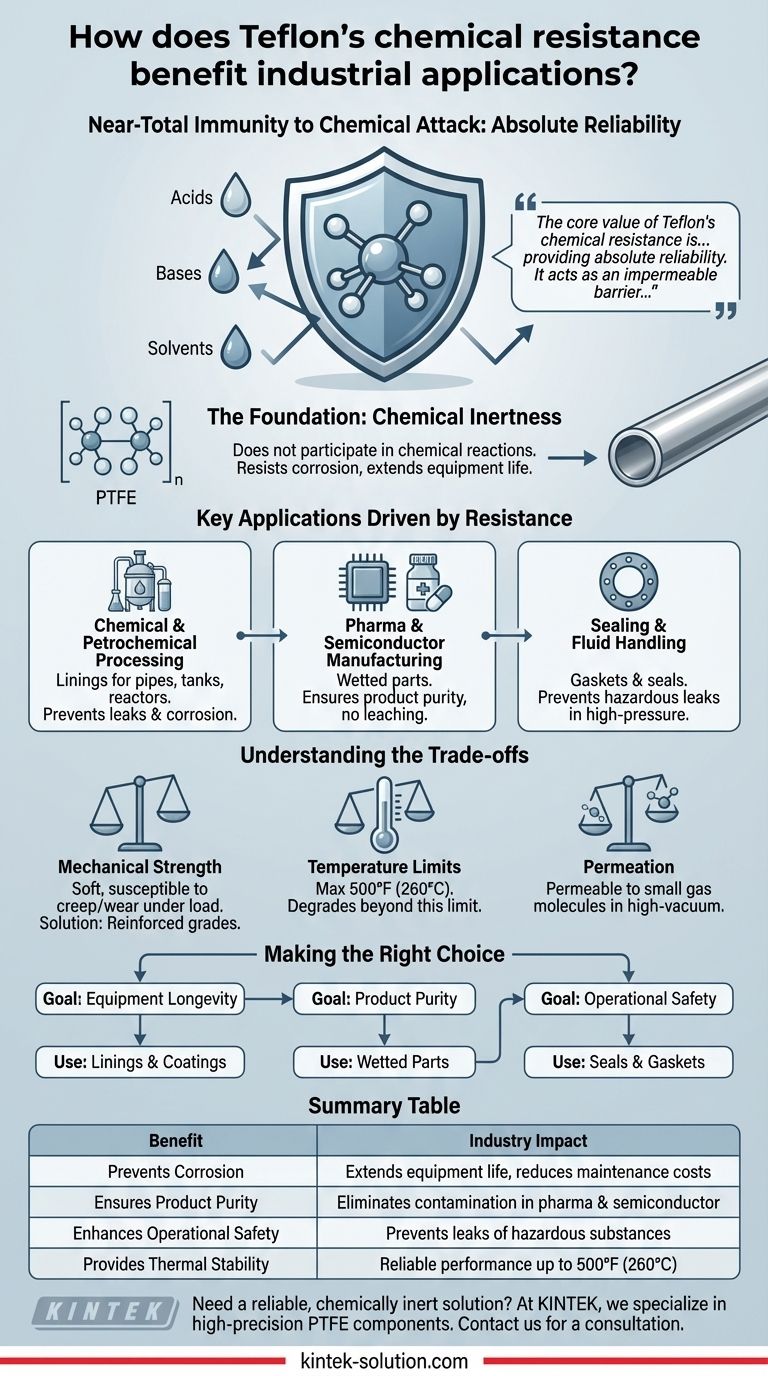
Teflon's primary industrial benefit is its near-total immunity to chemical attack. Because it is chemically inert, it does not react with or degrade when exposed to the vast majority of industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, and solvents. This unique stability protects equipment from corrosion, ensures the purity of materials it contacts, and enhances operational safety in harsh environments.
The core value of Teflon's chemical resistance is not just preventing damage, but providing absolute reliability. It acts as an impermeable barrier that extends equipment life, eliminates product contamination, and minimizes the risk of catastrophic failure when handling corrosive substances.

The Foundation of Resistance: Chemical Inertness
Teflon, or Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is renowned for a property known as chemical inertness. This is the fundamental reason it is so valuable in demanding industrial settings.
What "Chemically Inert" Means
This means that PTFE does not participate in chemical reactions with other substances. It can be exposed to highly corrosive materials like sulfuric acid, hydrofluoric acid, strong bases, and a wide array of organic solvents without breaking down or losing its structural integrity.
The Impact on Equipment Integrity
When materials corrode, equipment fails. By using Teflon as a liner or core component, you effectively shield the underlying structural material (often metal) from chemical attack. This directly prevents degradation, extending the lifespan of critical and expensive assets.
Key Applications Driven by Chemical Resistance
The benefits of Teflon's inertness are most evident in industries where material failure is not an option. Its application prevents costly damage and ensures operational consistency.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
In this sector, Teflon is used extensively for linings in pipes, storage tanks, and reactor vessels. This protects the steel structures from the aggressive chemicals being processed, preventing leaks and equipment failure while ensuring the purity of the chemical product.
Pharmaceutical and Semiconductor Manufacturing
The paramount concern in these industries is product purity. Teflon's inertness is critical because it will not leach contaminants into the high-purity fluids used in drug manufacturing or semiconductor fabrication. This guarantees that the final product meets strict quality and safety standards.
Sealing and Fluid Handling
Teflon is a superior material for gaskets, seals, and gland fillers. These components can maintain a reliable seal in high-pressure systems even when exposed to corrosive fluids and elevated temperatures, preventing dangerous leaks and costly downtime.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its chemical resistance is nearly unmatched, Teflon is not the ideal solution for every single application. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Mechanical Strength
Standard PTFE is a relatively soft material. In applications with high mechanical loads or abrasive forces, it can be susceptible to creep (deformation under load) and wear. For these scenarios, filled or reinforced grades of Teflon are often required.
Temperature Limits
Teflon maintains its exceptional properties up to approximately 500°F (260°C). Beyond this temperature, it will begin to degrade. This makes it unsuitable for environments that exceed this thermal limit.
Permeation
While Teflon is resistant to chemical attack, it is not completely impermeable to all substances. Very small gas molecules can, over time, slowly permeate through the material. This is a critical consideration in certain high-vacuum or gas-containment applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting Teflon is a strategic decision based on the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Use Teflon for linings and protective coatings to shield assets from corrosive chemicals, drastically reducing maintenance costs and extending service life.
- If your primary focus is product purity: Specify Teflon for all wetted parts in pharmaceutical, food, or semiconductor systems to eliminate the risk of chemical leaching and contamination.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Employ Teflon seals and gaskets in fluid handling systems to ensure reliable, long-term containment of hazardous and high-pressure substances.
Ultimately, leveraging Teflon's chemical resistance is a foundational strategy for building safer, more reliable, and more efficient industrial processes.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Application | Industry Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Prevents Corrosion | Linings for pipes, tanks, reactors | Extends equipment life, reduces maintenance costs |
| Ensures Product Purity | Wetted parts in fluid systems | Eliminates contamination in pharma & semiconductor manufacturing |
| Enhances Operational Safety | Seals, gaskets, and gland fillers | Prevents leaks of hazardous, high-pressure substances |
| Provides Thermal Stability | Components exposed to heat and chemicals | Reliable performance up to 500°F (260°C) |
Need a reliable, chemically inert solution for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE (Teflon) components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your equipment is protected from corrosion, your processes maintain purity, and your operations run safely and efficiently.
Let us provide you with a solution tailored to your specific needs, from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and see how our PTFE expertise can benefit your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications



















