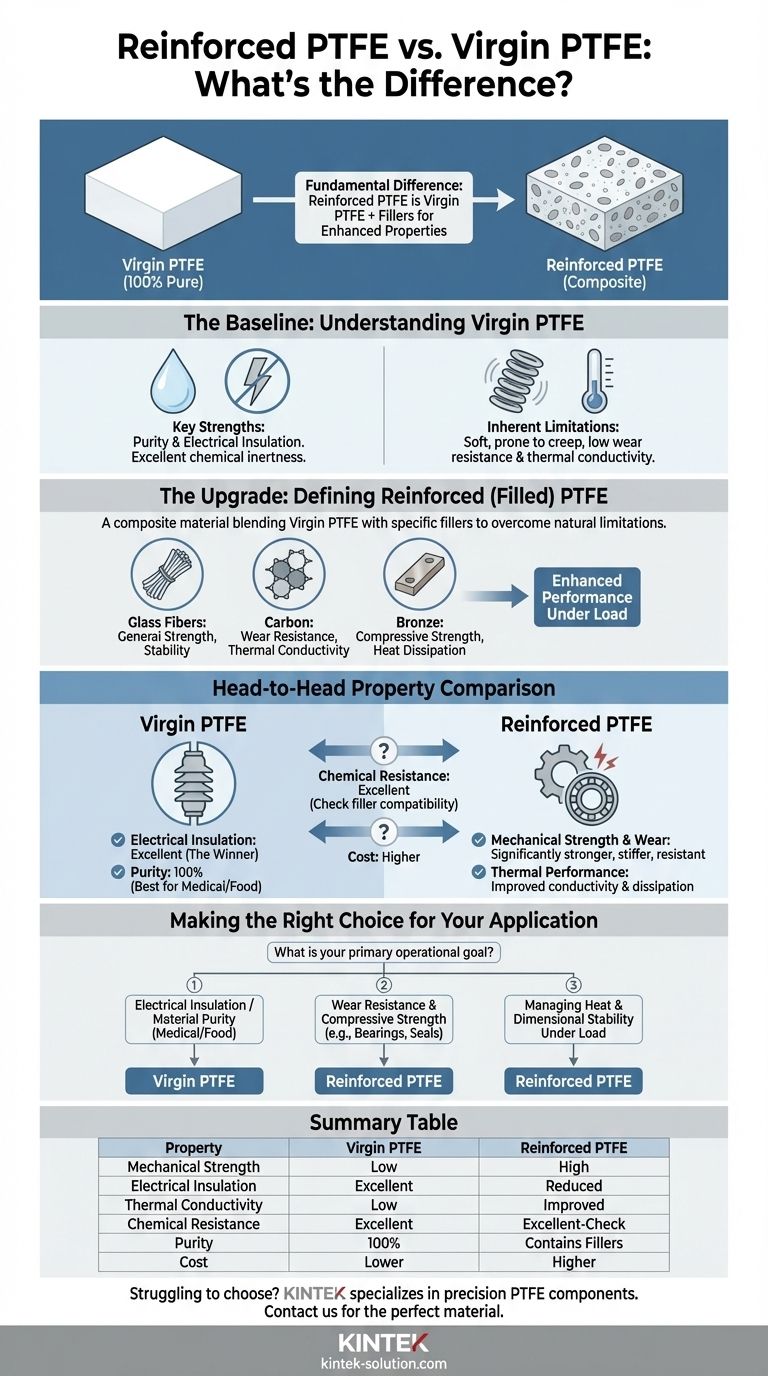
The fundamental difference is that Reinforced PTFE is a composite material created by adding fillers to Virgin PTFE. This process significantly enhances its mechanical properties like strength and wear resistance, but it also reduces its electrical insulation capabilities and increases its cost.
Choosing between these materials is not a matter of which is superior, but which is correct for your specific challenge. Virgin PTFE excels in applications demanding purity and electrical insulation, while Reinforced PTFE is engineered for superior performance under mechanical and thermal stress.

The Baseline: Understanding Virgin PTFE
Pure Polytetrafluoroethylene
Virgin PTFE is pure, unadulterated polytetrafluoroethylene. It contains no recycled material or additional fillers, making it the benchmark for the material's inherent properties.
Key Strengths: Purity and Insulation
Its two most defining characteristics are its exceptional chemical inertness across a wide range of substances and its outstanding performance as an electrical insulator.
Inherent Limitations
Virgin PTFE is relatively soft and prone to "creep" or deformation under a sustained load. Its resistance to wear and its ability to conduct heat are also quite low compared to engineered alternatives.
The Upgrade: Defining Reinforced (Filled) PTFE
A Composite Material
Reinforced PTFE, often called filled PTFE, is a composite. It blends a Virgin PTFE base with specific filler materials to systematically overcome its natural mechanical and thermal limitations.
The Role of Fillers
Fillers are added to impart specific, targeted properties. They physically reinforce the PTFE matrix, leading to dramatic improvements in performance under load.
Common Filler Types
Common fillers include glass fibers for general strength and stability, carbon for improved wear resistance and thermal conductivity, and bronze for high compressive strength and heat dissipation.
Head-to-Head Property Comparison
Mechanical Strength and Wear
Reinforced PTFE is significantly stronger, stiffer, and more resistant to wear and deformation. This is its primary advantage and the most common reason for its selection.
Thermal Performance
Fillers improve thermal conductivity, allowing heat to dissipate more effectively. This makes reinforced grades more dimensionally stable in applications with high temperatures or thermal cycling.
Chemical Resistance
Both materials offer excellent chemical resistance. However, the specific filler in Reinforced PTFE can affect its compatibility with certain highly aggressive chemicals, so verification is always required.
Electrical Insulation
Virgin PTFE is the clear winner for electrical applications. The addition of conductive or semi-conductive fillers like carbon or bronze drastically reduces the electrical insulating properties of Reinforced PTFE.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The Cost Factor
Reinforced PTFE is more expensive than its virgin counterpart. The cost increases with the addition of specialized filler materials and more complex manufacturing processes.
Purity is Compromised
The addition of fillers means the material is no longer pure PTFE. This can be a disqualifying factor for certain food-grade, medical, or high-purity semiconductor applications.
Sacrificing Insulation for Strength
The most significant trade-off is sacrificing electrical insulation for mechanical strength. You are fundamentally choosing one core property over the other, as you cannot have the best of both in a single material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation or material purity (medical/food): Virgin PTFE is the only suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and compressive strength (e.g., bearings, seals): Reinforced PTFE offers the necessary durability.
- If your primary focus is managing heat and dimensional stability under load: A thermally conductive Reinforced PTFE grade is the correct path.
By selecting the material based on its specific engineering trade-offs, you ensure your application is built for success.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Reinforced PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Low (soft, prone to creep) | High (strong, wear-resistant) |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Reduced (depends on filler) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low | Improved (better heat dissipation) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent (check filler compatibility) |
| Purity | 100% Pure | Contains fillers |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Struggling to choose between purity and performance? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from ultra-pure Virgin PTFE for medical and semiconductor applications to high-strength Reinforced PTFE for demanding industrial seals and bearings. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Let our experts help you select the perfect material for your project. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry



















