At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) protects against corrosion by creating an exceptionally durable and non-reactive physical barrier. This barrier isolates the underlying material from corrosive agents through a combination of chemical inertness, electrical insulation, and moisture repellency.
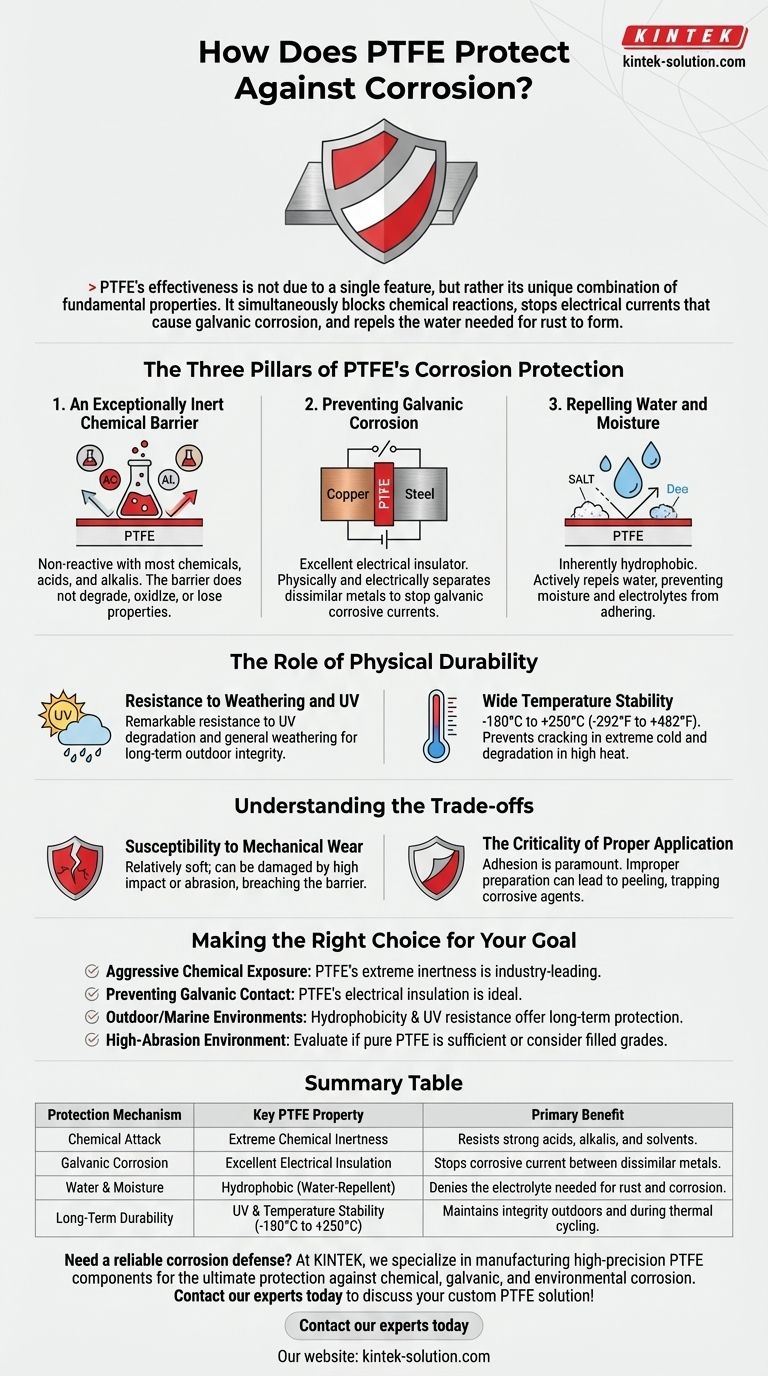
PTFE’s effectiveness is not due to a single feature, but rather its unique combination of fundamental properties. It simultaneously blocks chemical reactions, stops electrical currents that cause galvanic corrosion, and repels the water needed for rust to form.
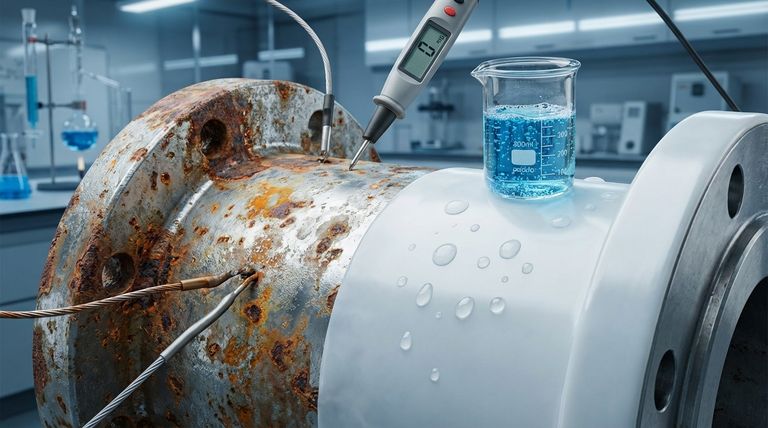

The Three Pillars of PTFE's Corrosion Protection
To understand PTFE's role, it's essential to break down the specific mechanisms it uses to prevent different types of degradation. It isn't just a simple coating; it's an engineered barrier that counters corrosion on multiple fronts.
1. An Exceptionally Inert Chemical Barrier
PTFE is renowned for its chemical resistance. It is non-reactive with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, including strong acids and alkalis.
This inertness means the PTFE barrier itself does not degrade, oxidize, or lose its properties when exposed to aggressive media. This makes it ideal for components like gaskets and liners in chemical processing.
2. Preventing Galvanic Corrosion
Galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals are in electrical contact in the presence of an electrolyte, causing one metal to corrode faster.
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. By using PTFE liners, gaskets, or slide bearings, you can physically and electrically separate different metals.
This separation breaks the corrosive circuit, effectively stopping galvanic corrosion in its tracks. It's a common strategy for protecting pipes from their metal supports or isolating components in complex assemblies.
3. Repelling Water and Moisture
Most forms of metallic corrosion require an electrolyte, with water being the most common. PTFE is inherently hydrophobic, meaning it actively repels water.
This property prevents moisture from adhering to the surface, denying the corrosion process a key ingredient. This makes PTFE coatings invaluable in marine, offshore, and automotive applications where exposure to water and salt is constant.
The Role of Physical Durability
A protective barrier is only as good as its ability to remain intact. PTFE's physical properties ensure its long-term reliability in demanding environments.
Resistance to Weathering and UV
Unlike many other polymers, PTFE shows remarkable resistance to degradation from UV light and general weathering.
This ensures that for outdoor applications, the protective barrier will not become brittle or break down over time, maintaining its integrity for years.
Wide Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its protective properties across an exceptionally broad temperature range, typically from -180°C to +250°C (-292°F to +482°F).
This stability prevents the material from cracking in extreme cold or degrading in high heat, ensuring the protective barrier remains consistent during thermal cycling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Susceptibility to Mechanical Wear
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be damaged by high-impact events or abrasive wear, which can physically breach the protective barrier.
In high-wear scenarios, this could expose the underlying substrate and create a localized point for corrosion to begin.
The Criticality of Proper Application
For PTFE coatings, adhesion to the substrate is paramount. Improper surface preparation can lead to poor bonding.
If the coating peels or delaminates, moisture can creep underneath, trapping corrosive agents against the metal and causing significant damage that is hidden from view.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right corrosion protection depends entirely on your specific environmental challenges and operational demands.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical exposure: PTFE is an industry-leading choice due to its extreme chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is preventing contact between dissimilar metals: PTFE's electrical insulation makes it an ideal solution for eliminating galvanic corrosion.
- If your primary focus is outdoor or marine environments: PTFE's combination of hydrophobicity and UV resistance offers durable, long-term protection.
- If your primary focus is a high-abrasion environment: You should evaluate if pure PTFE is sufficient or if a filled grade or alternative hard coating is more appropriate.
Ultimately, PTFE provides a versatile and robust defense against the most common forms of chemical and environmental corrosion.
Summary Table:
| Protection Mechanism | Key PTFE Property | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Attack | Extreme Chemical Inertness | Resists strong acids, alkalis, and solvents. |
| Galvanic Corrosion | Excellent Electrical Insulation | Stops corrosive current between dissimilar metals. |
| Water & Moisture | Hydrophobic (Water-Repellent) | Denies the electrolyte needed for rust and corrosion. |
| Long-Term Durability | UV & Temperature Stability (-180°C to +250°C) | Maintains integrity outdoors and during thermal cycling. |
Need a reliable corrosion defense for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware—that provide the ultimate protection against chemical, galvanic, and environmental corrosion. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures your parts are engineered to meet the specific demands of your industry, whether in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial settings.
Let us help you safeguard your equipment and processes. Contact our experts today to discuss your custom PTFE solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How was PTFE discovered and what were its initial findings? A Serendipitous Breakthrough in Material Science
- What is reprocessed PTFE? A Cost-Effective Alternative for Non-Critical Applications
- How is Teflon made? The Science Behind Its Incredible Properties
- What is the chemical composition of PTFE? Unlocking the Power of Carbon-Fluorine Bonds
- How do Teflon and UHMW compare in terms of applications and characteristics? Choose the Right High-Performance Polymer
- What makes Teflon suitable for low-friction applications? Unlock Superior Performance with Low-Friction PTFE
- What are the temperature range and mechanical properties of PTFE? The Ultimate Guide to Performance
- How does ePTFE's porosity benefit its applications? Achieve Selective Permeability for Your Designs



















