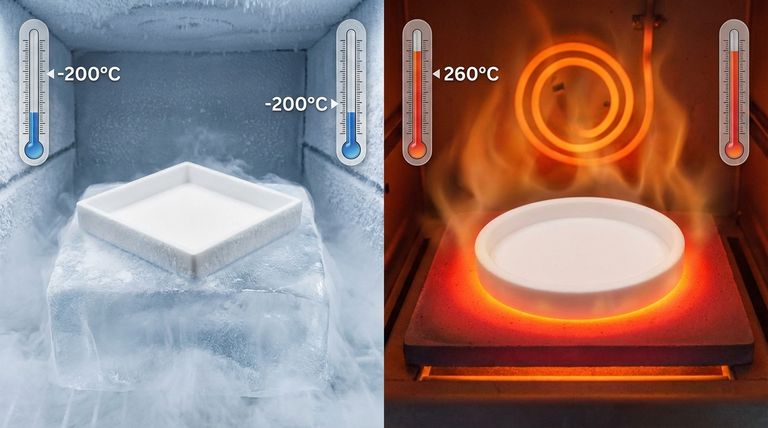
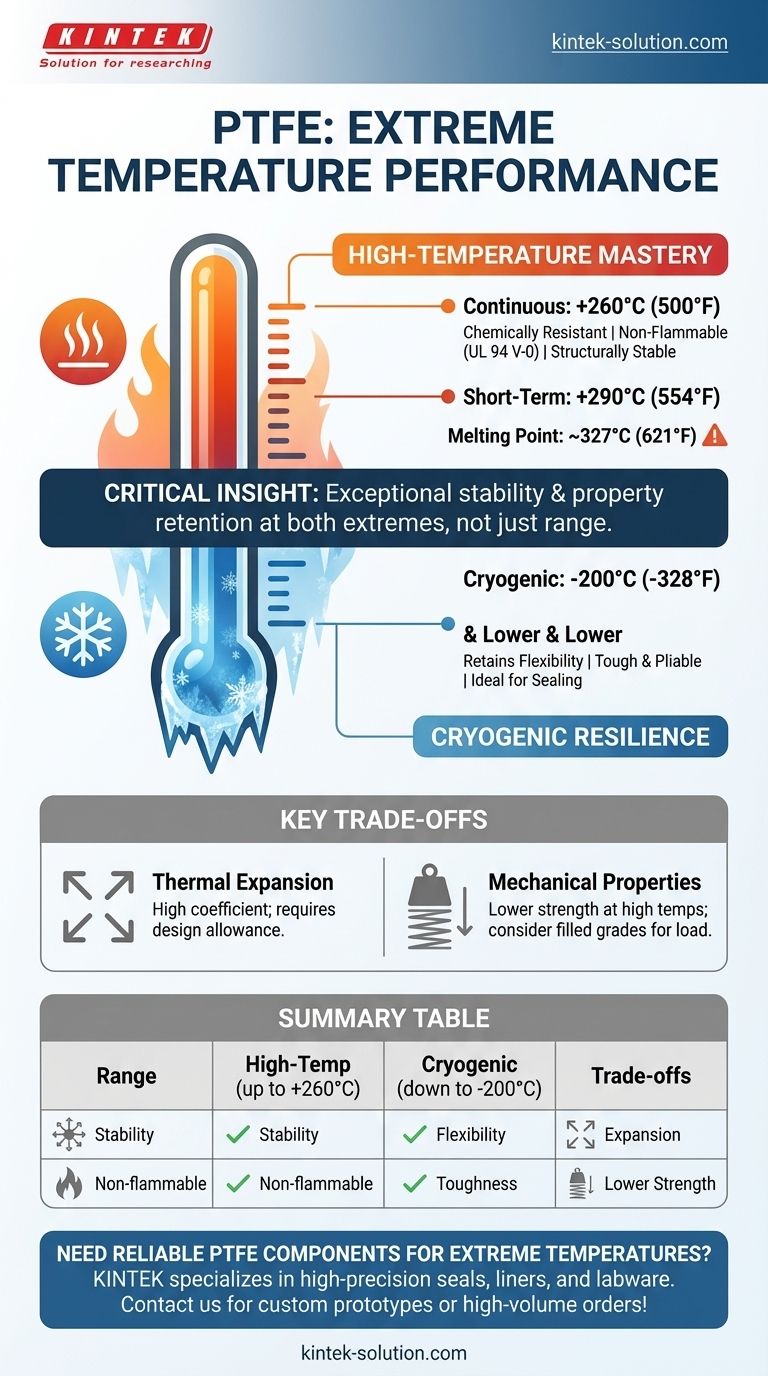
In short, PTFE exhibits exceptional thermal stability across an impressively wide spectrum. The material operates consistently and effectively in continuous service temperatures ranging from as low as -200°C (-328°F) up to a high of 260°C (500°F). This makes it one of the most versatile polymers for applications facing extreme heat, deep cold, or both.
The critical insight isn't just the wide temperature range of PTFE, but its stability and retention of key properties at those extremes. Unlike many materials that become brittle in the cold or degrade in the heat, PTFE maintains its flexibility and integrity, ensuring reliable performance.

Understanding High-Temperature Performance
PTFE's molecular structure, built on a strong carbon-fluorine bond, is the source of its remarkable high-temperature resistance. It does not melt in the conventional sense until it reaches a very high temperature.
Continuous Operating Temperature
The recognized upper limit for continuous, long-term use of PTFE is 260°C (500°F). Up to this point, it maintains its excellent chemical resistance, structural integrity, and electrical insulation properties without significant degradation.
Short-Term Exposure
For brief periods, PTFE can withstand even higher temperatures, approaching 290°C (554°F). Its actual melting point is approximately 327°C (621°F), providing a substantial safety margin for most high-heat applications.
Inherent Non-Flammability
A key safety benefit at high temperatures is that PTFE is inherently nonflammable. It carries a UL 94 V-0 flame rating, meaning it will self-extinguish after the flame source is removed, making it ideal for fire-critical environments.
Unpacking Low-Temperature and Cryogenic Behavior
While its heat resistance is well-known, PTFE's performance at the opposite end of the thermal scale is equally impressive. It is a premier choice for cryogenic applications where other polymers would fail.
Performance in Cryogenic Conditions
PTFE performs reliably down to -200°C (-328°F) and can be used in some applications approaching absolute zero, with sources citing limits as low as -270°C (-454°F).
Retained Flexibility
The most crucial characteristic of PTFE at low temperatures is its retention of flexibility. Unlike many plastics that become extremely brittle and prone to fracture in deep cold, PTFE remains pliable and tough, which is vital for performance.
Sealing in Extreme Cold
This retained flexibility makes PTFE an exceptional material for cryogenic seals and gaskets. It can maintain a reliable seal even as components contract and shift in extreme cold environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is without its limitations. To properly engineer a solution with PTFE, you must be aware of its specific behaviors across its temperature range.
Consideration: Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. In applications with tight tolerances that span a wide temperature range, components must be designed to accommodate the material's expansion and contraction to avoid stress or failure.
Consideration: Mechanical Properties
While thermally stable, PTFE is a relatively soft material with lower tensile strength and creep resistance compared to other engineering plastics. At the upper end of its temperature range, this softness can be more pronounced, which must be considered in high-load mechanical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application will determine if PTFE is the optimal choice. Use these points as a guide for your decision-making.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability (up to 260°C): PTFE is an excellent choice for gaskets, insulators, and linings, especially where superior chemical resistance and non-flammability are also needed.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance (below -150°C): PTFE's unique ability to retain flexibility without becoming brittle makes it a premier material for seals, washers, and components in extreme cold.
- If your application involves both extreme temperatures and mechanical load: Consider filled grades of PTFE (e.g., glass- or carbon-filled), which can improve mechanical strength and reduce thermal expansion while retaining excellent temperature resistance.
By understanding both its exceptional range and its inherent material properties, you can confidently leverage PTFE in the most demanding thermal environments.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|
| High-Temp (up to 260°C) | Maintains chemical resistance, structural integrity, and electrical insulation; non-flammable (UL 94 V-0 rated). |
| Cryogenic (down to -200°C) | Retains flexibility and toughness; ideal for seals and gaskets in extreme cold without becoming brittle. |
| Trade-offs | High coefficient of thermal expansion; lower mechanical strength at high temperatures. |
Need reliable PTFE components for extreme temperatures? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Whether you require custom prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your components perform flawlessly in the most demanding thermal environments. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE and what are its main properties? Discover the Ultimate High-Performance Polymer
- How does PTFE perform in harsh weather conditions? Unmatched Resistance for Extreme Environments
- What issues arise when using reprocessed PTFE in chemical applications? Avoid Costly Contamination and Failure
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE improve operational efficiency in machinery? Reduce Energy, Downtime & Costs
- What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and what are its main types? Unlock High-Performance Solutions
- What are the thermal and electrical properties of PTFE? A Guide to Its Extreme Performance
- What makes Teflon chemically resistant? Discover the Power of Carbon-Fluorine Bonds



















