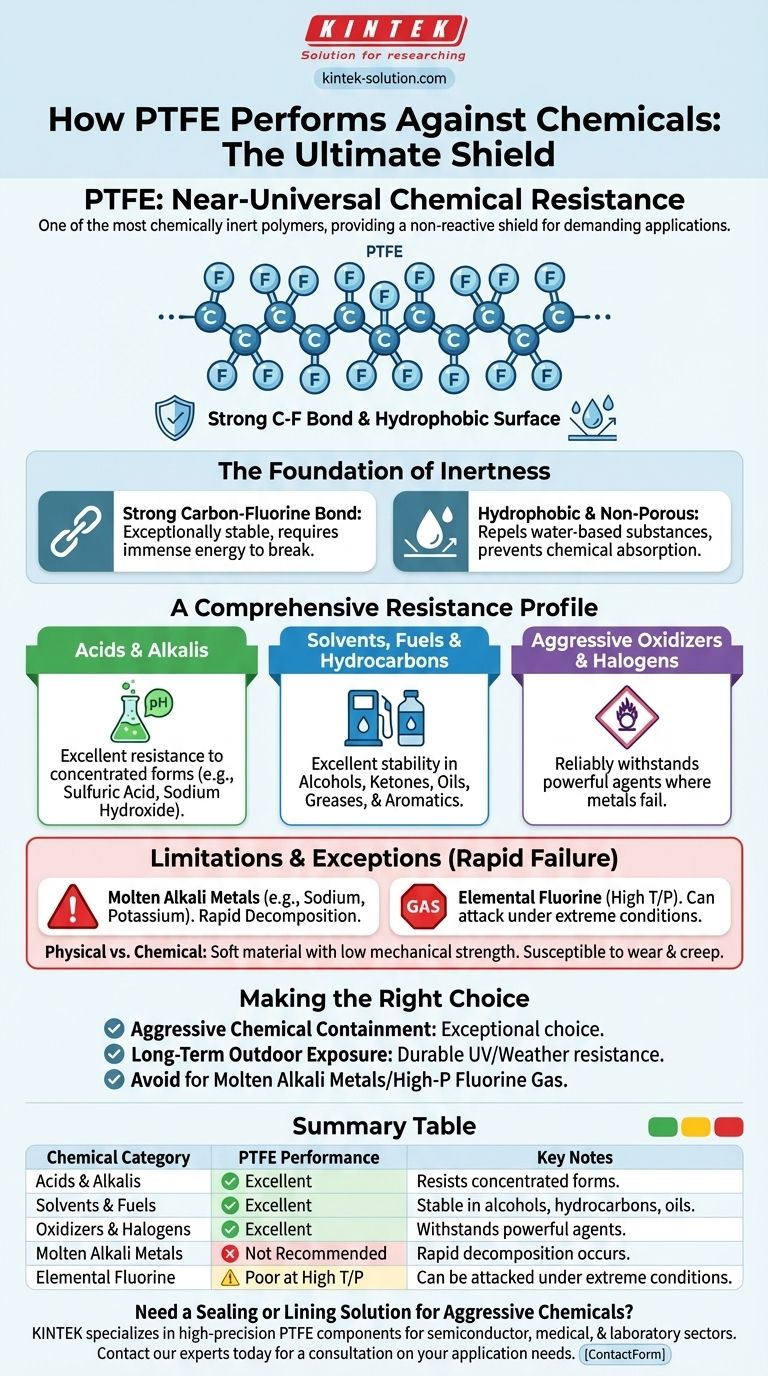
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has near-universal chemical resistance. It is one of the most chemically inert polymers known to science, remaining stable and unreactive when exposed to the vast majority of industrial chemicals, including concentrated acids, alkalis, solvents, and powerful oxidizers.
PTFE's exceptional performance stems from its unique molecular structure, which creates a non-reactive shield against chemical attack. This makes it a default material choice for the most demanding applications, with only a few highly specific and extreme substances capable of degrading it.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Inertness
To understand PTFE's performance, we must look at its molecular architecture. Its properties are not incidental; they are a direct result of its simple, stable, and tightly bonded structure.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE consists of a chain of carbon atoms completely sheathed by fluorine atoms. The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable, requiring a tremendous amount of energy to break.
This molecular armor is the primary reason for PTFE's extreme resistance. Chemicals that would readily attack other polymers simply cannot find a weak point to initiate a reaction.
A Hydrophobic and Non-Porous Surface
PTFE is inherently hydrophobic, meaning it actively repels water and water-based substances. It does not absorb moisture, which prevents chemicals from seeping into the material and causing degradation from within.
This property also contributes to a self-cleaning effect, as liquids tend to bead up and roll off the surface rather than wetting it.
A Comprehensive Resistance Profile
PTFE’s inertness gives it a remarkably broad resistance profile. It is a reliable choice for sealing, lining, or containing nearly any fluid.
Acids and Alkalis
PTFE shows no degradation when exposed to even highly concentrated acids and alkalis. This includes substances like sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and sodium hydroxide that are destructive to lesser materials.
Solvents, Fuels, and Hydrocarbons
It maintains its integrity in a wide range of organic compounds. This includes alcohols, ketones, aromatic and halogenated hydrocarbons, fuels, greases, and oils.
Aggressive Oxidizers and Halogens
PTFE reliably withstands powerful oxidizing agents and halogens, environments where many other plastics and even metals would quickly fail.
Understanding the Limitations and Exceptions
While its resistance is nearly absolute, PTFE is not invincible. It is critical to understand the few specific conditions where it is unsuitable. Its failure in these environments can be rapid and catastrophic.
Molten Alkali Metals
The primary exception to PTFE's chemical resistance is molten alkali metals, such as sodium or potassium. In their molten state, these metals are reactive enough to strip the fluorine atoms from the polymer backbone, causing complete decomposition.
Elemental Fluorine and Related Compounds
Under certain conditions of high temperature and pressure, elemental fluorine gas and similar highly reactive fluorinating agents (like chlorine trifluoride) can attack PTFE. This is a rare and extreme industrial scenario.
Physical vs. Chemical Properties
It is important to distinguish chemical resistance from physical properties. PTFE is a relatively soft and formable material with low mechanical strength compared to metals or engineered plastics. While it will not be chemically attacked, it can be susceptible to wear, abrasion, and creep under mechanical load.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is often a straightforward decision when chemical compatibility is the dominant concern. Use these points to guide your evaluation.
- If your primary focus is containing aggressive acids, bases, or solvents: PTFE is an exceptionally safe and reliable choice, outperforming nearly every other polymer.
- If your primary focus is long-term outdoor exposure: PTFE's inherent resistance to weather, ozone, and UV radiation makes it a highly durable option.
- If your application involves molten alkali metals or high-pressure fluorine gas: You must seek an alternative material, as PTFE is chemically incompatible with these specific substances.
Ultimately, for the vast majority of chemical handling applications, PTFE provides an unparalleled level of safety and material integrity.
Summary Table:
| Chemical Category | PTFE Performance | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Acids & Alkalis | Excellent | Resists even concentrated forms (e.g., sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide). |
| Solvents & Fuels | Excellent | Stable in alcohols, ketones, hydrocarbons, oils, and greases. |
| Oxidizers & Halogens | Excellent | Withstands powerful agents that degrade other materials. |
| Molten Alkali Metals | Not Recommended | Rapid decomposition occurs (e.g., molten sodium, potassium). |
| Elemental Fluorine | Poor at High T/P | Can be attacked under extreme temperature and pressure. |
Need a sealing or lining solution that can handle your most aggressive chemicals?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your equipment operates with maximum safety and material integrity, even when exposed to concentrated acids, powerful solvents, and harsh oxidizers.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailoring PTFE parts to your exact specifications. Let us help you solve your toughest chemical resistance challenges.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your specific application needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What industries commonly use PTFE and for what purposes? Unlock Its Unique Properties
- What is the coefficient of friction (COF) and why is it important? Master Efficiency, Longevity, and Control
- What temperature range can Teflon withstand? From Cryogenic -328°F to High Heat 500°F
- What is PTFE and what are its primary properties? Discover the Ultimate High-Performance Polymer
- What makes PTFE coatings unique in terms of their chemical makeup? The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
- What makes PTFE ideal for electrical insulation? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- How is graphite packing made? Discover the Braiding Process for Superior Seals
- How is PTFE utilized in the medical and pharmaceutical industries? Ensure Purity and Biocompatibility



















