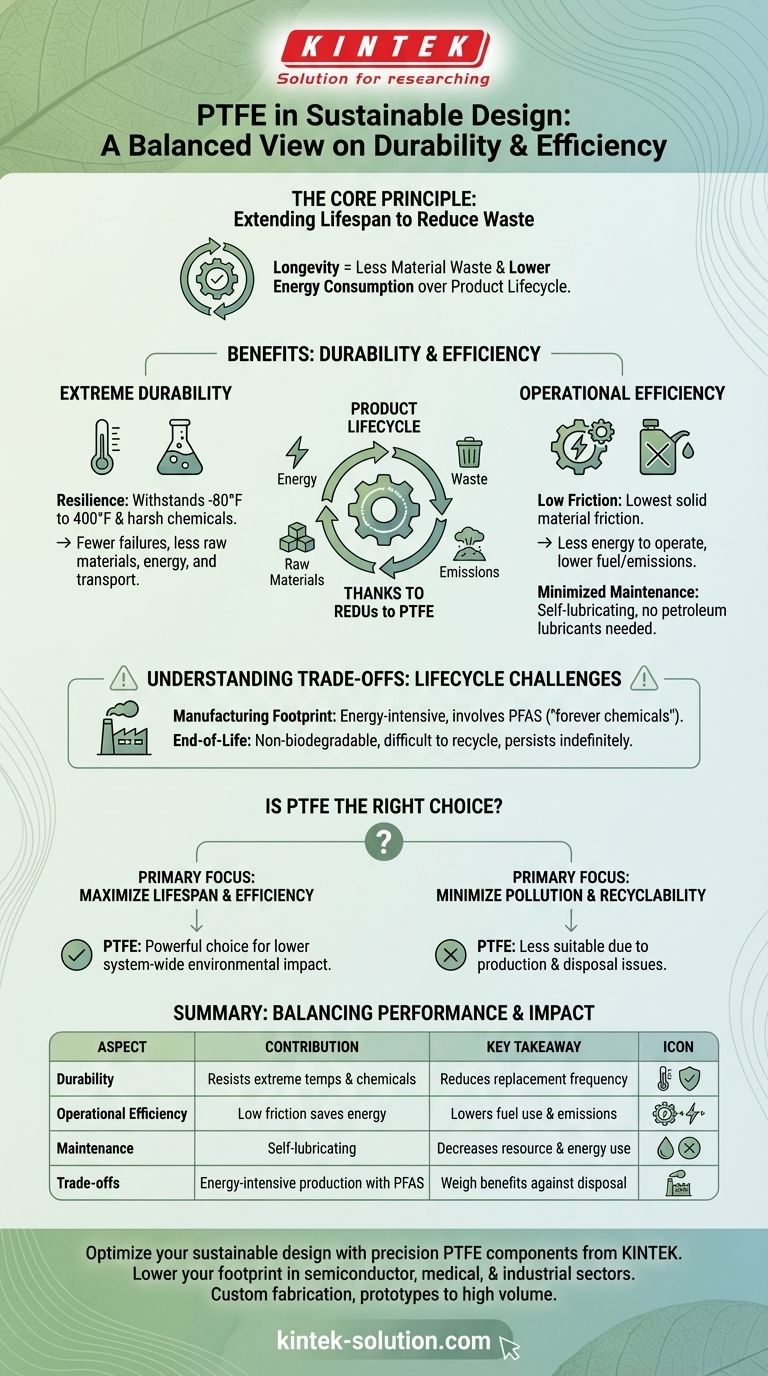
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) contributes to sustainable design through its exceptional durability and operational efficiency. By creating components that last significantly longer and require less energy to operate, PTFE reduces the need for frequent replacements and minimizes energy consumption over a product's entire lifecycle. This longevity directly translates to less material waste and a lower overall environmental footprint.
The primary sustainability benefit of PTFE is not found in its creation or disposal, but in its performance during use. Its ability to radically extend the functional life of components and improve energy efficiency offers a compelling argument for its use, provided designers weigh this against its known environmental challenges.

The Core Principle: Extending Lifespan to Reduce Waste
The most significant environmental contribution of PTFE comes from its ability to reduce the cycle of manufacturing, replacement, and disposal.
Extreme Durability and Resilience
PTFE is renowned for its resistance to harsh conditions. It can withstand extreme temperatures, from cryogenic lows (-80°F) to high heat (400°F), without degrading.
This resilience means components made from or coated with PTFE fail far less frequently. Fewer failures result in less consumption of raw materials, energy for manufacturing, and transportation emissions associated with producing and shipping replacement parts.
Resistance to Chemical Degradation
The material is nearly inert, meaning it does not react with most chemicals. In industrial or environmental applications, this prevents corrosion and material breakdown.
This property protects not only the PTFE component but also the larger system it is a part of, preventing premature failure of more resource-intensive equipment.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Beyond just lasting longer, PTFE makes systems run better, which has a direct impact on energy and resource consumption.
The Impact of Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. In mechanical applications like bearings and gears, this translates directly to higher efficiency.
Systems with low-friction components require less energy to perform the same amount of work. In the automotive and aerospace industries, this means lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions over the vehicle's operational life.
Minimizing Maintenance Requirements
Components made from PTFE, such as bearings, are often self-lubricating and require minimal maintenance.
This reduces the need for petroleum-based lubricants that must be regularly applied and disposed of. It also cuts down on the energy and labor associated with maintenance schedules, further lowering the lifecycle impact.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Balanced View
An objective analysis requires acknowledging the significant environmental drawbacks associated with PTFE. True sustainable design involves a full lifecycle assessment.
The Manufacturing Footprint
The production of PTFE and other fluoropolymers is an energy-intensive process. It also involves the use of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
PFAS are often called "forever chemicals" because they are extremely persistent in the environment and have been linked to health concerns. This makes the manufacturing stage a point of significant environmental impact.
End-of-Life Challenges
PTFE is not biodegradable and is very difficult to recycle effectively. Most PTFE products end up in landfills at the end of their life, where they persist indefinitely.
While its durability reduces the frequency of disposal, the ultimate fate of the material is an environmental consideration that cannot be ignored.
Is PTFE the Right Choice for Your Sustainable Design?
Choosing a material requires balancing its in-use benefits against its production and disposal costs. The decision to use PTFE should be a deliberate one based on your primary sustainability goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product lifespan and in-use energy efficiency: PTFE is a powerful choice, as its durability and low-friction properties can dramatically lower the environmental impact of the entire system it serves.
- If your primary focus is minimizing chemical pollution and using easily recyclable materials: The challenges related to PFAS in manufacturing and the lack of viable recycling paths for PTFE make it a less suitable option.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE for sustainable design requires a holistic view, carefully weighing its unmatched performance benefits against its significant environmental liabilities.
Summary Table:
| Sustainability Aspect | PTFE's Contribution | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Withstands extreme temperatures (-80°F to 400°F) and chemical degradation | Reduces replacement frequency and material waste |
| Operational Efficiency | Low friction minimizes energy consumption in systems like bearings and gears | Lowers fuel use and emissions over product lifecycle |
| Maintenance | Self-lubricating properties cut need for petroleum-based lubricants | Decreases resource use and maintenance energy |
| Trade-offs | Energy-intensive production involving PFAS; difficult to recycle | Weigh in-use benefits against manufacturing and disposal impacts |
Optimize your sustainable design with precision PTFE components from KINTEK.
For industries like semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial manufacturing, PTFE’s durability and efficiency can significantly lower your environmental footprint. At KINTEK, we specialize in custom PTFE fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensuring components that extend product life, reduce energy use, and minimize waste.
Let’s collaborate to balance performance with sustainability. Contact us today to discuss your project needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the culinary applications of Teflon? Leverage Non-Stick Performance for Cooking & Processing
- What benefits does Teflon coating offer in chemical manufacturing? Boost Equipment Lifespan & Purity
- What are the chemical compatibility characteristics of PTFE? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications
- Why is virgin PTFE preferred for certain applications? Ensuring Purity for Critical Performance
- What are some industrial applications of Teflon? Unlock High-Performance Solutions Across Industries
- What does PTFE coating thickness refer to? The Key to Durability and Performance
- What are the key properties of Teflon (PTFE) that make it suitable for industrial applications?
- What modifications can be made to PTFE for enhanced performance? Boost Wear Resistance & Strength with Fillers



















