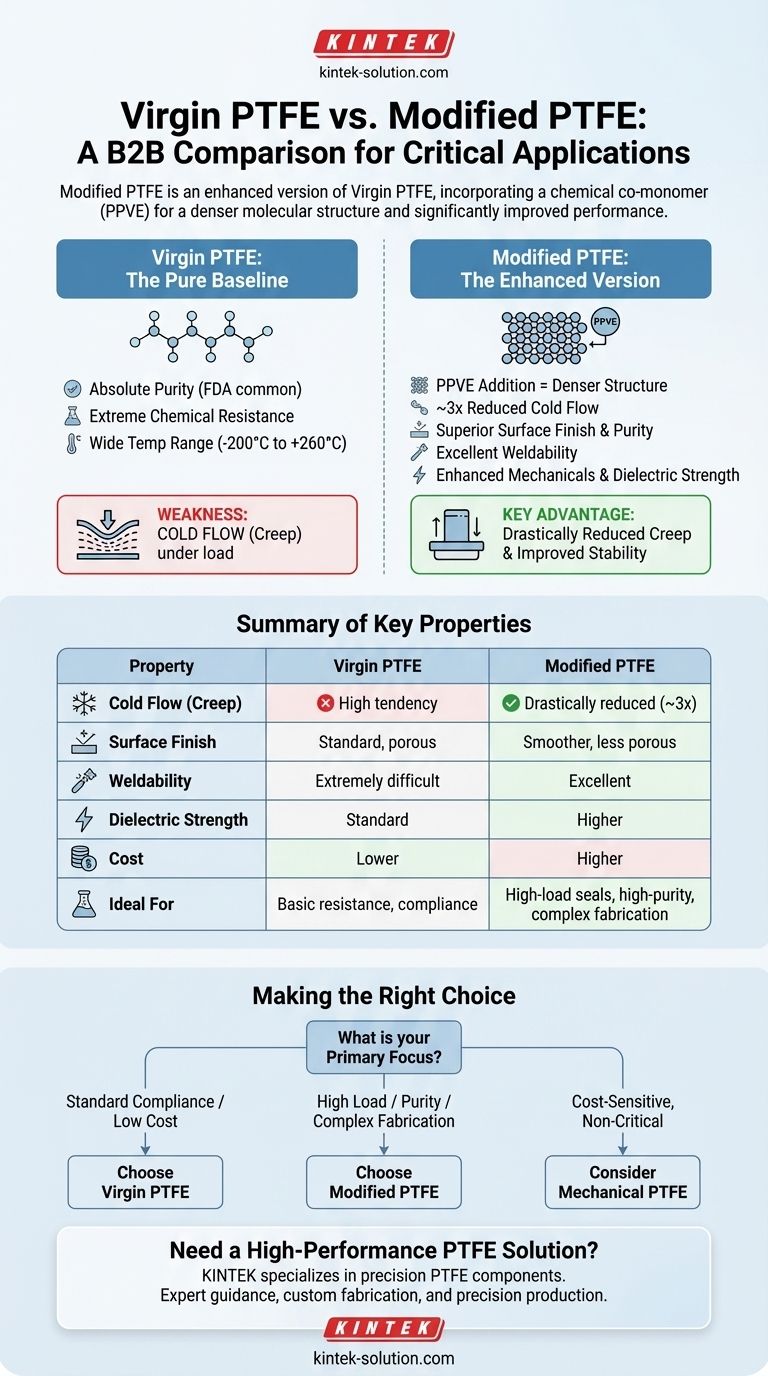
In essence, modified PTFE is an enhanced version of virgin PTFE. It incorporates a chemical co-monomer, specifically perfluoropropylvinylether (PPVE), during the polymerization process. This seemingly small change creates a denser molecular structure, resulting in significant improvements such as drastically reduced cold flow, superior surface finish, enhanced mechanical properties, and the ability to be welded.
While both materials share PTFE's legendary chemical inertness and temperature resistance, the choice between them hinges on a single question: Do you need to overcome the inherent physical and processing limitations of the pure material?

Establishing the Baseline: Virgin PTFE
Virgin PTFE is the pure, unadulterated form of the polymer, made directly from resin without any recycled content or performance-enhancing additives. Its reputation is built on a few core characteristics.
The Pure Foundation
Virgin PTFE is valued for its absolute purity. This quality makes it a default choice for industries where contamination is a major concern, leading to its common FDA approval for food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications.
Core Strengths
This material is known for its exceptional chemical inertness, making it resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. It also has a remarkably wide service temperature range (from -200°C to +260°C) and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material.
The Inherent Limitation: Cold Flow
The primary weakness of virgin PTFE is creep, also known as cold flow. Under compressive load, especially over time, the material has a tendency to deform and "flow" away from the pressure point. This can be a significant issue in critical sealing and structural applications.
What Makes PTFE "Modified"?
Modified PTFE isn't just PTFE with fillers mixed in; it represents a fundamental change to the polymer's molecular backbone.
The Chemical Modifier
The most common type, often designated as PTFE-TFM, is created by adding a small amount of perfluoropropylvinylether (PPVE) as a second monomer during manufacturing. This modification results in a denser, less porous polymer matrix.
The Impact of the Change
This denser structure is the source of all of modified PTFE's advantages. The polymer chains are packed more tightly, reducing the voids that contribute to permeation, porosity, and the tendency for the material to deform under pressure.
Key Performance Advantages of Modified PTFE
The engineering goal of modified PTFE is to retain the benefits of the original while directly addressing its key weaknesses.
Dramatically Reduced Creep (Cold Flow)
This is the most significant improvement. Modified PTFE reduces cold flow by a factor of three compared to virgin PTFE, making it far more stable and reliable in components that are under constant mechanical stress, like valve seats and gaskets.
Superior Surface Finish and Purity
When machined, modified PTFE produces a noticeably smoother, less porous surface. This is critical in high-purity or sanitary applications, as it reduces the potential for trapping contaminants and lowers gas permeation rates.
Enhanced Mechanical and Electrical Properties
The denser structure leads to increased stiffness, a longer flex life, and improved wear resistance. Furthermore, it boasts a higher dielectric strength, making it a superior choice for high-voltage electrical insulation.
Unlocking New Processing Capabilities
A key advantage is its excellent weldability. Unlike virgin PTFE, which is extremely difficult to weld, modified PTFE can be thermally bonded, allowing for the fabrication of more complex shapes and robust vessel linings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a high-performance material always involves balancing benefits with practical considerations.
Cost Considerations
Modified PTFE is a more advanced material, and its manufacturing process is more complex. As a result, it is generally more expensive than standard virgin PTFE.
Specification and Compliance
Virgin PTFE is the established standard in many industries and specifications. While modified PTFE is often a superior material, using it in an application historically designed for virgin PTFE may require re-qualification or specific engineering approval.
When Purity is the Only Priority
For applications where only the fundamental properties of PTFE are required—such as basic chemical resistance in a low-load environment or meeting a legacy FDA specification—the added performance and cost of modified PTFE may be unnecessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be driven entirely by the demands of your specific project.
- If your primary focus is meeting standard food/pharma specifications or low-cost chemical lining: Virgin PTFE is often the sufficient and pre-approved choice.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under load or high-purity sealing: Modified PTFE's superior creep resistance and smoother surface make it the clear technical winner.
- If your primary focus is complex fabrication or high-voltage insulation: Modified PTFE is the only viable option due to its unique weldability and higher dielectric strength.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, non-critical mechanical parts: You may also consider Mechanical PTFE, which includes reprocessed resin for less demanding applications.
Ultimately, selecting the right material depends on a clear understanding of your application's specific mechanical, chemical, and processing demands.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Modified PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Flow (Creep) | High tendency to deform under load | Drastically reduced (by ~3x) |
| Surface Finish | Standard, more porous | Smoother, less porous |
| Weldability | Extremely difficult | Excellent |
| Dielectric Strength | Standard | Higher |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Ideal For | Basic chemical resistance, food/pharma compliance | High-load seals, high-purity, complex fabrication |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Solution for Your Critical Components?
Choosing between virgin and modified PTFE is crucial for the success of your application in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—that meet the exacting demands of specialized industries.
We deliver value by:
- Providing expert material selection guidance to ensure your components perform reliably under stress, in high-purity environments, or in complex assemblies.
- Offering custom fabrication services from rapid prototypes to high-volume production runs, leveraging the unique properties of materials like modified PTFE for weldable liners or high-voltage insulation.
- Ensuring precision production that prioritizes quality and consistency for your most demanding applications.
Let us help you select and fabricate the ideal PTFE component for your needs. Contact our experts today for a consultation and quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















