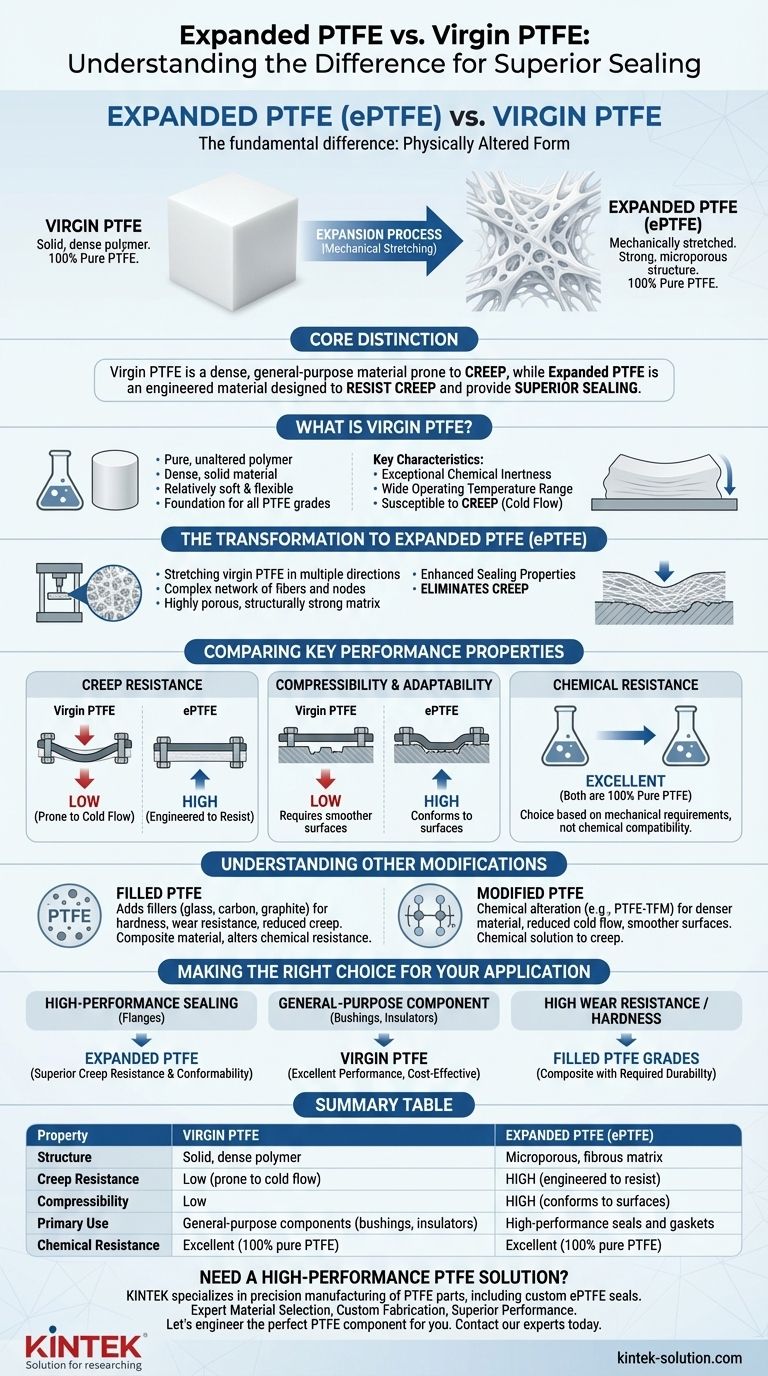
The fundamental difference is that expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is a physically altered form of virgin PTFE. While both are 100% pure PTFE, virgin PTFE is a solid, dense polymer, whereas ePTFE has been mechanically stretched to create a strong, microporous structure with entirely new mechanical properties.
The core distinction lies in their physical form and resulting behavior. Virgin PTFE is a dense, general-purpose material prone to creep under load, while expanded PTFE is an engineered material specifically designed to resist creep and provide superior sealing.

What is Virgin PTFE?
Virgin PTFE is the pure, raw form of Polytetrafluoroethylene. It is a dense, solid material created directly from the polymerization process without any additives or structural modifications.
The Pure, Unaltered Polymer
As the base material, virgin PTFE is known for being relatively soft and flexible. It is the foundation from which all other grades, including expanded and filled PTFE, are derived.
Key Characteristics
The defining feature of virgin PTFE is its exceptional chemical inertness and wide operating temperature range. It is chemically stable and non-reactive, making it a default choice for components like bushings, insulators, and lab equipment. However, it is susceptible to creep, or "cold flow," where the material deforms permanently under sustained pressure.
The Transformation to Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Expanded PTFE begins as virgin PTFE but undergoes a specific mechanical process that dramatically changes its properties. It is not chemically different, but its physical structure is completely re-engineered.
The Expansion Process
ePTFE is created by stretching virgin PTFE in multiple directions under controlled conditions. This process pulls the material's molecular structure apart, transforming the solid block into a complex network of fibers and nodes.
A Strong, Microporous Structure
The result of this expansion is a material that is no longer solid but is instead a highly porous, yet structurally strong, matrix. This new form retains the chemical resistance of virgin PTFE but introduces vastly improved mechanical characteristics.
Enhanced Sealing Properties
This unique structure gives ePTFE high compressibility and excellent adaptability. It can conform to irregular or damaged surfaces, creating an extremely effective seal. Most importantly, the fibrous structure effectively eliminates the creep that affects virgin PTFE.
Comparing Key Performance Properties
While chemically identical, the physical differences between virgin and expanded PTFE lead to stark contrasts in performance, especially in mechanical applications like gasketing.
Creep Resistance
This is the most significant differentiator. Virgin PTFE will deform and thin out over time when compressed, leading to potential leaks. ePTFE is specifically engineered to resist creep, maintaining a reliable seal under bolt load.
Compressibility and Adaptability
The soft, porous nature of ePTFE allows it to compress easily and fill in surface imperfections on flanges. Solid virgin PTFE is far less compressible and requires smoother, more uniform surfaces to seal effectively.
Chemical Resistance
Both materials offer exceptional, broad chemical resistance because they are both 100% pure PTFE. Your choice between them should be based on mechanical requirements, not chemical compatibility.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Other Modifications
Expanded PTFE is just one way to modify virgin PTFE. Understanding other methods helps clarify its specific purpose.
The Role of Fillers
Filled PTFE grades add materials like glass, carbon, or graphite to the virgin PTFE base. These fillers increase hardness, improve wear resistance, and reduce creep, but they do so by creating a composite material, which can alter chemical resistance.
The Concept of Modified PTFE
Modified PTFE (like PTFE-TFM) involves a chemical alteration to the polymer itself, creating a denser material with reduced cold flow, smoother surfaces, and better weldability compared to virgin PTFE. This is a chemical, not physical, solution to the problem of creep.
Application-Specific Choices
The original, unmodified virgin PTFE is an excellent general-purpose material. However, for specialized applications like high-performance sealing in the chemical industry, the engineered structure of ePTFE provides reliability that virgin PTFE cannot match.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct form of PTFE requires matching the material's physical properties to the mechanical demands of your task.
- If your primary focus is high-performance sealing for flanges: Expanded PTFE is the definitive choice for its superior creep resistance and conformability.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose, chemically inert component like a bushing or insulator: Virgin PTFE provides excellent performance and is the standard, cost-effective option.
- If your primary focus is high wear resistance or hardness for a mechanical part: Investigate filled PTFE grades to find a composite with the required durability.
Ultimately, choosing the right PTFE variant means looking beyond chemical resistance and focusing on the physical structure best suited for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Solid, dense polymer | Microporous, fibrous matrix |
| Creep Resistance | Low (prone to cold flow) | High (engineered to resist) |
| Compressibility | Low | High (conforms to surfaces) |
| Primary Use | General-purpose components (bushings, insulators) | High-performance seals and gaskets |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (100% pure PTFE) | Excellent (100% pure PTFE) |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Solution for Your Application?
Choosing between virgin PTFE, expanded PTFE (ePTFE), or filled grades is critical for the success and reliability of your components. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE parts, including custom ePTFE seals and liners designed to solve problems like creep and sealing failure.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors by providing:
- Expert Material Selection: We'll help you choose the right PTFE variant—whether virgin, expanded, or filled—based on your specific mechanical and chemical requirements.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume production, we manufacture components to your exact specifications.
- Superior Performance: Leverage the benefits of ePTFE, such as exceptional creep resistance and conformability, for seals that last.
Let's engineer the perfect PTFE component for you. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















