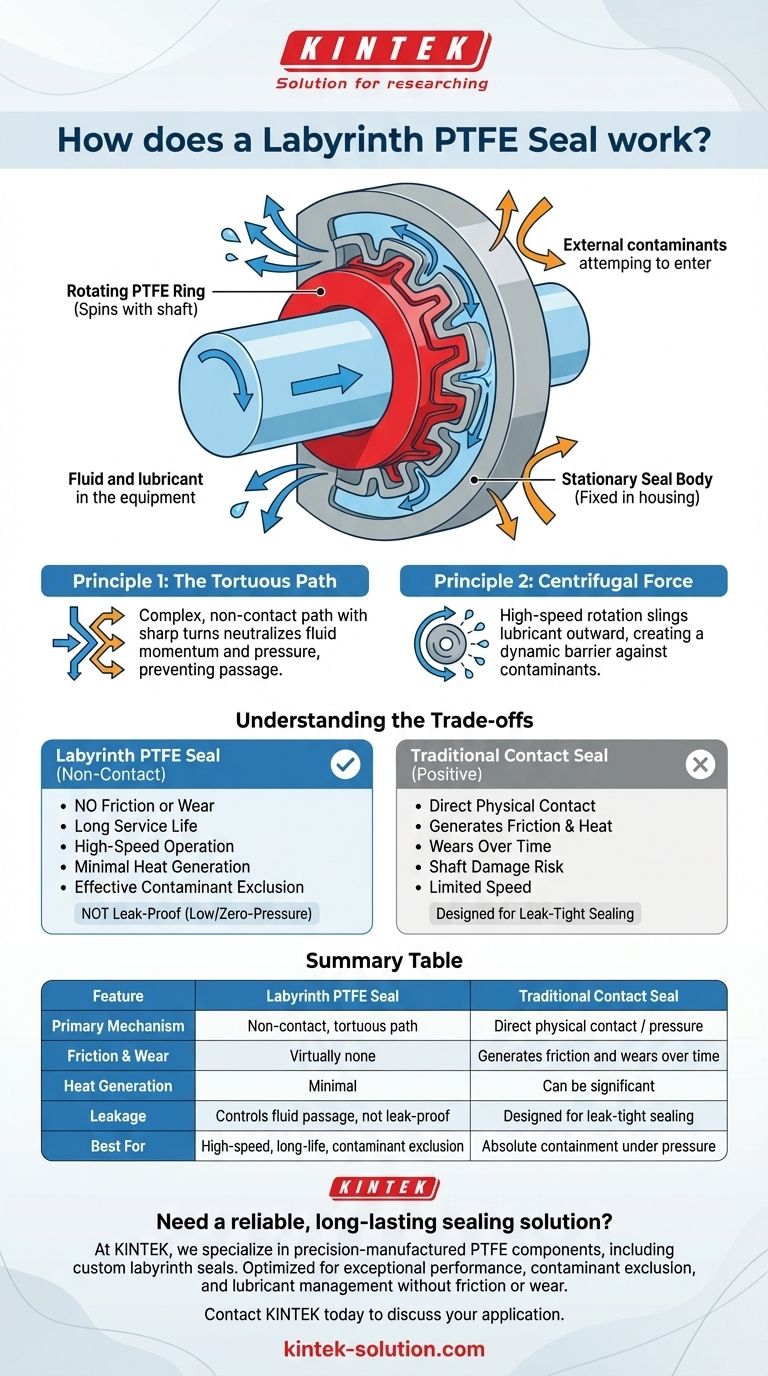
At its core, a Labyrinth PTFE seal works by creating a complex, non-contact path instead of a direct physical barrier. A PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) ring spins with the equipment's shaft, and its intricate grooves interlock with stationary grooves in the seal body. This arrangement forms a difficult, maze-like journey—the "labyrinth"—that uses fluid dynamics and centrifugal force to contain lubricants and block contaminants without any parts wearing against the shaft.
The crucial concept to grasp is that a Labyrinth PTFE Seal is not designed to be leak-proof. Instead, its purpose is to provide exceptional, long-term reliability in low-pressure applications by controlling fluid passage and blocking contaminants without the wear, friction, and heat generation of a traditional contact seal.

The Anatomy of a Non-Contact Seal
To understand how the seal functions, we must first look at its two primary components and the pathway they create together.
The Stationary Seal Body
This component is fixed within the equipment housing. It features a series of machined grooves on its internal diameter that face the rotating shaft.
The Rotating PTFE Ring
The PTFE ring is the dynamic component. It is designed to fit into a groove on the seal body and spin in unison with the shaft. Like the body, its face contains a pattern of grooves.
The Labyrinth Path
When assembled, the grooves on the rotating ring and the stationary body interlock without touching. This creates a narrow, convoluted, and tortuous path that any fluid or contaminant must navigate to pass through the seal.
The Two Core Sealing Principles
A Labyrinth PTFE Seal relies on two physical principles working in concert, rather than simple surface pressure.
Principle 1: The Tortuous Path
The primary sealing mechanism is the complex path itself. For fluid to escape or contaminants to enter, they must travel through a long series of sharp turns and expansions.
Each turn causes the fluid to lose energy and pressure, effectively neutralizing its momentum and preventing it from passing through the seal.
Principle 2: Centrifugal Force
As the shaft and PTFE ring rotate at high speed, they act like a centrifuge. Any oil mist or lubricant that enters the labyrinth is immediately thrown outward by centrifugal force.
This force creates a dynamic barrier, constantly pushing the lubricant back toward the bearing it's meant to protect and slinging external contaminants away from the seal's interior. Using multiple rings significantly enhances this effect.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Labyrinth vs. Positive Seals
Choosing a labyrinth seal requires understanding its specific strengths and limitations, especially when compared to a traditional positive-contact seal like a lip seal.
The Non-Contact Advantage
Because the rotating ring never touches the stationary body or the shaft, there is virtually no friction or wear.
This design leads to a much longer service life, generates less heat, and allows for operation at very high speeds where a contact seal would quickly fail. It also means the shaft itself will not be grooved or damaged over time.
The Critical Limitation: Not Leak-Proof
The non-contact design means a Labyrinth PTFE Seal is not a positive, leak-tight seal. It is engineered for containment and exclusion in low or zero-pressure environments.
It excels at keeping oil mist inside a gearbox or preventing dust from entering a bearing housing. However, it will not hold back a static fluid level or any significant pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal is about aligning the technology with the operational goal.
- If your primary focus is longevity and reliability in high-speed equipment: A Labyrinth PTFE seal is an excellent choice due to its non-contact, wear-free design that eliminates heat and friction.
- If your primary focus is absolute, leak-proof containment under pressure: You should use a traditional positive contact seal, as a labyrinth seal is not designed for zero leakage.
- If your primary focus is protecting bearings from external contaminants: The labyrinth design provides a superior and permanent barrier against dust and moisture without adding friction or causing shaft wear.
Ultimately, understanding that this seal manages fluid rather than blocking it is the key to deploying it successfully.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Labyrinth PTFE Seal | Traditional Contact Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Non-contact, tortuous path | Direct physical contact / pressure |
| Friction & Wear | Virtually none | Generates friction and wears over time |
| Heat Generation | Minimal | Can be significant |
| Leakage | Controls fluid passage, not leak-proof | Designed for leak-tight sealing |
| Best For | High-speed, long-life, contaminant exclusion | Absolute containment under pressure |
Need a reliable, long-lasting sealing solution for your high-speed or sensitive equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision-manufactured PTFE components, including custom labyrinth seals. Our expertise ensures your seals are optimized for performance, providing exceptional contaminant exclusion and lubricant management without the friction, wear, or heat of traditional seals.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors with custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE seals can enhance your application's reliability and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry



















