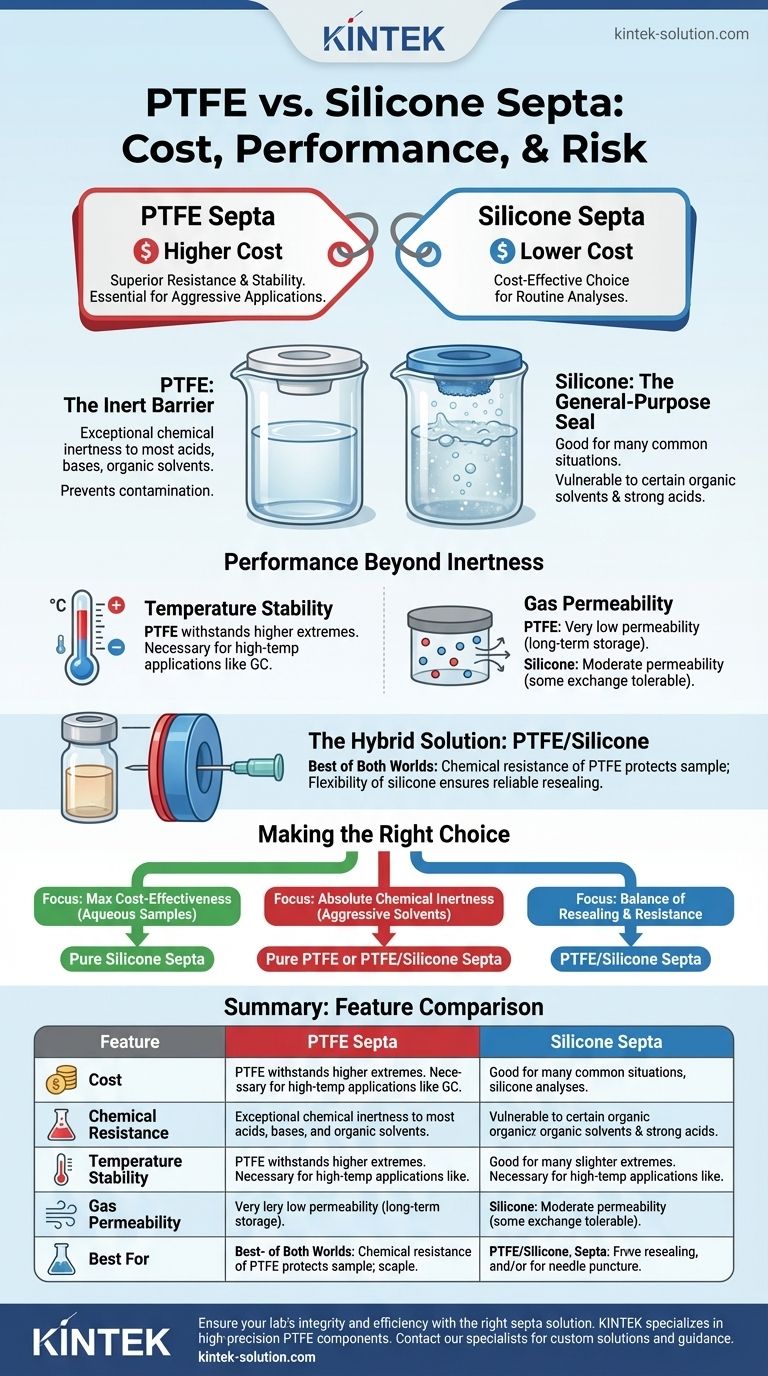
In short, PTFE septa are more expensive than silicone septa. This price difference is a direct reflection of PTFE's significantly superior chemical resistance and thermal stability. While silicone is a cost-effective choice for routine analyses, PTFE is the required material for applications involving aggressive solvents or extreme temperatures where sample integrity is paramount.
The choice between PTFE and silicone is not simply about initial cost, but about managing risk. Selecting the wrong septum can lead to sample contamination, instrument damage, and failed analyses—outcomes far more costly than the price of the component itself.

The Core Difference: Chemical Resistance
The primary factor driving the cost and application of these materials is their ability to withstand chemical attack. This single property dictates where each septum can be safely and effectively used.
PTFE: The Inert Barrier
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for its exceptional chemical inertness. It is virtually unaffected by most acids, bases, organic solvents, and other reactive chemicals.
This makes it the essential choice for applications where the septum will come into contact with aggressive substances, ensuring no contaminants leach into the sample or vial headspace.
Silicone: The General-Purpose Seal
Silicone is a versatile and more economical material that is chemically inert in many common situations.
However, it has known vulnerabilities. Certain organic solvents and strong acids can cause silicone to swell or degrade, compromising the seal and potentially contaminating the sample.
Performance Beyond Chemical Inertness
While chemical stability is the main story, other performance characteristics play a critical role in justifying the cost difference and guiding your selection.
Temperature Stability
Both materials perform well across a broad temperature range. However, PTFE can withstand higher temperature extremes than silicone, making it necessary for high-temperature applications like gas chromatography.
Gas Permeability
PTFE has very low permeability, creating an excellent barrier against gas exchange. This is ideal for long-term sample storage or when protecting a sample from atmospheric contamination is critical.
Silicone has moderate permeability, which is perfectly acceptable for many routine procedures and can even be advantageous in specific applications like headspace sampling where some gas exchange is tolerable.
The Hybrid Solution: PTFE/Silicone
A third, very common option combines both materials. PTFE/Silicone septa consist of a durable, resealable silicone body with a thin layer of PTFE laminated on the side that faces the sample.
This design offers an excellent compromise: the chemical resistance of PTFE protects the sample, while the flexibility and resealing capability of silicone provide a reliable mechanical seal after multiple needle punctures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a septum requires balancing budget against the technical demands of your analysis. Misjudging this balance has clear consequences.
The Risk of Over-Specifying
Using a pure PTFE or PTFE-lined septum for a simple analysis with a non-aggressive aqueous sample is unnecessary. In this case, you are paying a premium for chemical resistance you do not need, and a simple silicone septum would perform just as well at a lower cost.
The Danger of Under-Specifying
Using a silicone septum with an aggressive organic solvent is a critical error. The solvent can extract plasticizers and other compounds from the silicone, introducing contaminant peaks into your analysis. It can also cause the septum to swell or break down, leading to leaks and failed runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your analytical goal should be the final determinant of which septum you choose.
- If your primary focus is maximum cost-effectiveness for aqueous or non-aggressive samples: A pure silicone septum is the most economical and practical choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute chemical inertness for aggressive solvents, acids, or bases: A pure PTFE or, more commonly, a PTFE/Silicone septum is required to protect your sample.
- If your primary focus is a balance of reliable resealing and high chemical resistance: A PTFE/Silicone septum provides the best overall performance and value for most demanding chromatography applications.
Ultimately, selecting the correct septum is a crucial step in ensuring the integrity of your data and the efficiency of your lab.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Septa | Silicone Septa |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional (inert to most solvents) | Good, but can swell/degrade |
| Temperature Stability | Higher extremes | Broad, but lower than PTFE |
| Gas Permeability | Very low | Moderate |
| Best For | Aggressive solvents, extreme temps, sample integrity | Routine analyses, aqueous samples, cost-effectiveness |
Ensure your lab's integrity and efficiency with the right septa solution.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including septa, seals, liners, and custom labware. Whether you need the superior chemical resistance of PTFE or a cost-effective silicone alternative, our experts can guide you to the optimal choice for your application in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring every component meets your exact specifications for performance and reliability. Don't let the wrong septum compromise your analysis—contact us today for a consultation and let us provide a solution that protects your samples and your budget.
Contact our specialists now to discuss your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- PTFE Deep Evaporating Dishes Customizable Laboratory and Industrial Solutions
People Also Ask
- How do PTFE syringe filters compare to membrane filters? A Guide to Chemical Compatibility
- What types of labware or tools are commonly made from PTFE? Essential Chemically-Resistant Equipment for Your Lab
- What are some specific applications of PTFE shovels in the laboratory? Ensure Sample Purity and Safety
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What types of products are related to headspace septa? Essential Components for Leak-Proof Analysis
- Why are PTFE silicone septa important in laboratory settings? Essential for Sample Integrity and Accuracy
- What are the key features of PTFE-lined bottle caps? Ensure Chemical Integrity and Purity for Your Samples
- How does the transparency feature of PTFE vials aid in laboratory work? Enhance Visibility and Efficiency



















