For applications involving sticky or adhesive substances, the choice of impeller material directly impacts process efficiency and cleanliness. While both stainless steel and PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) are common, PTFE impellers offer vastly superior non-stick properties. Stainless steel, though easier to clean than many other metals, is more prone to material buildup when mixing moderately to highly adhesive compounds.
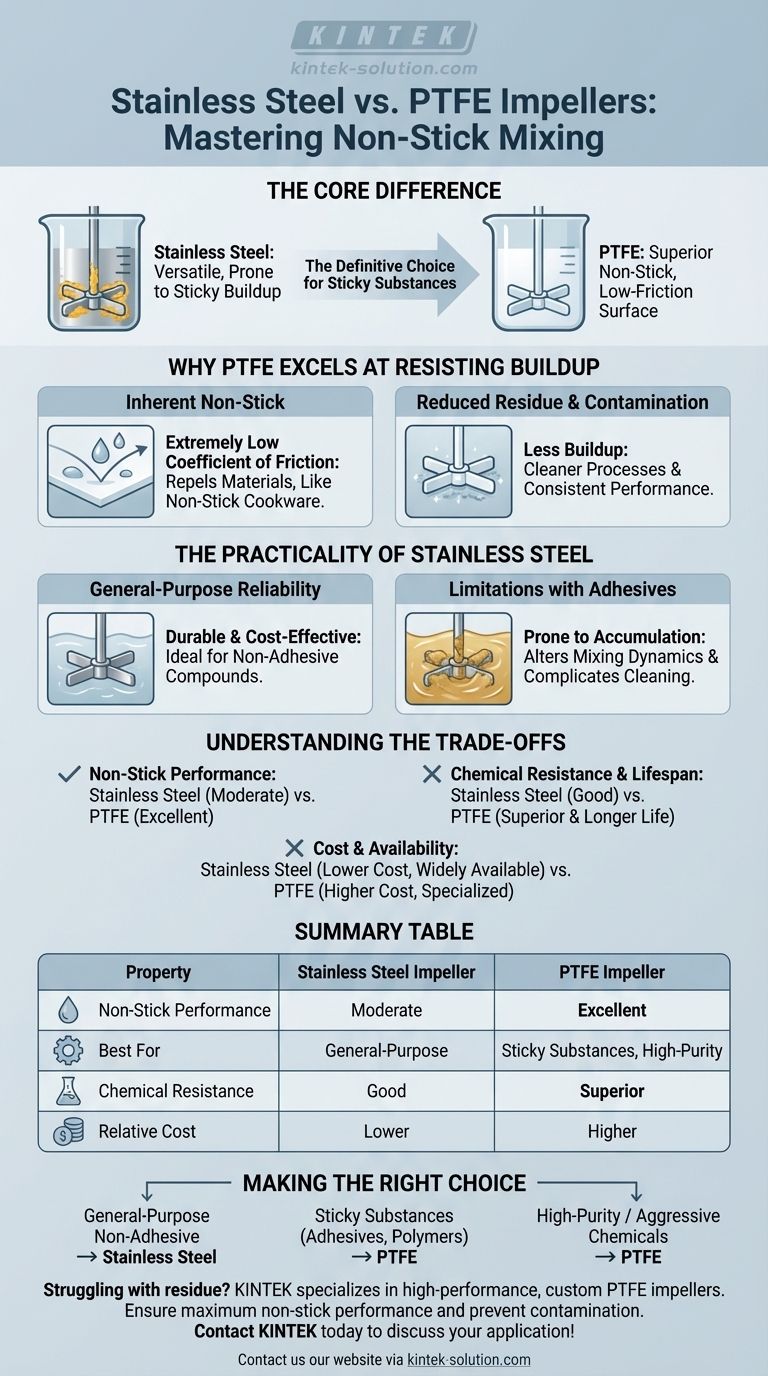
The core difference is fundamental: Stainless steel is a versatile default material, but PTFE's inherent low-friction, non-stick surface makes it the definitive choice for preventing residue, ensuring purity, and maintaining consistent flow with sticky substances.

Why PTFE Excels at Resisting Buildup
Inherent Non-Stick Properties
PTFE is renowned for its extremely low coefficient of friction. Its surface is engineered to repel other substances, which is why it is used as a coating on non-stick cookware.
This characteristic directly translates to mixing applications. Materials, especially polymers and adhesives, have a very difficult time adhering to a PTFE surface.
Reduced Residue and Contamination
Because materials do not stick to PTFE, there is significantly less buildup or residue left on the impeller after mixing.
This is critical in applications requiring high purity or where cross-contamination between batches is a concern. The result is a cleaner process and more consistent mixing performance.
The Practicality of Stainless Steel
General-Purpose Reliability
Stainless steel remains a common choice because it is a durable, cost-effective, and widely available material for general mixing tasks.
For processes involving non-adhesive compounds, its performance is more than adequate, and it is generally easy to clean.
Limitations with Adhesive Compounds
The challenge with stainless steel arises when working with moderately to highly adhesive substances.
Material can begin to accumulate on the impeller blades. This buildup can alter the mixing dynamics, reduce efficiency, and complicate the cleaning process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Non-Stick Performance
PTFE is the clear winner for non-stick performance. It is specifically designed to prevent adhesion, making it ideal for sticky materials. Stainless steel is functional but can struggle with residue.
Cost and Availability
Stainless steel impellers are typically cheaper and more widely available in a vast range of styles and sizes.
PTFE impellers often come at a higher cost and may require more effort to source, but this is frequently justified by their specialized performance benefits.
Chemical Resistance and Lifespan
PTFE offers superior chemical resistance compared to most traditional materials, including stainless steel, especially against aggressive chemicals.
This resistance, combined with reduced wear from its low-friction properties, often results in a longer, low-maintenance lifespan in demanding chemical environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct impeller material is a strategic decision based on your specific process requirements and the nature of the substances you are mixing.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose mixing of non-adhesive fluids: Stainless steel is the most practical and cost-effective choice due to its availability and durability.
- If your primary focus is working with sticky substances like adhesives or polymers: PTFE is the superior option to minimize residue, ensure process cleanliness, and maintain consistent mixing.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or chemically aggressive applications: PTFE's excellent chemical resistance and non-stick surface make it the safest and most reliable choice.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of your materials is the key to selecting an impeller that enhances, rather than complicates, your process.
Summary Table:
| Property | Stainless Steel Impeller | PTFE Impeller |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Stick Performance | Moderate; prone to buildup with adhesives | Excellent; inherent low-friction surface |
| Best For | General-purpose, non-adhesive mixing | Sticky substances (polymers, adhesives), high-purity applications |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Superior; excellent for aggressive chemicals |
| Relative Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized |
Struggling with impeller residue or contamination? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including impellers—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision-engineered PTFE impellers ensure maximum non-stick performance, reduce downtime for cleaning, and prevent cross-contamination in your critical processes. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver solutions that enhance your efficiency and product purity.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and receive a custom solution quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does bearing pressure affect the coefficient of friction in PTFE slide bearings? Maximize Performance with Higher Loads
- What are the notable performance characteristics of PTFE seals? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How should Teflon O-rings be maintained? A Proactive Guide to Prevent Seal Failure
- What temperature range can PTFE expansion bellows withstand? Endure Extremes from -200°C to 260°C
- What is the purpose of sintering in the PTFE bush manufacturing process? | Achieve Superior Component Performance
- What are the key differences between monoaxial and multidirectional expanded PTFE? Choose the Right ePTFE for Your Seal
- What types of fillers are commonly used in PTFE? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- In which industries are Teflon (PTFE) balls commonly used? Key Applications & Benefits



















