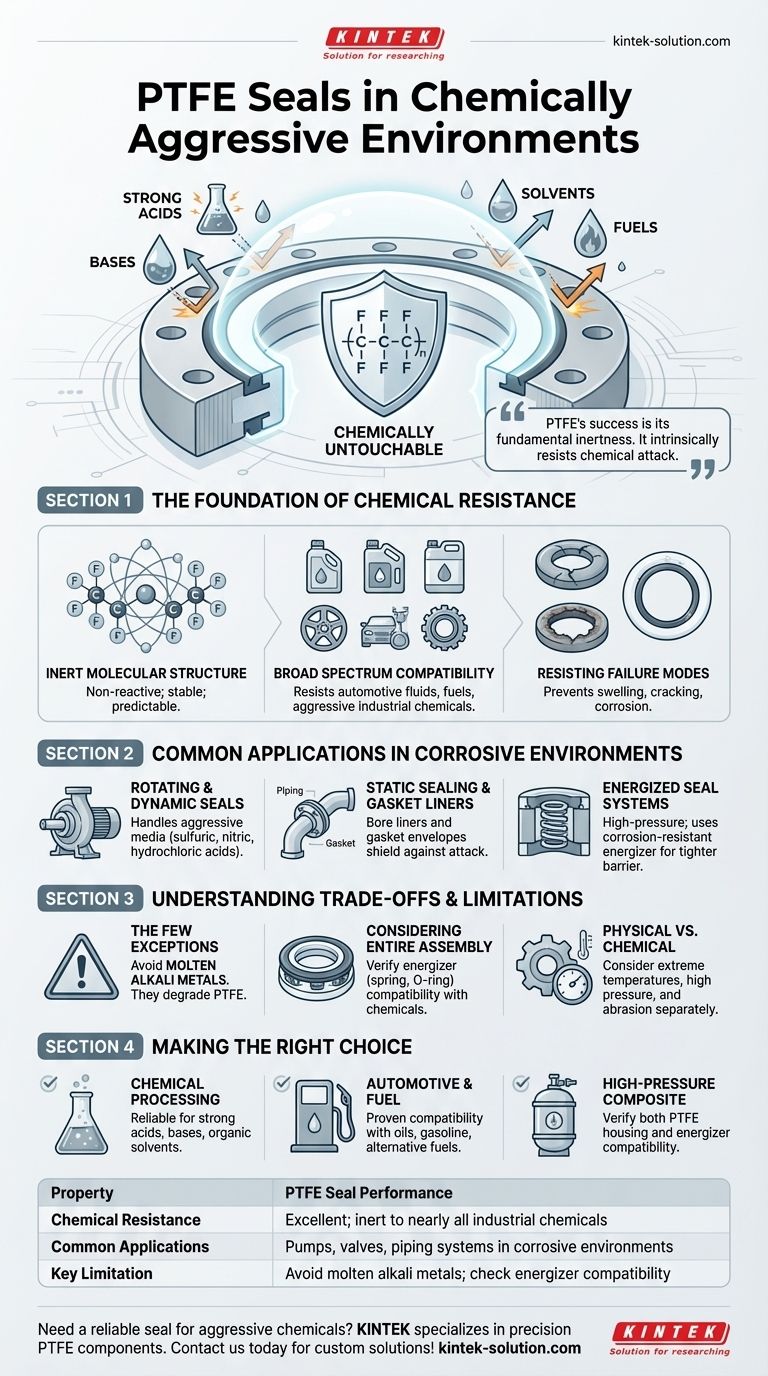
In chemically aggressive environments, PTFE seals deliver exceptionally reliable performance. They are among the most chemically resistant polymers available, remaining inert and non-reactive when exposed to nearly all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, bases, solvents, and fuels. This unique resilience prevents material degradation, swelling, or cracking, ensuring a durable and consistent seal under the most demanding conditions.
The core reason for PTFE's success is its fundamental inertness. Its reliability in harsh environments comes from a molecular structure that intrinsically resists chemical attack, rather than merely tolerating it for a limited time.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Resistance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not just resistant; for most practical purposes, it is chemically untouchable. This capability is not an additive feature but a result of its core molecular makeup.
An Inert Molecular Structure
PTFE is non-reactive by nature. It does not degrade, corrode, or react with the substances it contacts, making it a stable and predictable material for critical sealing applications.
Broad Spectrum Compatibility
This material offers near-universal chemical compatibility. It remains unaffected by substances ranging from automotive fluids and fuels to the most aggressive industrial chemicals.
Resisting Common Failure Modes
PTFE's inertness directly prevents common material failures seen in lesser polymers. It is not susceptible to swelling, cracking, or corrosion that can be caused by chemical exposure over time, ensuring long-term operational integrity.
Common Applications in Corrosive Environments
The properties of PTFE make it the material of choice for a wide variety of sealing applications where chemical exposure is a primary concern.
Rotating and Dynamic Seals
PTFE rotating shaft seals and bellow seals are standard in pumps and machinery handling aggressive media. They maintain their integrity even when exposed to concentrated sulfuric, nitric, or hydrochloric acid, even under boiling conditions.
Static Sealing and Gasket Liners
In piping systems, PTFE can be used as a bore liner or "envelope" for gaskets. This design shields a standard gasket from chemical attack, using the PTFE as a protective, non-reactive barrier.
Energized Seal Systems
For high-pressure applications, energized PTFE seals are common. These designs use a corrosion-resistant energizer (often a spring or elastomer) inside a machined PTFE jacket. The energizer provides the initial sealing force, which is then amplified by system pressure for an even tighter barrier against leakage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PTFE's chemical resistance is nearly absolute, a comprehensive technical assessment requires acknowledging its few limitations and system-level considerations.
The Few Chemical Exceptions
PTFE can be attacked by a very small and specific group of substances. The most notable exceptions are molten alkali metals, which will degrade the material.
Considering the Entire Seal Assembly
In composite seals, such as energized seals, the overall chemical resistance is only as strong as its weakest component. The energizer material (whether a metal spring or a rubber O-ring) must also be compatible with the chemical environment.
Physical vs. Chemical Properties
Exceptional chemical resistance does not guarantee performance against all operational stresses. Factors like extreme temperatures, high pressure, and abrasive media must be considered separately to ensure the physical durability of the seal in its application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a sealing material requires matching its properties to the primary demands of the system.
- If your primary focus is reliability in chemical processing: PTFE is an industry-standard choice for sealing against strong acids, bases, and organic solvents.
- If your primary focus is automotive or fuel systems: PTFE's proven compatibility with aggressive oils, gasoline, and alternative fuels ensures long-term seal integrity.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure, composite seal: Always verify the chemical compatibility of both the PTFE housing and any internal energizing materials.
By understanding its inherent chemical stability, you can specify PTFE with confidence for your most demanding sealing challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Seal Performance |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent; inert to nearly all industrial chemicals |
| Common Applications | Pumps, valves, piping systems in corrosive environments |
| Key Limitation | Avoid molten alkali metals; check energizer compatibility in composite seals |
Need a reliable seal for aggressive chemicals? KINTEK specializes in precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensures your equipment is protected against harsh media. Contact us today to discuss your specific sealing challenge!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE oil seals? Superior Performance for Extreme Conditions
- What advantage does the low coefficient of friction of PTFE balls provide? Boost Durability and Efficiency
- How does the built-in spring help PTFE shaft seals adapt to varying conditions? Ensure a Reliable, Long-Lasting Seal
- What maintenance advantages do PTFE compensators offer? Maximize Uptime with Self-Cleaning Design
- What are the key properties of Teflon sheets? A Guide to PTFE's Versatility
- What tooling strategies are effective for machining PTFE? Achieve Precision and a Clean Finish
- What is a floating ball valve and how does it seal line pressure? A Guide to Pressure-Actuated Sealing
- What are the benefits of using PTFE reducing flanges? Achieve Superior Flow & Corrosion Resistance



















