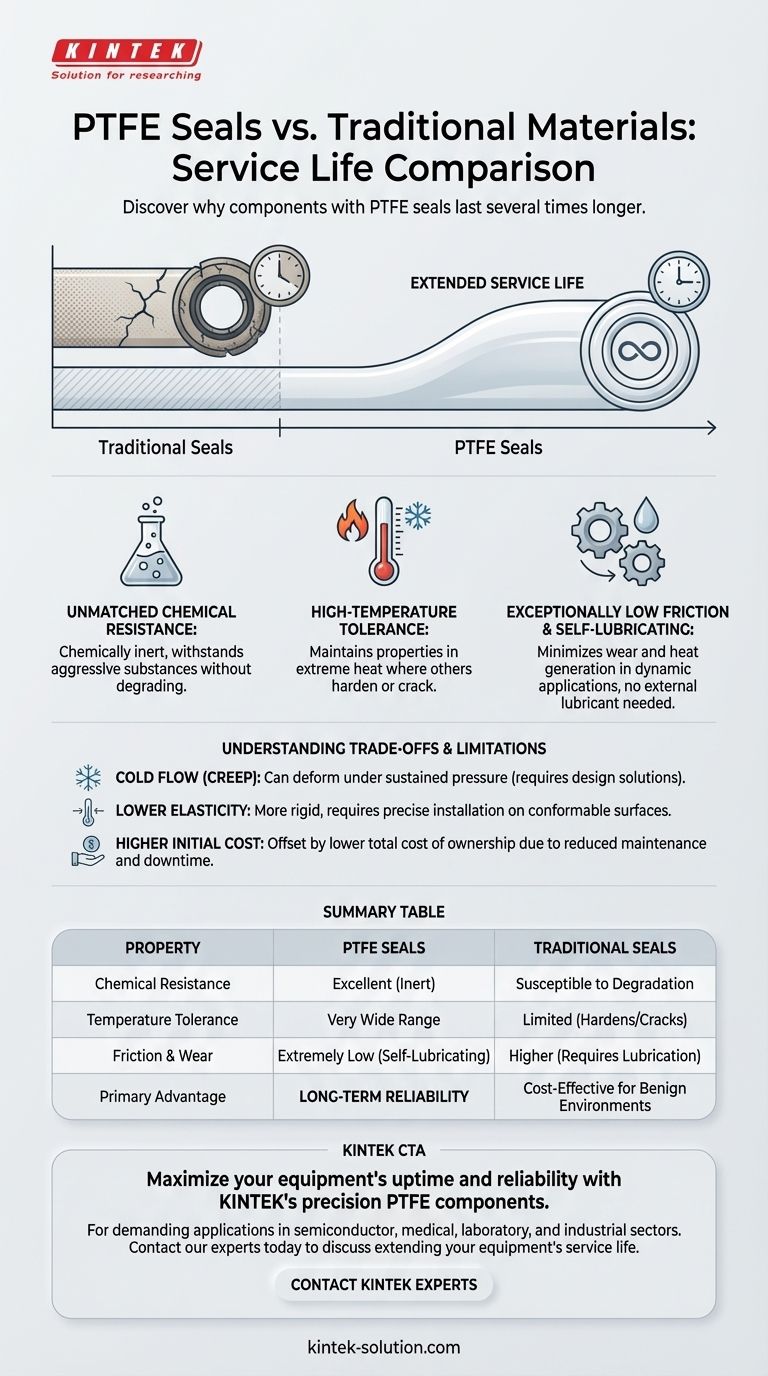
In a direct comparison, studies show that components using Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) seals have a service life several times longer than those with traditional sealing materials. This significant increase in longevity is not arbitrary; it is a direct result of PTFE's unique molecular structure, which provides superior resistance to high temperatures, chemical corrosion, and operational friction.
The extended service life of a PTFE seal is its primary advantage, stemming directly from its inherent chemical inertness, thermal stability, and low-friction, self-lubricating surface. For demanding applications, this makes it a fundamentally more durable choice than traditional rubber or elastomer seals.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE's Durability
To understand why PTFE seals last longer, we must look at the specific material properties that prevent the common modes of failure seen in traditional seals like degradation, wear, and hardening.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert polymers known. This means it can withstand exposure to a vast range of aggressive chemicals, acids, and bases without degrading, swelling, or losing its structural integrity. Traditional rubber seals, in contrast, are often susceptible to chemical attack, which quickly compromises their sealing ability.
High-Temperature Tolerance
Many traditional sealing materials will harden, crack, or lose their elasticity when exposed to high operating temperatures. PTFE maintains its key properties across a very wide temperature range, making it exceptionally reliable in applications involving extreme heat where other materials would fail prematurely.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. In dynamic sealing applications where parts are in motion, this dramatically reduces the wear and tear on the seal's surface. Less friction means less heat generation and less material abrasion over millions of cycles.
Self-Lubricating Nature
This low-friction characteristic also means PTFE is self-lubricating. It does not require external lubricants to ensure smooth operation, which simplifies system design and eliminates a common point of failure. This prevents the "stick-slip" phenomenon that can cause jerky movement and accelerated wear in other seals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While its advantages are significant, PTFE is not the universally perfect solution for every scenario. Acknowledging its limitations is key to making a correct engineering decision.
Cold Flow (Creep)
Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can be prone to "creep" or "cold flow," where the material slowly deforms over time. In high-pressure static sealing applications, this can eventually lead to a loss of sealing force if the seal is not properly designed (e.g., with fillers or a spring-energizing element).
Lower Elasticity
Compared to rubber and other elastomers, PTFE is a relatively rigid material. It has less "memory" and is not as compliant, meaning it won't conform as easily to rough or imperfect sealing surfaces. This also means installation can require more care to avoid damaging the seal.
Initial Cost vs. Total Cost
The initial procurement cost of a PTFE seal is often higher than that of a standard rubber seal. However, this higher upfront cost is frequently offset by a lower total cost of ownership due to significantly reduced maintenance, less downtime, and a much longer replacement interval.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires matching the material's strengths to the application's demands.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh chemical or high-temperature environments: PTFE is the definitive choice, as its chemical and thermal stability will prevent the rapid degradation that other materials would suffer.
- If your primary focus is service life in a dynamic (moving) application: The self-lubricating, low-friction properties of PTFE will minimize wear and dramatically extend the operational life of the seal.
- If your primary focus is a low-pressure, static seal in a benign environment: A traditional, more elastic rubber seal may be a more cost-effective choice, provided the conditions do not challenge its material properties.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental properties of PTFE allows you to move beyond simple material selection and engineer for long-term reliability.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Seals | Traditional Seals (e.g., Rubber) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (chemically inert) | Susceptible to degradation |
| Temperature Tolerance | Very wide range | Limited, can harden/crack |
| Friction & Wear | Extremely low, self-lubricating | Higher, requires lubrication |
| Primary Advantage | Long-term reliability in harsh conditions | Cost-effective for benign environments |
Maximize your equipment's uptime and reliability with KINTEK's precision PTFE components.
For demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, our custom-fabricated PTFE seals, liners, and labware are engineered for superior longevity. We combine precision production with deep material expertise to deliver solutions that reduce maintenance, minimize downtime, and lower your total cost of ownership—from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can extend the service life of your critical equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry



















