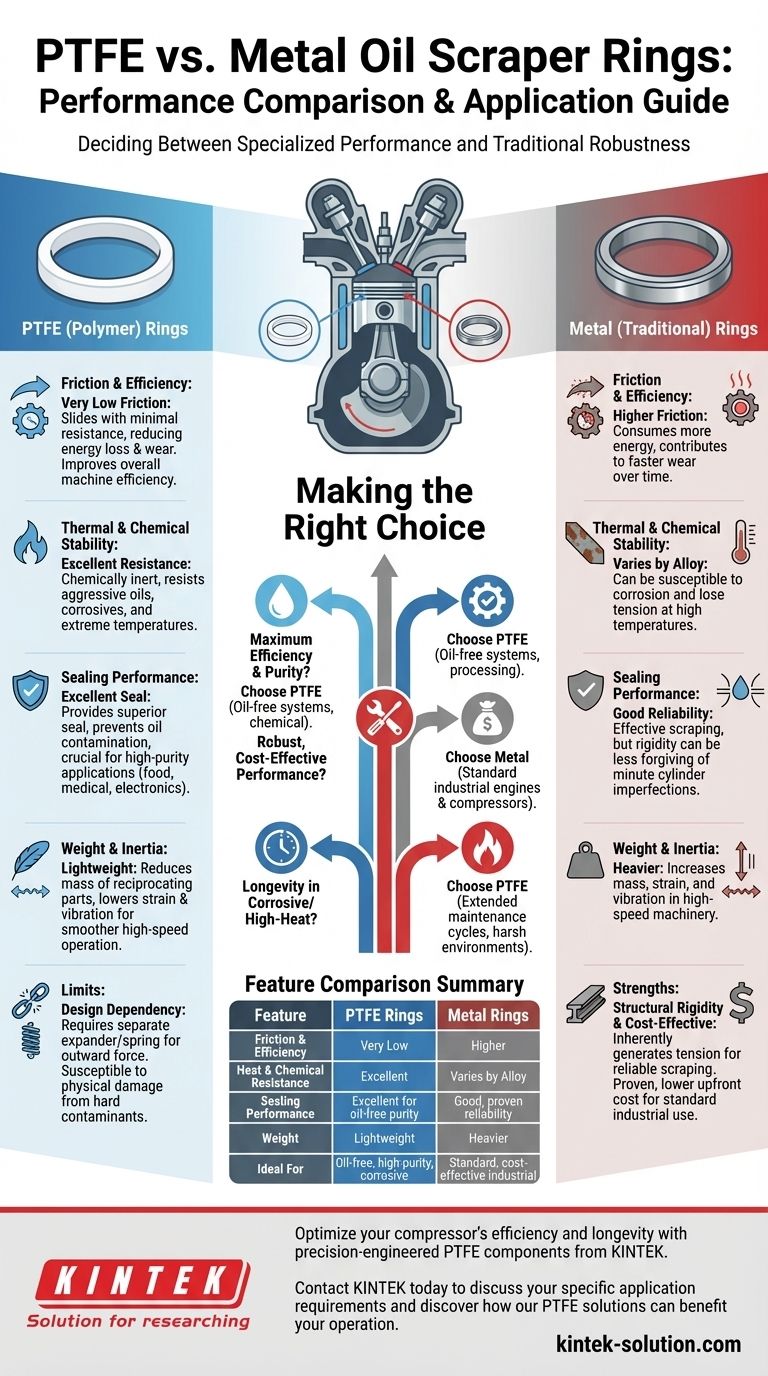
In short, PTFE oil scraper rings generally outperform traditional metal rings by offering lower friction, superior heat and chemical resistance, and lighter weight. This translates to improved efficiency and durability, especially in demanding or specialized applications like oil-free compressors.
The choice between PTFE and metal is a decision between specialized performance and traditional robustness. PTFE rings excel at reducing friction and resisting harsh environments, while metal rings provide proven structural strength and cost-effectiveness for standard industrial use.
The Core Performance Differences
To understand which ring is right for your equipment, you must look beyond the material and consider its impact on day-to-day operation, efficiency, and long-term maintenance.
Friction and Efficiency
PTFE, known for its extremely low coefficient of friction, slides against the cylinder wall with minimal resistance. This directly reduces energy loss, minimizes wear on both the ring and the cylinder, and improves the overall efficiency of the machine.
Metal rings inherently have higher friction, which consumes more energy and contributes to faster wear over time.
Thermal and Chemical Stability
PTFE is chemically inert and has outstanding heat resistance. It will not degrade or lose its mechanical properties when exposed to aggressive oils, corrosive substances, or the extreme temperatures found in many compressors.
Metal rings, depending on the alloy, can be susceptible to corrosion from certain chemicals and moisture. They can also lose their temper and tension if operating temperatures exceed their design limits.
Sealing Performance and Contamination
The design and material properties of PTFE rings allow them to provide an excellent seal against the cylinder wall. This is critical for preventing lubricating oil from contaminating the compressed air or gas stream, a key requirement in food, medical, and electronics applications.
While metal rings provide effective scraping, their rigidity can make them less forgiving of minute cylinder imperfections, potentially impacting sealing efficiency over time.
Weight and Inertia
Being significantly lighter than metal, PTFE rings reduce the mass of reciprocating components. This lowers strain and vibration, which is particularly beneficial in high-speed machinery, contributing to smoother operation and longer component life.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Specialization
No material choice is without compromise. The advantages of one are often balanced by the strengths of the other in different contexts.
The Case for Metal: Structural Rigidity and Tension
The primary strength of a metal ring is its inherent structural rigidity. It generates its own tension to press firmly and consistently against the cylinder wall, providing reliable and effective oil scraping.
This makes metal rings a robust, proven, and often more cost-effective solution for a vast range of standard engines and compressors where operational conditions are not extreme.
The Limits of PTFE: Design Dependency
PTFE is a polymer, not a metal, and lacks the same structural strength. A PTFE scraper ring's performance is highly dependent on a separate component—an expander or spring—that sits behind it to provide the necessary outward force.
This design dependency means its effectiveness is tied to the entire assembly. While durable against chemicals, PTFE can be more susceptible to physical damage from hard contaminants within the system compared to a solid metal ring.
Application and Cost
PTFE solutions may have a higher initial cost. However, in the correct application—such as an oil-free compressor running continuously—the return on investment comes from improved efficiency, reduced contamination, and longer maintenance intervals. For general-purpose equipment, the reliability and lower upfront cost of metal often make it the more practical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your operational goal is the most important factor in selecting the right material.
- If your primary focus is maximum efficiency and purity: Choose PTFE rings for their low-friction and inert properties, which are ideal for oil-free systems and chemical processing.
- If your primary focus is robust, cost-effective performance: Choose metal rings for their proven reliability and structural strength in standard industrial engines and compressors.
- If your primary focus is longevity in a corrosive or high-heat environment: Choose PTFE for its superior resistance to chemical attack and thermal degradation, which extends maintenance cycles.
Ultimately, aligning the material's properties with the specific demands of your equipment is the key to optimizing performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Rings | Metal Rings |
|---|---|---|
| Friction & Efficiency | Very Low | Higher |
| Heat & Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Varies by Alloy |
| Sealing Performance | Excellent for oil-free purity | Good, proven reliability |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Ideal For | Oil-free, high-purity, corrosive environments | Standard, cost-effective industrial use |
Optimize your compressor's efficiency and longevity with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
Our expertise in custom fabricating high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and labware ensures a perfect match for the demanding environments of the semiconductor, medical, and specialized industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, we prioritize precision production to deliver components that enhance your equipment's performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application requirements and discover how our PTFE solutions can benefit your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Scrapers and Shovels for Demanding Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















