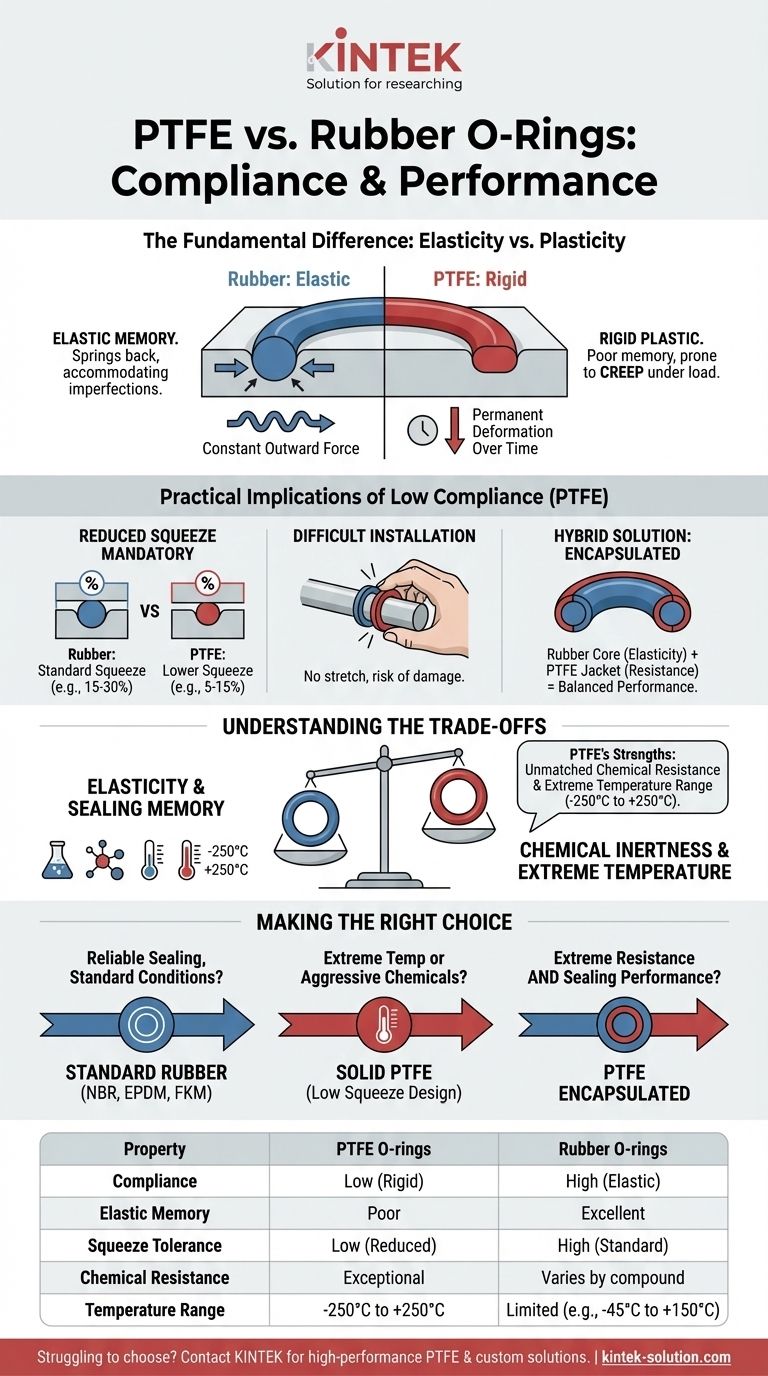
In short, PTFE O-rings are significantly less compliant than rubber O-rings. This means they are much stiffer, more rigid, and lack the inherent "springiness" or elastic memory that makes rubber an effective sealing material by default. This fundamental difference in mechanical properties has critical implications for design, installation, and overall sealing performance.
The core decision between PTFE and rubber is a trade-off. You are exchanging the superior elasticity and sealing memory of rubber for the exceptional chemical inertness and extreme temperature resistance of PTFE.
The Fundamental Difference: Elasticity vs. Plasticity
The contrast in compliance between rubber and PTFE stems from how each material behaves under compressive force. This behavior is the single most important factor in its function as a seal.
The Elastic Memory of Rubber
Rubber O-rings are elastomers. When compressed in a groove, they behave like a spring, always pushing back against the mating surfaces.
This constant outward force, known as elastic memory, allows the seal to accommodate surface imperfections, pressure fluctuations, and minor hardware misalignments, maintaining a tight seal.
The Rigidity of PTFE
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a fluoropolymer, which behaves more like a rigid plastic than a flexible rubber. It does not compress easily and has very poor elastic memory.
Under a sustained load, PTFE is prone to creep or cold flow, meaning it can permanently deform over time, potentially reducing its sealing force and leading to leaks.
Practical Implications of Low Compliance
The stiffness of PTFE is not just a theoretical property; it directly impacts how you must design your system and handle the O-ring itself.
Reduced Squeeze is Mandatory
Because PTFE is so rigid, it cannot tolerate the same amount of compression, or "squeeze," as a rubber O-ring.
Attempting to use the standard squeeze calculations for an elastomer will overstress the PTFE, making installation nearly impossible and risking damage to the O-ring or the hardware. A reduced squeeze is a critical design adjustment.
Installation Becomes a Challenge
The lack of elasticity makes solid PTFE O-rings difficult to install. They cannot be easily stretched over shafts or manipulated into tight grooves without a high risk of scratching or permanently deforming them.
The Hybrid Solution: Encapsulated O-Rings
To overcome these limitations, PTFE encapsulated O-rings were developed. These combine a rubber core (like FKM or Silicone) with a thin, seamless outer jacket of PTFE.
This design provides the high compliance and elastic memory of the rubber core while offering the chemical and temperature resistance of the PTFE surface. It is often the ideal solution for demanding applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing PTFE despite its low compliance is a decision driven by environments where no elastomer can survive. Its strengths are profound but specific.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, acids, and bases. Rubber compounds, even highly resistant ones like FKM or FFKM, will swell or degrade in contact with certain aggressive media.
Extreme Temperature Range
Solid PTFE offers a remarkably wide service temperature range, typically from -250°C to +250°C (-418°F to +482°F).
This far exceeds the capabilities of most common elastomers like NBR (-30°C to +120°C) or EPDM (-45°C to +150°C), making PTFE essential for both cryogenic and high-heat applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your operational environment and sealing requirements will determine the correct material choice.
- If your primary focus is reliable sealing in standard conditions: A standard rubber O-ring (like NBR, EPDM, or FKM) is almost always the superior and more cost-effective choice due to its excellent elasticity.
- If your primary focus is surviving extreme temperatures or aggressive chemicals: A solid PTFE O-ring is necessary, but you must design the groove with a lower squeeze percentage to accommodate its rigidity.
- If you need both extreme resistance and reliable sealing performance: A PTFE encapsulated O-ring provides the best combination of chemical/thermal protection and the elastic recovery needed for a durable seal.
Choosing the right seal requires understanding that material properties and mechanical design are inextricably linked.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE O-rings | Rubber O-rings |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance | Low (Rigid) | High (Elastic) |
| Elastic Memory | Poor | Excellent |
| Squeeze Tolerance | Low (Reduced squeeze required) | High (Standard squeeze) |
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional | Varies by compound |
| Temperature Range | -250°C to +250°C | Limited (e.g., -45°C to +150°C for EPDM) |
Struggling to choose the right O-ring material for your extreme environment? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom labware, for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Whether you need the unmatched chemical resistance of solid PTFE or the balanced performance of an encapsulated O-ring, our precision production and custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure a perfect fit for your application. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution that delivers reliability and durability under pressure.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for drilling and tapping PTFE? Achieve Clean, Precise Machining
- Why is specialized equipment needed for PTFE impeller manufacturing? Precision Machining for Critical Performance
- Why is professional consultation recommended for custom seal solutions? Mitigate Risk and Ensure Operational Integrity
- What are the key features of PTFE ball valves? Superior Chemical Resistance & Reliable Flow Control
- In which industries are PTFE rotary shaft seals commonly used? The Standard for Extreme Conditions
- In which industries are PTFE tri clamp gaskets commonly used? Essential for Purity & Chemical Resistance
- What tools and processes are involved in machining PTFE? A Guide to Precision Manufacturing
- Why are PTFE spring-energized seals ideal for semiconductor manufacturing? Ensure Purity and Maximize Yield



















