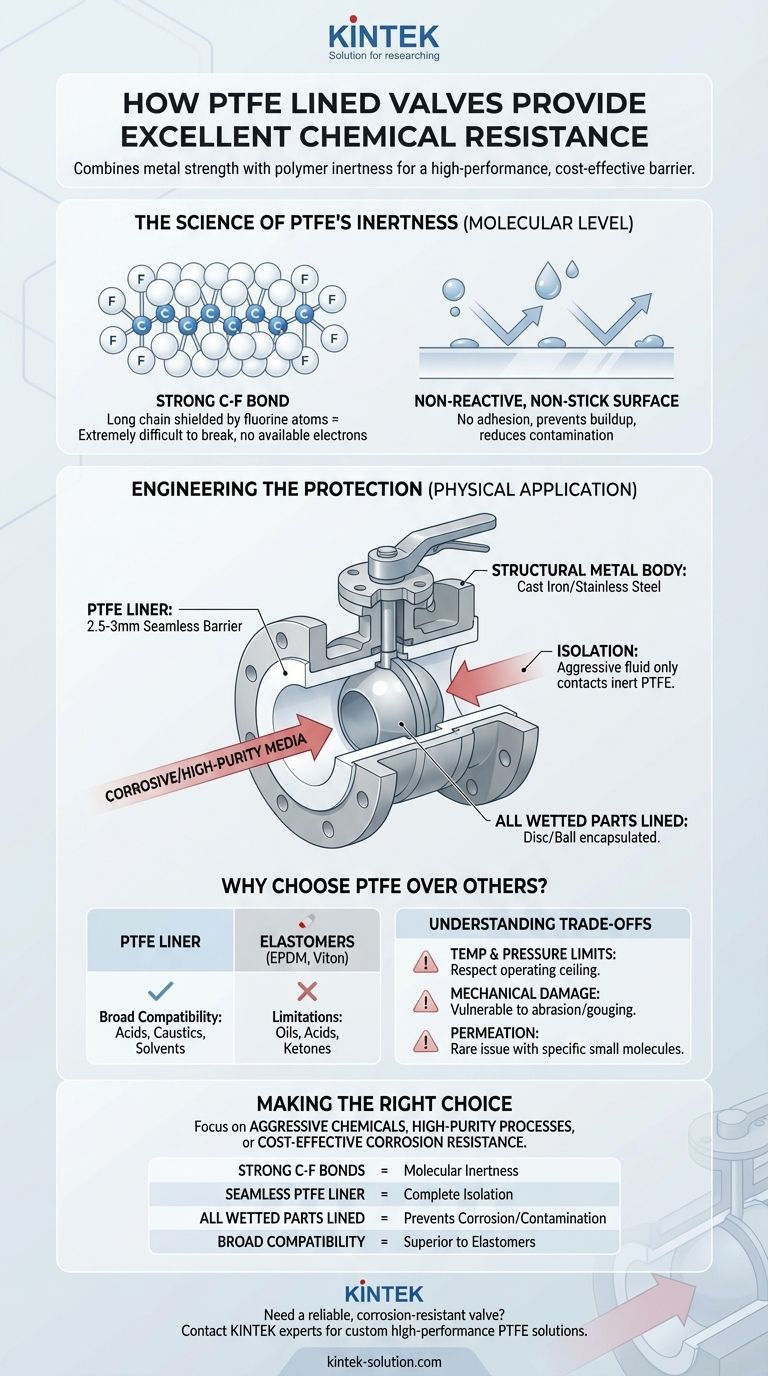
The chemical resistance of a PTFE lined valve comes from two key factors: its molecular structure and its physical application. The Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) polymer is built on incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bonds, making it one of the most non-reactive substances known. In a valve, this material is used as a thick, seamless liner that completely isolates the metal valve body from the corrosive or high-purity media passing through it, acting as an impenetrable chemical barrier.
The core principle is simple yet powerful: PTFE lined valves combine the structural strength and affordability of a standard metal body with the near-universal chemical inertness of a specialized polymer liner. This creates a high-performance, cost-effective solution for managing aggressive fluids.
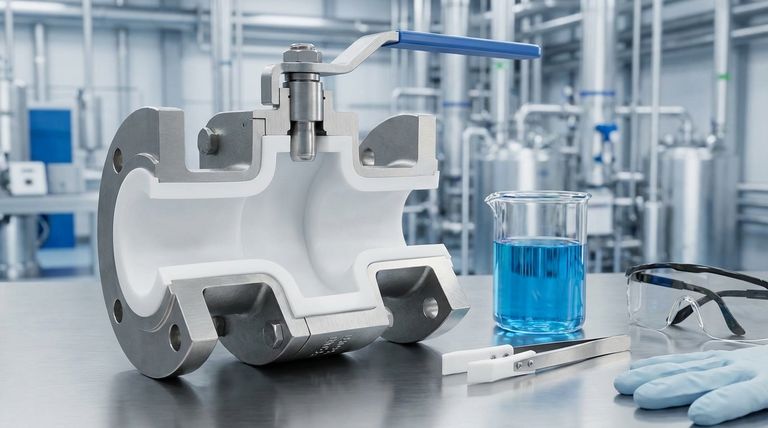

The Science of PTFE's Inertness
At a molecular level, PTFE's resilience is not an accident. It's a direct result of its unique chemical composition, which makes it fundamentally unreactive to almost all industrial chemicals.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between carbon and fluorine atoms is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry.
PTFE's structure consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by a sheath of fluorine atoms. This powerful bond is extremely difficult to break, meaning the molecule does not have available electrons to participate in chemical reactions.
A Non-Reactive, Non-Stick Surface
This molecular stability gives PTFE its famous non-stick, or hydrophobic, properties.
Because the surface is so non-reactive, other materials have nothing to adhere to. This prevents buildup and reduces the potential for contamination, which is critical in sanitary or high-purity applications.
How This Inertness is Engineered into a Valve
A valve's function is mechanical, but its survival in a corrosive environment is a matter of material science. PTFE lining is an engineering solution that leverages the polymer's properties to protect the valve's structural components.
The Liner as a Protective Barrier
The most critical concept is isolation. The valve body, typically made of cast iron or stainless steel, provides the mechanical strength to handle system pressure.
A thick liner of PTFE, often 2.5-3mm, is molded to the interior surfaces of the valve. This liner ensures that the aggressive chemical medium never touches the structural metal, preventing corrosion and equipment failure.
Complete Isolation of "Wetted Parts"
This lining isn't just applied to the valve body. All parts that come into contact with the fluid—known as wetted parts—are covered.
In a butterfly valve, this includes the disc. In a ball valve, it includes the ball. This complete encapsulation guarantees that the process fluid only ever interacts with the inert PTFE.
A Superior Alternative to Most Elastomers
While seals made from materials like EPDM or Viton offer chemical resistance, they have significant limitations.
EPDM performs poorly with oils and many acids, while Viton is susceptible to ketones. PTFE, in contrast, provides a much broader range of compatibility, handling everything from strong acids like sulfuric and hydrochloric acid to caustics and solvents.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE offers exceptional chemical performance, no single solution is perfect for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to proper application.
Temperature and Pressure Limitations
Although PTFE has a high temperature tolerance for a polymer, it is not metal. It has a distinct operating ceiling for both temperature and pressure that must be respected to prevent liner failure.
Susceptibility to Mechanical Damage
The PTFE liner provides a chemical barrier, not a mechanical one. It can be damaged by abrasive slurries containing sharp particles. Care must also be taken during installation to avoid scratching or gouging the liner, which would create a path for corrosion.
Permeation by Specific Molecules
While PTFE is resistant to virtually all chemicals, extremely small molecules like certain gases or halogens can, over time, slowly permeate through the polymer matrix. This is a rare concern but can be a factor in very specific high-pressure gas or ultra-high-purity applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve depends entirely on the demands of your system. A PTFE lined valve excels where chemical compatibility is the primary driver.
- If your primary focus is handling a wide range of aggressive chemicals: A PTFE lined valve offers one of the most versatile and reliable solutions, preventing corrosion where most metals and elastomers would fail.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or sanitary processes: The inert, non-leaching nature of a PTFE liner is critical for preventing fluid contamination in pharmaceutical, food, or semiconductor manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective corrosion resistance: A PTFE lined valve delivers the performance of an expensive exotic alloy valve by protecting a standard, affordable metal body.
Ultimately, a PTFE lined valve is a specialized tool designed to solve the difficult problem of safely containing and controlling chemically aggressive fluids.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Strong C-F Bonds | Fundamental molecular inertness to most chemicals. |
| Seamless PTFE Liner | Complete isolation of metal body from corrosive media. |
| All Wetted Parts Lined | Prevents corrosion and contamination of the valve interior. |
| Broad Chemical Compatibility | Resists strong acids, caustics, and solvents better than most elastomers. |
Need a reliable, corrosion-resistant valve for your aggressive chemical process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom-lined valves, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision engineering ensures your valves provide the ultimate chemical barrier, protecting your equipment and maintaining process purity.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailoring the solution to your specific fluid handling challenges.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a quote for a valve that won't let you down.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















