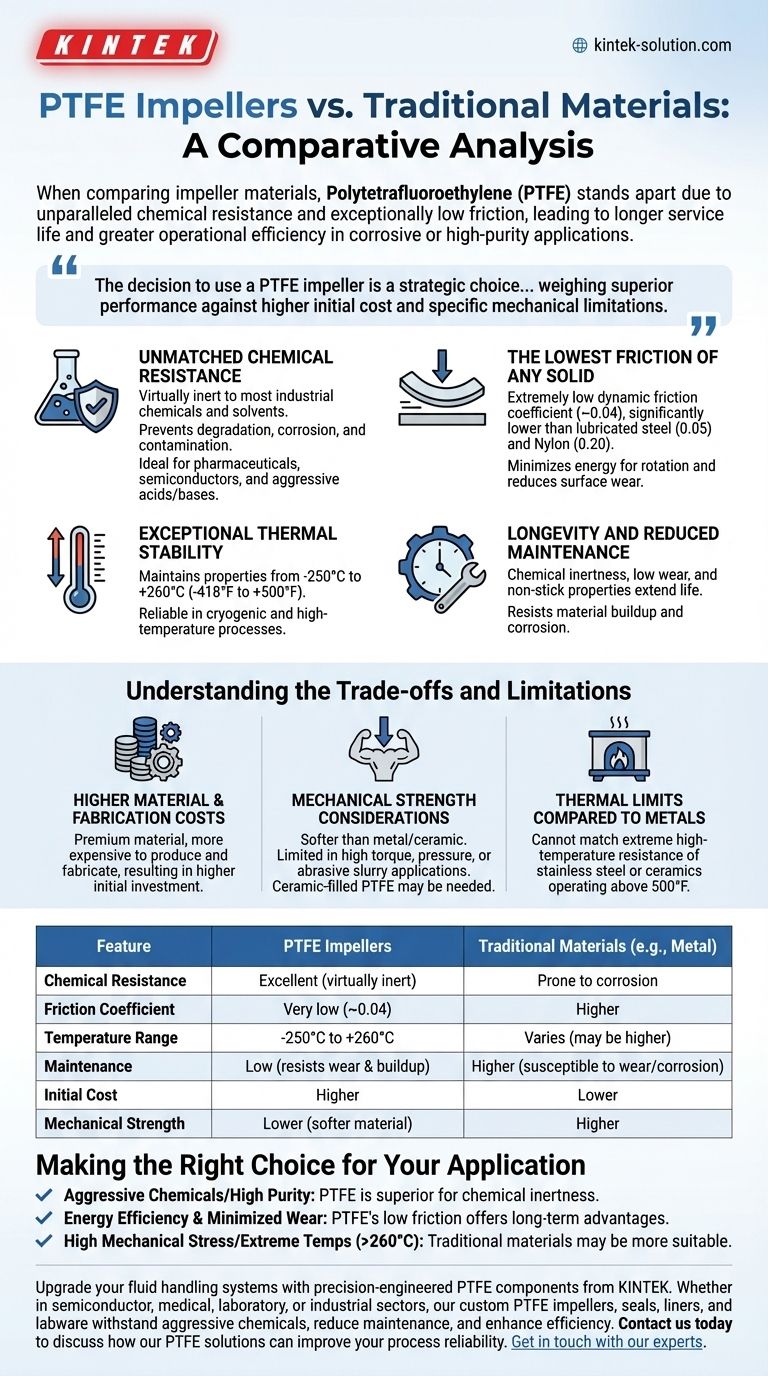
When comparing impeller materials, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) stands apart from traditional options like metals and ceramics due to its unparalleled chemical resistance and exceptionally low friction. These properties translate directly into a longer service life, reduced maintenance requirements, and greater operational efficiency, especially in corrosive or high-purity applications.
The decision to use a PTFE impeller is a strategic choice for applications where chemical inertness and energy efficiency are paramount. This choice requires weighing its superior performance in these areas against its higher initial cost and specific mechanical limitations.

The Core Advantages of PTFE in Impeller Design
Understanding the fundamental properties of PTFE reveals why it is often the superior choice for demanding fluid-handling scenarios.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This prevents the impeller from degrading, corroding, or leaching contaminants into the fluid being pumped.
This makes PTFE ideal for high-purity industries like pharmaceuticals and semiconductors, as well as for handling highly aggressive acids and bases.
The Lowest Friction of Any Solid
PTFE possesses an extremely low coefficient of friction, with a dynamic value around 0.04. This is significantly lower than lubricated steel (0.05) and other plastics like Nylon (0.20).
This ultra-low friction minimizes the energy required to rotate the impeller, leading to direct power savings. It also dramatically reduces surface wear, extending the operational life of the entire pump assembly.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE maintains its properties across a vast temperature range, typically from -250°C to +260°C (-418°F to +500°F).
This range is far wider than most other polymers, allowing PTFE impellers to function reliably in both cryogenic applications and high-temperature processes without becoming brittle or deforming.
Longevity and Reduced Maintenance
The combination of chemical inertness, low wear, and non-stick properties means PTFE impellers last longer and require far less maintenance than their metal or ceramic counterparts. They resist the buildup of material and are not susceptible to the corrosion that plagues metal components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment must include its inherent limitations.
Higher Material and Fabrication Costs
PTFE is a premium material that is both more expensive to produce and more complex to fabricate than common metals or other plastics. This results in a higher initial investment for a PTFE impeller.
Mechanical Strength Considerations
While highly durable against chemical attack and frictional wear, PTFE is a softer material than metal or ceramic. In applications involving very high torque, high pressure, or the pumping of abrasive slurries, its mechanical strength can be a limiting factor.
For such demanding physical environments, specialized compounds like ceramic-filled PTFE may be required to enhance mechanical and thermal properties, though this further increases cost.
Thermal Limits Compared to Metals and Ceramics
Although its temperature range is excellent for a polymer, PTFE cannot match the extreme high-temperature resistance of many stainless steel alloys or specialized ceramic materials, which can operate well above 500°F.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right impeller material depends entirely on your operational priorities and the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals or high-purity fluids: PTFE is the superior choice due to its chemical inertness, which prevents both impeller corrosion and product contamination.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing wear: PTFE's extremely low friction coefficient offers significant long-term advantages in reduced power consumption and longer service intervals.
- If your primary focus is managing high mechanical stress or extreme temperatures above 260°C (500°F): Traditional materials like stainless steel or ceramics may be more suitable unless a specialized filled-PTFE composite is considered.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE impeller is an investment in operational resilience and long-term efficiency for chemically demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Impellers | Traditional Materials (e.g., Metal) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (virtually inert) | Prone to corrosion |
| Friction Coefficient | Very low (~0.04) | Higher |
| Temperature Range | -250°C to +260°C | Varies (may be higher for some metals) |
| Maintenance | Low (resists wear and buildup) | Higher (susceptible to wear/corrosion) |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower (softer material) | Higher |
Upgrade your fluid handling systems with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our custom PTFE impellers, seals, liners, and labware are designed to withstand aggressive chemicals, reduce maintenance, and enhance operational efficiency. We specialize in fabricating high-performance components from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring they meet the exact demands of your application.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can improve your process reliability and longevity. Get in touch with our experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the main differences between FR4 and PTFE PCB laminate materials? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- How is flow rate controlled in PTFE ball valves? Leverage Simple, Reliable Rotary Control
- Why is PTFE often chosen for extreme temperatures or corrosive environments? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are common applications of machined Teflon parts? Solve Friction, Chemical, and Electrical Challenges
- Why is the non-stick property of Teflon sheets advantageous? Boost Efficiency & Reduce Waste
- Why are PTFE-based materials preferred for RF PCB designs? Achieve Superior Signal Integrity at High Frequencies
- Are PTFE lined butterfly valves cost-effective? Maximize ROI in Corrosive Applications
- What were the benefits of PTFE wear plates in the die-casting industry case study? Reduce Downtime & Boost Production



















