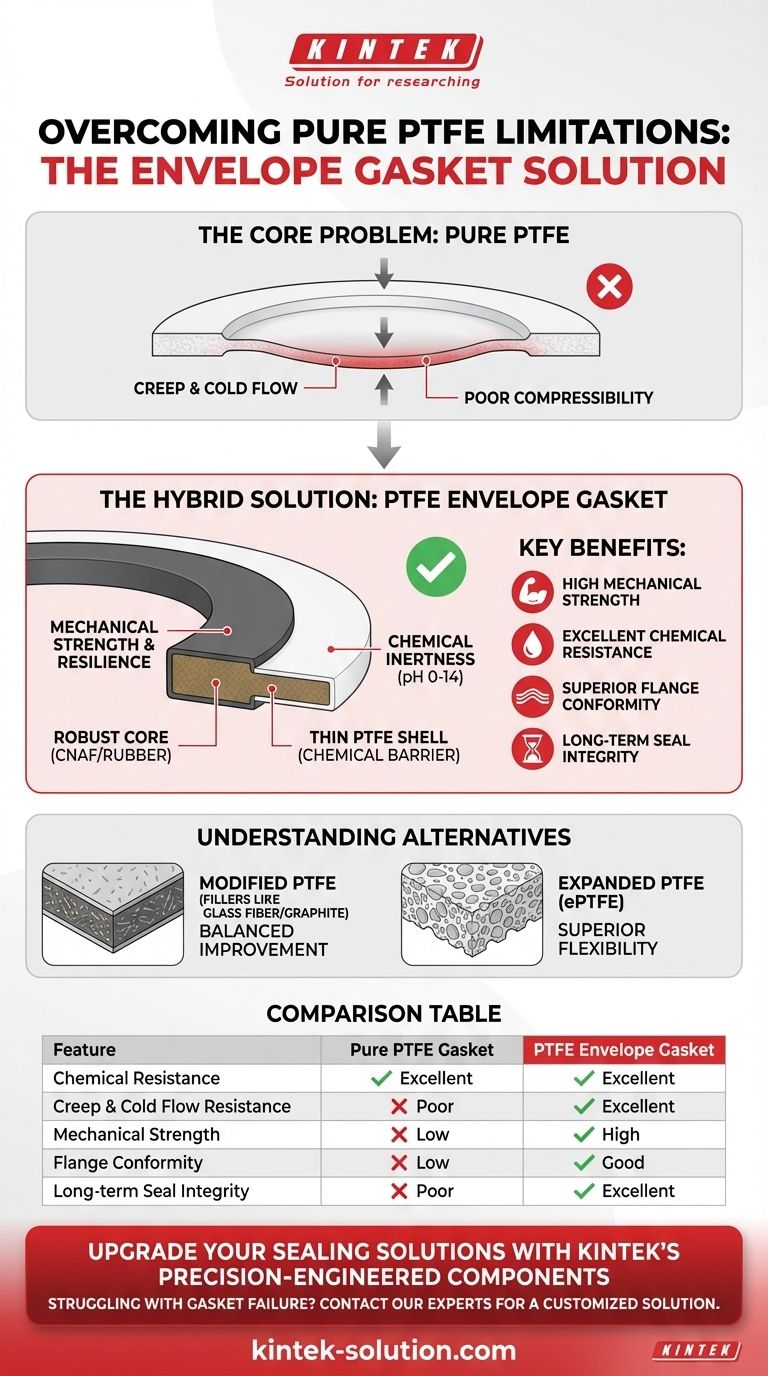
To overcome the key weaknesses of pure PTFE, PTFE envelope gaskets use a composite design. They combine a chemically inert Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) outer layer with a more mechanically robust core material, such as compressed non-asbestos fiber (CNAF) or rubber. This hybrid construction leverages the chemical resistance of PTFE while using the core to provide the mechanical strength, resilience, and resistance to deformation that pure PTFE lacks.
While pure PTFE offers unmatched chemical resistance, it fails mechanically under pressure through creep and cold flow. PTFE envelope gaskets solve this by using a stronger core material to provide structural integrity, while a thin PTFE shell maintains chemical protection.

The Core Problem with Pure PTFE Gaskets
Understanding the limitations of pure PTFE is essential to appreciate why alternative designs were developed. The material is chemically brilliant but mechanically flawed for many sealing applications.
Mechanical Weakness: Creep and Cold Flow
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under sustained pressure and temperature, it is highly susceptible to two forms of deformation.
Creep is the gradual deformation of the gasket material under long-term stress. Cold flow is the tendency to deform under even low stress, particularly at elevated temperatures. Both phenomena cause the gasket to thin out, leading to a loss of bolt torque and, ultimately, seal failure.
Poor Compressibility and Sealing
The rigid nature of pure PTFE gaskets means they have limited compressibility. This makes it difficult for them to conform to even minor imperfections on flange surfaces.
Achieving a reliable seal requires perfectly smooth flanges and consistent, high pressure, which is not always practical in real-world industrial settings.
The Envelope Gasket Solution: A Hybrid Approach
PTFE envelope gaskets were engineered specifically to counteract the mechanical deficiencies of pure PTFE without sacrificing its primary benefit.
The Composite Structure
An envelope gasket consists of two parts: a thin outer "envelope" made of PTFE and an inner core made of a different material.
This core is typically made from elastomers, rubber, or CNAF, which possess superior mechanical properties compared to PTFE.
How the Core Enhances Performance
The inner core provides the structural backbone of the gasket. It offers the resilience and compressibility needed to conform to flange surfaces and maintain a tight seal under pressure.
This design significantly improves the gasket's resistance to creep and cold flow, ensuring long-term sealing integrity in applications where pure PTFE would quickly fail.
Preserving Chemical Inertness
The PTFE envelope fully encases the core material, ensuring that only the PTFE comes into contact with the process media.
This allows the gasket to handle highly corrosive fluids and seal across the full pH range (0-14), just like a pure PTFE gasket. It also allows these gaskets to meet stringent FDA and USP Class VI standards.
Understanding Alternatives and Trade-offs
While effective, the envelope gasket is not the only solution. The choice of gasket depends entirely on the specific demands of the application.
Alternative 1: Modified PTFE
Modified PTFE gaskets are not layered; instead, fillers like glass fiber or graphite powder are mixed directly into the PTFE material during production.
These fillers enhance the strength, durability, and creep resistance of the final product, creating a homogenous material that is superior to pure PTFE but may not have the same resilience as an envelope gasket's core.
Alternative 2: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Expanded PTFE is created through a special process that results in a porous, highly flexible material structure.
ePTFE offers superior resistance to creep and cold flow and is exceptionally conformable. Its soft, flexible nature allows it to seal effectively on irregular or damaged flange surfaces where more rigid gaskets would fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the gasket's properties to the system's pressure, temperature, media, and flange condition.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical resistance with moderate pressure: The PTFE envelope gasket is an excellent choice, providing a significant mechanical upgrade over pure PTFE.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular or damaged flanges: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is the superior option due to its exceptional flexibility and compressibility.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose upgrade for strength and durability: Modified PTFE offers a balanced improvement in mechanical properties while maintaining a solid, homogenous structure.
Ultimately, selecting the correct PTFE gasket is about matching the material's mechanical properties to your specific operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pure PTFE Gasket | PTFE Envelope Gasket |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent (PTFE outer layer) |
| Creep & Cold Flow Resistance | Poor | Excellent (robust core) |
| Mechanical Strength | Low | High |
| Flange Conformity | Low | Good |
| Long-term Seal Integrity | Poor | Excellent |
Upgrade your sealing solutions with KINTEK's precision-engineered PTFE components.
Struggling with gasket failure due to creep, cold flow, or chemical corrosion? Our PTFE envelope gaskets are specifically designed to overcome the limitations of pure PTFE, providing superior mechanical strength and long-term reliability without sacrificing chemical resistance.
At KINTEK, we manufacture high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and labware for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. We specialize in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensuring precise, durable components tailored to your exact requirements.
Let us help you enhance your system's performance and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and receive a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components



















