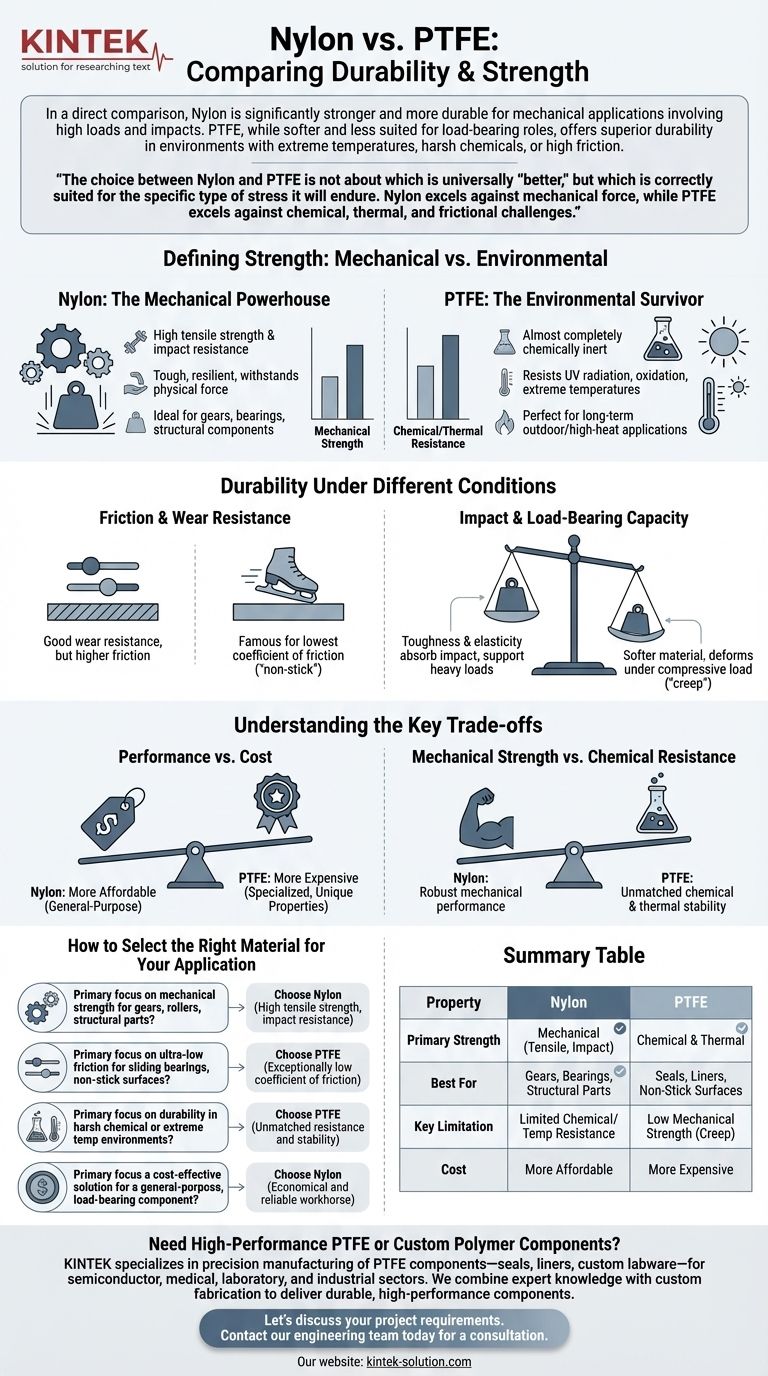
In a direct comparison, Nylon is significantly stronger and more durable for mechanical applications involving high loads and impacts. PTFE, while softer and less suited for load-bearing roles, offers superior durability in environments with extreme temperatures, harsh chemicals, or high friction.
The choice between Nylon and PTFE is not about which is universally "better," but which is correctly suited for the specific type of stress it will endure. Nylon excels against mechanical force, while PTFE excels against chemical, thermal, and frictional challenges.

Defining Strength: Mechanical vs. Environmental
The terms "strength" and "durability" mean different things under different conditions. Understanding this distinction is the key to selecting the right material.
Nylon: The Mechanical Powerhouse
Nylon exhibits high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance. This combination makes it tough, resilient, and capable of withstanding significant physical force without fracturing.
It is the ideal choice for parts that bear loads, absorb shocks, or transmit power, such as gears, bearings, and structural components.
PTFE: The Environmental Survivor
PTFE's strength is not mechanical but chemical and thermal. It is almost completely inert, resisting nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents.
Furthermore, PTFE is exceptionally durable against weathering. It withstands UV radiation, oxidation, and extreme temperatures without degrading, making it perfect for long-term outdoor or high-heat applications.
Durability Under Different Conditions
How a material wears down over time is a critical aspect of its durability. Nylon and PTFE have fundamentally different profiles.
Friction and Wear Resistance
Nylon has good wear resistance, but it has a relatively high coefficient of friction compared to PTFE.
PTFE is famous for having one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This "non-stick" quality makes it the superior choice for high-speed, sliding applications where minimizing friction and wear is the primary goal.
Impact and Load-Bearing Capacity
This is Nylon's core advantage. Its toughness and elasticity allow it to absorb sudden impacts and support heavy, consistent loads.
PTFE is a much softer material. Under compressive load, it can deform or "creep," making it unsuitable for most structural or load-bearing roles.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing between these materials requires balancing their opposing strengths and weaknesses.
Performance vs. Cost
Nylon is significantly more affordable than PTFE. Its excellent mechanical properties and low cost make it a default choice for a wide range of general-purpose engineering applications.
PTFE is a more expensive, specialized polymer. Its higher cost is justified only when its unique properties—such as chemical inertness, temperature range, or low friction—are mission-critical.
Mechanical Strength vs. Chemical Resistance
This is the central trade-off. Nylon provides the robust mechanical performance needed for moving parts and structural elements but has limited resistance to certain chemicals and temperatures.
PTFE provides the unmatched chemical and thermal stability needed for seals, liners, and insulators but lacks the raw strength for mechanical tasks.
How to Select the Right Material for Your Application
Use the primary stress of your application to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength for gears, rollers, or structural parts: Choose Nylon for its high tensile strength and impact resistance.
- If your primary focus is ultra-low friction for sliding bearings or non-stick surfaces: Choose PTFE for its exceptionally low coefficient of friction.
- If your primary focus is durability in harsh chemical or extreme temperature environments: Choose PTFE for its unmatched resistance and stability.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective solution for a general-purpose, load-bearing component: Choose Nylon as the economical and reliable workhorse.
By aligning the material's inherent properties with the specific demands of your application, you ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Summary Table:
| Property | Nylon | PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Mechanical (Tensile, Impact) | Chemical & Thermal |
| Best For | Gears, Bearings, Structural Parts | Seals, Liners, Non-Stick Surfaces |
| Key Limitation | Limited Chemical/Temp Resistance | Low Mechanical Strength (Creep) |
| Cost | More Affordable | More Expensive |
Need High-Performance PTFE or Custom Polymer Components?
Selecting the right material is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine expert material knowledge with custom fabrication capabilities, from prototypes to high-volume orders, to deliver components that meet your exact specifications for durability and performance.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
People Also Ask
- How was PTFE discovered and when was it patented? The Accidental Invention of Teflon
- How is FEP Teflon different from other types in terms of properties? The Key is Fabrication Flexibility
- What is the difference between suspension and dispersion polymerization of PTFE? Choose the Right Process for Your Application
- How is ePTFE structured and what are its properties? Unlock Advanced Performance with Microporous PTFE
- How does PTFE's molecular neutrality affect its properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical and Electrical Performance
- What are some physical properties of PTFE? Master Its Unique Properties for Extreme Applications
- How do PTFE and Teflon differ in terms of applications? Clarifying the Brand vs. Material Confusion
- What is PTFE and what makes it versatile? The Ultimate High-Performance Polymer



















