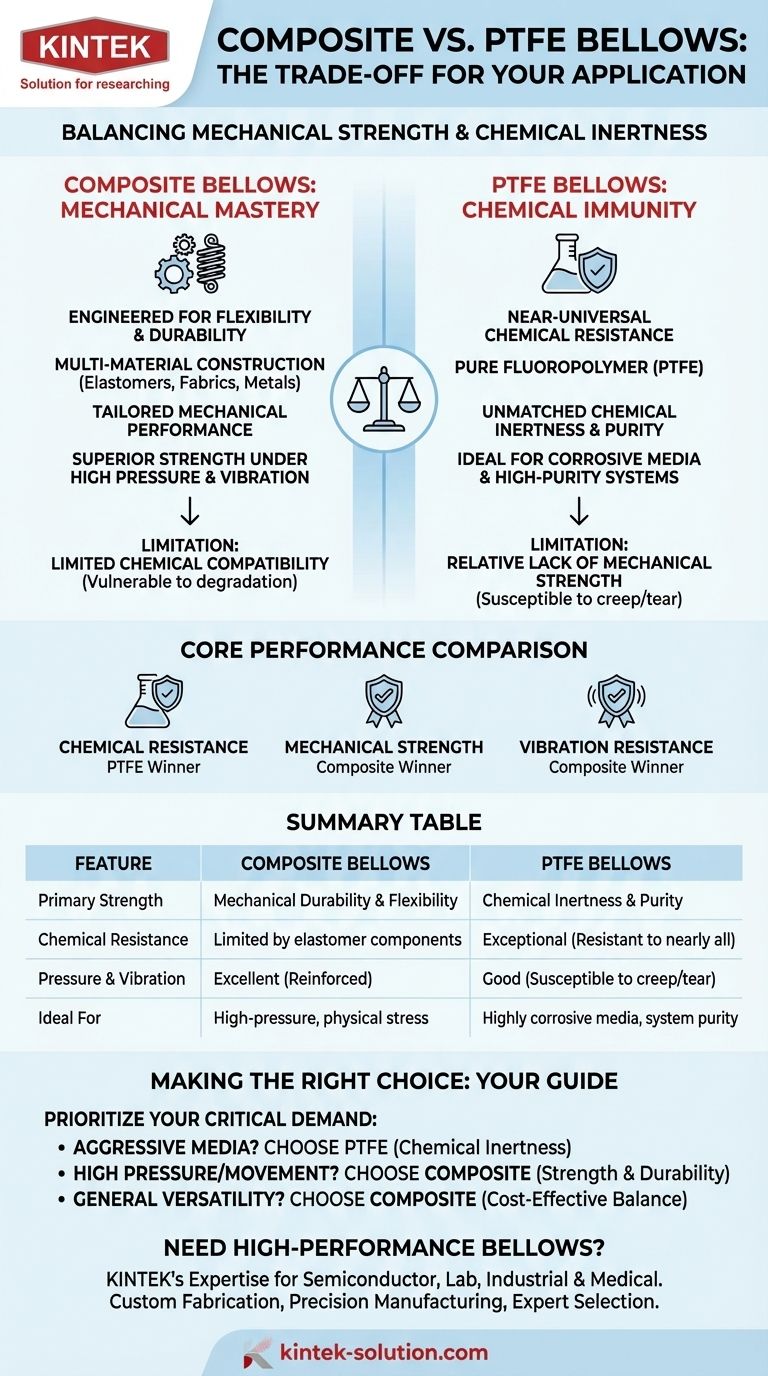
The primary difference between composite and PTFE bellows lies in a trade-off between mechanical strength and chemical inertness. Composite bellows are engineered for a balanced profile of flexibility and durability, making them highly versatile. PTFE bellows, in contrast, offer near-universal chemical resistance, making them the default choice for highly corrosive environments.
Choosing between composite and PTFE bellows is not about which material is inherently superior, but which property is non-negotiable for your application. Composites provide tailored mechanical performance, while PTFE provides unparalleled chemical immunity.

Deconstructing the Materials
To understand the performance differences, we must first understand the fundamental nature of each material. Their construction directly dictates their ideal use case.
What Defines PTFE Bellows?
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a fluoropolymer prized for one dominant characteristic: its extreme chemical inertness. It is non-reactive to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents.
This singular focus on chemical immunity means PTFE bellows are the definitive solution for sealing or conveying the most aggressive media where other materials, including many metals and elastomers, would quickly corrode and fail.
What Defines Composite Bellows?
The term "composite" signifies that these bellows are constructed from multiple, distinct materials bonded together. This often includes layers of elastomers, reinforcing fabrics, and sometimes metal rings.
This layered construction allows them to be engineered for specific mechanical challenges. By combining materials, designers can create a bellow with a precise balance of flexibility, pressure resistance, and durability against physical stress and vibration.
Core Performance Comparison
The choice between these two materials hinges on the specific demands of the operational environment. One excels where the other shows its inherent limitations.
Chemical Resistance: The Uncontested Winner
PTFE is the clear victor in terms of chemical resistance. Its molecular structure makes it impervious to chemical attack, ensuring system purity and long service life in harsh chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and food-grade applications.
Composite bellows, while versatile, are limited by the chemical compatibility of their weakest component, typically the elastomer. Exposure to an incompatible chemical can cause swelling, degradation, and premature failure.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Composite bellows are engineered for superior mechanical performance. Their reinforced structure provides greater strength to withstand high pressure, system vibration, and frequent movement cycles without fatiguing.
Pure PTFE is a softer material and can be more susceptible to physical damage or creep under high mechanical load. While it can be reinforced, a purpose-built composite is often the more robust solution for mechanically demanding applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material choice is without its compromises. Acknowledging these limitations is critical for preventing system failure and ensuring operational safety.
The Limitation of PTFE
The primary trade-off for PTFE's chemical inertness is its relative lack of mechanical strength. In high-pressure systems or applications with significant physical stress, unreinforced PTFE bellows may not be suitable. The material's properties must be carefully matched to the system's mechanical demands.
The Limitation of Composites
The core vulnerability of a composite bellow is its limited chemical compatibility. The very nature of its multi-material construction means there are more potential points of failure when exposed to aggressive media. A thorough chemical compatibility check is mandatory before specifying a composite bellow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the most critical demand of your system. Prioritize the single most important factor to make the correct selection.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive or corrosive media: PTFE bellows are the safest and most reliable choice due to their unmatched chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is managing high pressure or frequent mechanical movement: A composite bellow is the superior option, as it is specifically engineered for strength and durability.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose versatility in a less aggressive environment: Composite bellows often provide an excellent and cost-effective balance of operational properties.
Ultimately, a clear understanding of your specific chemical, thermal, and mechanical loads is the key to selecting the material that ensures reliability and safety.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Composite Bellows | PTFE Bellows |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Mechanical Durability & Flexibility | Chemical Inertness & Purity |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited by elastomer components | Exceptional; resistant to nearly all chemicals |
| Pressure & Vibration | Excellent; reinforced construction | Good; can be susceptible to creep/tear |
| Ideal For | High-pressure systems, physical stress | Highly corrosive media, system purity |
Need High-Performance Bellows for Your Critical Application?
Choosing the wrong bellow material can lead to system failure, downtime, and safety risks. Let KINTEK's expertise guide you to the optimal solution.
We provide precision-engineered solutions for:
- Semiconductor & Laboratory Equipment: Ensuring purity and reliability with chemically inert PTFE components.
- Industrial & Medical Applications: Delivering durable, custom-fabricated parts that withstand demanding mechanical and environmental conditions.
Our value to you:
- Expert Material Selection: We help you navigate the trade-offs between chemical resistance and mechanical strength.
- Precision Manufacturing: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we guarantee quality and consistency.
- Custom Fabrication: Get bellows and components tailored to your exact specifications and performance requirements.
Ensure your system's integrity and performance. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation on your specific bellow needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry



















