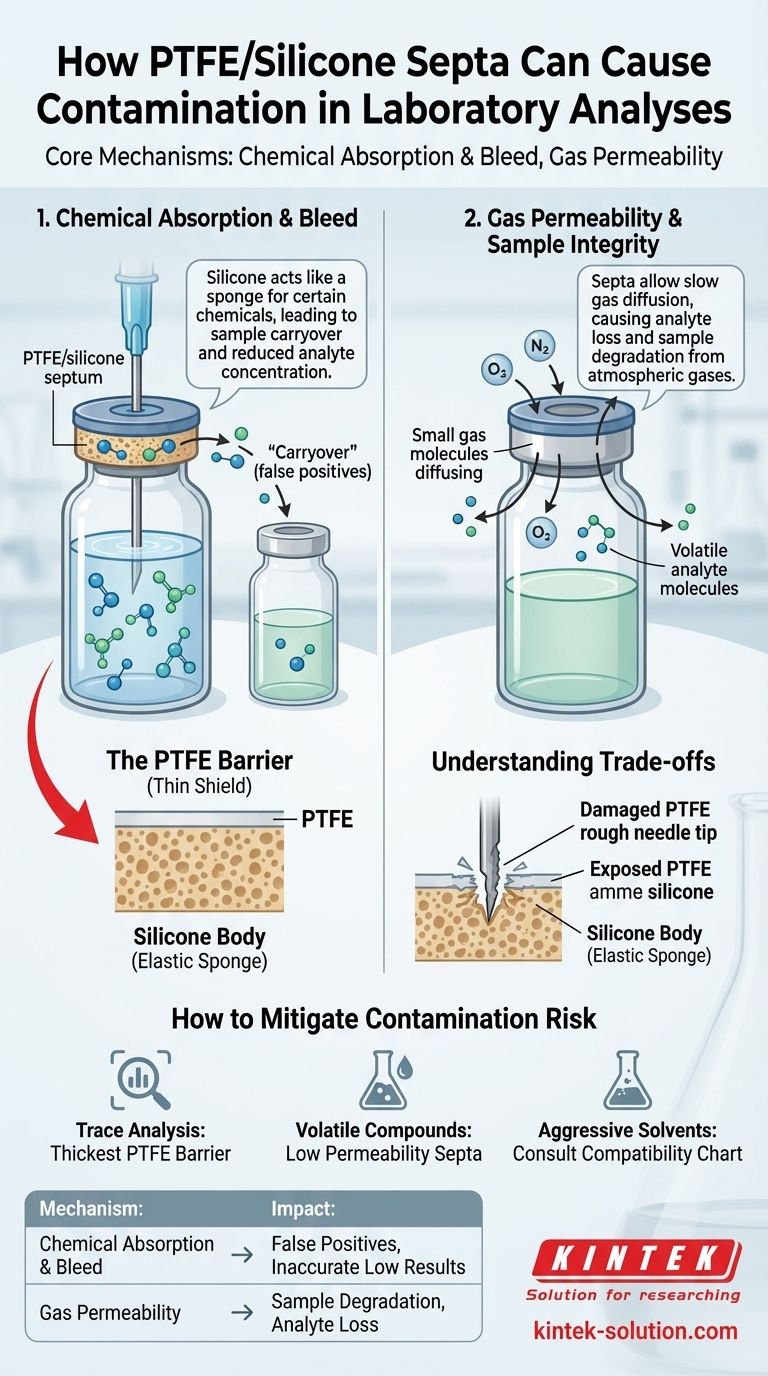
At its core, PTFE/silicone septa cause contamination through two primary mechanisms: the absorption and subsequent release of chemical compounds, and the permeation of gases. The silicone layer can act like a sponge for certain chemicals, leading to sample carryover, while the entire septum can allow gases to diffuse in or out, compromising sample integrity.
While designed to be a protective barrier, the very material properties of a septum can become a source of analytical error. The key to preventing contamination is not just choosing a high-quality septum, but choosing the correct septum for your specific sample matrix and analytical conditions.
The Dual Role of Septa: Barrier and Potential Contaminant
The primary job of a septum is to create a resealable barrier for a sample vial. This allows a needle to pierce the seal for sample extraction or injection while preventing the sample from leaking or becoming contaminated by the outside environment.
Understanding PTFE/Silicone Construction
A standard PTFE/silicone septum is a two-part system. It has a thin, chemically inert Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) layer facing the sample and a thicker, softer silicone layer on the outside.
The PTFE provides a crucial barrier of chemical resistance. The silicone provides the physical elasticity needed for the septum to reseal effectively after being punctured by a needle.
Primary Mechanisms of Septa-Induced Error
The problem arises when the septum's materials interact negatively with your sample, solvent, or the surrounding environment. This interaction typically manifests in two ways.
Chemical Absorption and Bleed
The silicone body of the septum can absorb volatile or semi-volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from a sample. This can cause two distinct problems.
First, analytes of interest can be absorbed into the septum, reducing their concentration in the sample and leading to inaccurately low results.
Second, and more critically for contamination, these absorbed compounds can be released—or "bleed"—into a subsequent, different sample. This phenomenon, known as carryover, introduces contamination that can create false positive results.
Gas Permeability and Sample Integrity
No material is a perfect gas barrier. PTFE/silicone septa can exhibit a degree of gas permeability, allowing gases to slowly diffuse through the material over time.
For volatile samples, this can mean a gradual loss of the analyte, leading to lower-than-expected concentrations.
Conversely, atmospheric gases like oxygen or nitrogen can permeate into the vial. This can degrade sensitive samples or interfere with analyses that require a specific gaseous environment, such as headspace analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right septum involves balancing chemical compatibility with physical performance. Ignoring these trade-offs is a common source of analytical error.
The PTFE Barrier vs. The Silicone Body
The PTFE layer is your main defense against chemical interaction. However, it is extremely thin. A dull or rough needle tip can tear the PTFE, exposing your sample directly to the much more absorptive silicone layer.
This bypasses the primary protective feature and dramatically increases the risk of both analyte absorption and chemical bleed from the silicone itself.
Solvent and Matrix Incompatibility
Not all solvents are compatible with silicone. Aggressive organic solvents can cause the silicone to swell, compromising the seal of the vial.
A swollen septum loses its resealing capability, leading to leaks and rapid sample evaporation. It also increases the surface area of silicone exposed to the sample, accelerating the absorption of compounds and potential bleed.
How to Mitigate Contamination Risk
Choosing the correct septum is a critical step in method development that directly impacts the quality and reliability of your data.
- If your primary focus is trace analysis or avoiding carryover: Select septa with the thickest possible PTFE barrier to maximize chemical resistance and minimize interaction with the silicone.
- If your primary focus is working with volatile compounds: Choose septa specifically rated for low gas permeability and ensure you have a perfect vial seal.
- If your primary focus is compatibility with aggressive solvents: Always consult a manufacturer's chemical compatibility chart to match your solvent and sample matrix to the correct septum material.
Ultimately, treating your septum choice with the same diligence as your other analytical parameters is the key to ensuring sample integrity.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | How It Causes Contamination | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Absorption & Bleed | Silicone absorbs VOCs from the sample, then releases them into later samples (carryover). | False positives, inaccurate low results. |
| Gas Permeability | Gases (e.g., O₂) permeate into the vial, or volatile analytes permeate out. | Sample degradation, analyte loss, interference in headspace analysis. |
Eliminate septa-induced contamination from your analyses. KINTEK manufactures high-precision PTFE components, including specialized septa designed for superior chemical resistance and minimal gas permeability. Whether you need standard solutions or custom-fabricated prototypes for the semiconductor, medical, or laboratory industries, we prioritize the precision and material integrity critical to your success. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and ensure uncompromised sample integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















