In the medical field, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sheets are primarily utilized for creating vascular grafts, surgical patches, implantable device components, and advanced wound dressings. Their use is driven by a unique combination of material properties, most notably biocompatibility and an exceptionally non-stick surface.
The core reason PTFE is so valuable in medicine is its inert nature. It is one of the few materials that can be placed inside the human body for long periods without causing an adverse reaction, while its low-friction surface is critical for both internal and external medical devices.
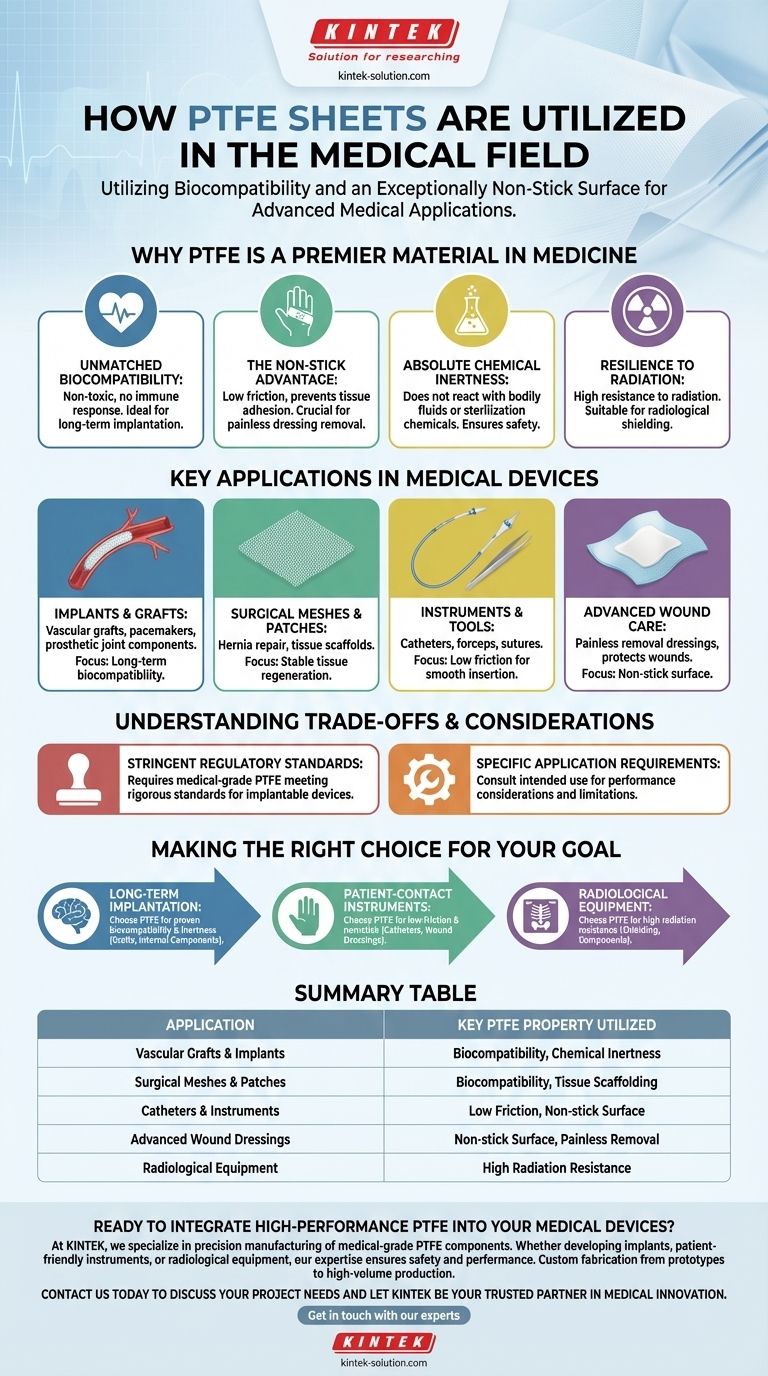
Why PTFE is a Premier Material in Medicine
The selection of any material for medical use is subject to intense scrutiny. PTFE has become a trusted standard because its intrinsic properties solve several fundamental challenges in medical device engineering.
Unmatched Biocompatibility
PTFE is highly biocompatible, meaning it is non-toxic and does not provoke an immune response from the body's tissues. This makes it an ideal candidate for devices that are implanted for the long term.
The Non-Stick Advantage
The material is famous for its low coefficient of friction and non-stick surface. In a medical context, this prevents tissues from adhering to it, which is crucial for wound dressings that need to be removed without disturbing the healing process.
Absolute Chemical Inertness
PTFE is almost completely chemically inert. It does not react with bodily fluids or the aggressive chemicals used in sterilization processes, ensuring the material's integrity and the patient's safety.
Resilience to Radiation
The material also exhibits a high resistance to radiation. This property makes it suitable for manufacturing shielding components used in X-ray machines and other radiological equipment where material degradation is a concern.
Key Applications in Medical Devices
These core properties translate into a range of critical applications, from life-saving implants to everyday medical instruments.
Implants and Grafts
PTFE is frequently used to create vascular grafts to repair or bypass diseased blood vessels. It is also used to manufacture components for other implantable devices, such as pacemakers and parts of prosthetic joints, where biocompatibility is non-negotiable.
Surgical Meshes and Patches
As a surgical mesh, PTFE provides a stable, biocompatible scaffold for repairing hernias and other tissue defects. It reinforces the damaged area and encourages natural tissue regeneration around it.
Instruments and Tools
The low-friction and inert properties of PTFE make it ideal for manufacturing instruments that come into contact with patients. This includes devices like catheters, which require smooth insertion, as well as forceps and sutures.
Advanced Wound Care
In wound dressings, the non-stick quality of PTFE is paramount. It allows the dressing to protect the wound without adhering to it, enabling painless removal and preventing disruption to new tissue growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While PTFE is exceptionally useful, it's important to recognize its context and limitations within the highly regulated medical field.
Stringent Regulatory Standards
Not all PTFE is created equal. Medical applications require materials that meet specific, rigorous standards. There are strict regulations governing the use of any polymer in an implantable medical device, and only medical-grade PTFE can be considered.
Specific Application Requirements
The properties that make PTFE ideal for one application may not be suitable for another. Engineers and device designers must always consult the specific requirements for their intended use, as there can be restrictions or performance considerations to manage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating PTFE for a medical application, your decision should be guided by the primary functional requirement of the device.
- If your primary focus is long-term implantation: PTFE's proven biocompatibility and chemical inertness make it a top-tier choice for grafts and internal components.
- If your primary focus is patient-contact instruments: Its exceptionally low-friction, non-stick surface is the key property for catheters and advanced wound dressings.
- If your primary focus is radiological equipment: The material's high resistance to radiation makes it a reliable option for shielding and other components.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique profile of inertness and performance makes it an indispensable tool for advancing modern medical technology.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key PTFE Property Utilized |
|---|---|
| Vascular Grafts & Implants | Biocompatibility, Chemical Inertness |
| Surgical Meshes & Patches | Biocompatibility, Tissue Scaffolding |
| Catheters & Instruments | Low Friction, Non-stick Surface |
| Advanced Wound Dressings | Non-stick Surface, Painless Removal |
| Radiological Equipment | High Radiation Resistance |
Ready to integrate high-performance PTFE into your medical devices?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of medical-grade PTFE components. Whether you are developing life-saving implants, patient-friendly instruments, or durable equipment for radiological settings, our expertise ensures your devices meet the highest standards of safety and performance.
We offer custom fabrication from initial prototypes to high-volume production, tailored to the stringent requirements of the medical industry.
Contact us today to discuss your project needs and let KINTEK be your trusted partner in medical innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Three Neck Flasks for Advanced Chemical Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What role do Teflon PTFE sheets play in sewing projects? Achieve Flawless, Professional Results
- What is the difference between etched one side and pressure sensitive tape in PTFE? Choose the Right Bonding Method
- What are the benefits of using PTFE valves in the food processing industry? Ensure Safety, Purity, and Efficiency
- How can Teflon (PTFE) be processed into parts? A Guide to Compression Molding & CNC Machining
- What are the three primary application areas for PTFE O-rings? Master Sealing in Harsh Environments
- What are the key differences between PTFE and EPDM valve seats? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the key technical features of Teflon backup rings? Essential Support for High-Pressure Seals
- What are the primary materials used for oil seals? NBR vs. PTFE for Your Application



















