At extremely low temperatures, PTFE (Teflon) stands apart from nearly all other polymers. It is unique in its ability to retain a degree of compressive plasticity and sealing capability at temperatures that approach absolute zero (0 K, -273.15°C / -459.67°F), a point where most materials become catastrophically brittle.
While most materials fail in cryogenic conditions, PTFE's molecular structure allows it to avoid the brittleness that affects other polymers. The critical factor is not a single failure temperature, but understanding how its stiffness and thermal contraction affect its ability to maintain a sealing force as temperatures drop.

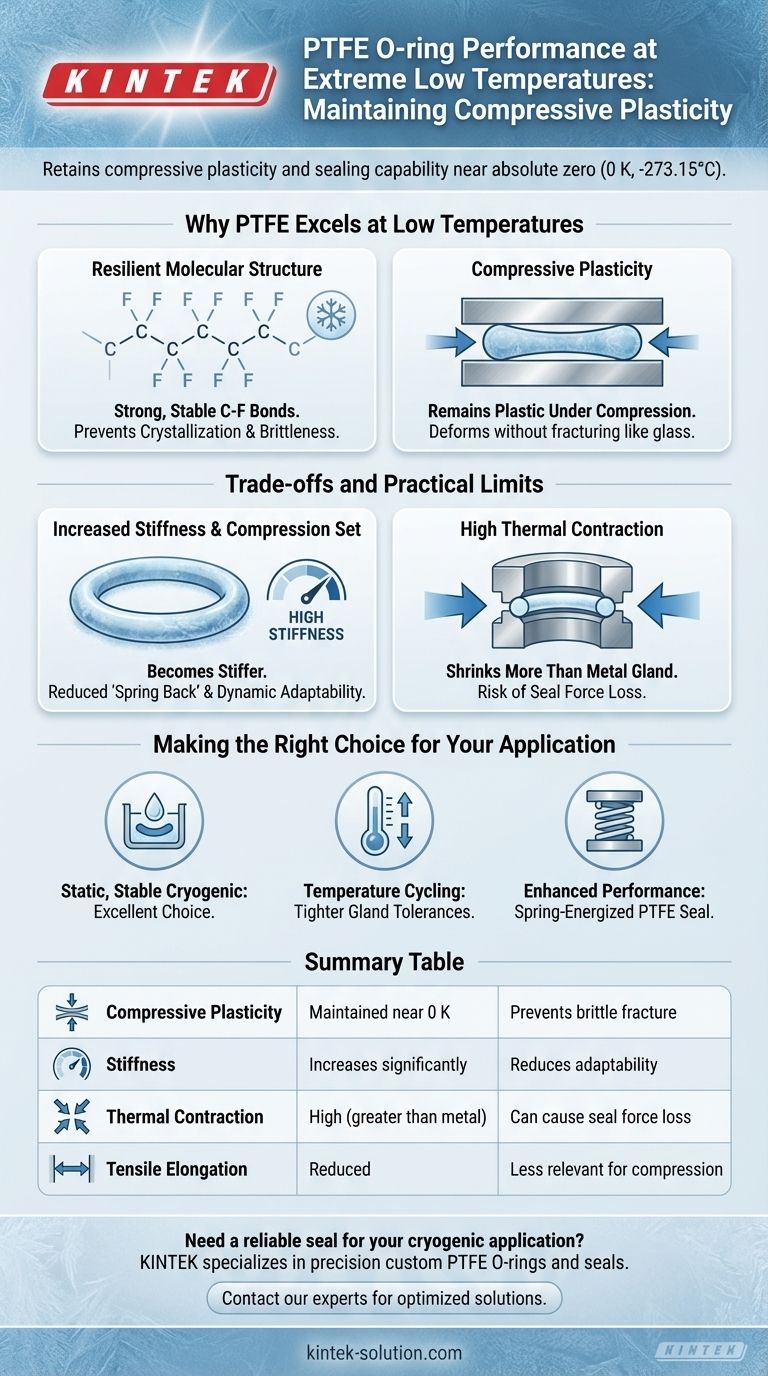
Why PTFE Excels at Low Temperatures
The common failure mode for materials at low temperatures is embrittlement—they lose their ability to deform and instead fracture like glass. PTFE largely avoids this, especially under the compressive forces an O-ring experiences.
The Resilient Molecular Structure
PTFE's resilience comes from the incredibly strong and stable bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms. This structure prevents the polymer chains from crystallizing into a rigid, brittle state at low temperatures, which is a common point of failure for other plastics.
Compressive vs. Tensile Properties
It is crucial to understand that while PTFE remains plastic under compression, its properties do change. As it gets colder, it becomes much stiffer and its ability to stretch (tensile elongation) is significantly reduced. For an O-ring, which functions by being compressed, this retention of compressive plasticity is the key to its performance.
The Absence of a "Brittle Point"
Many materials have a distinct "glass transition temperature" where they rapidly transform from a rubbery to a glass-like state. PTFE does not exhibit this sharp transition point in the same way, allowing it to maintain its integrity across an exceptionally wide cryogenic range.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Limits
Exceptional low-temperature performance does not mean PTFE is without challenges. A successful cryogenic seal design requires acknowledging two critical physical behaviors.
Increased Stiffness and Compression Set
As PTFE cools, it becomes progressively harder and less able to "spring back" after being compressed. This means that if a seal is assembled at room temperature and then cooled, the O-ring may not be able to dynamically adapt to changes in pressure or flange movement, potentially compromising the seal.
High Thermal Contraction
PTFE has a significantly higher coefficient of thermal contraction than most metals. When a system is cooled, a PTFE O-ring will shrink more than the metal gland it is seated in. This shrinkage can lead to a complete loss of the initial "squeeze" required to form a seal, resulting in a leak path. This is often the primary cause of seal failure in cryogenic applications, not material brittleness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Successfully using PTFE O-rings at low temperatures depends entirely on accounting for its physical changes. The design of the gland and the operational conditions are as important as the material itself.
- If your primary focus is a static seal in a stable cryogenic environment: PTFE is an outstanding choice, as it will not shatter or crack under the compressive load.
- If your application involves significant temperature cycling: You must design the gland with tighter tolerances to account for PTFE's thermal contraction and ensure sealing pressure is maintained at the lowest operating temperature.
- If you require enhanced performance and leak prevention: Consider using a spring-energized PTFE seal, where a metal spring provides a constant load, compensating for the material's increased stiffness and thermal shrinkage at low temperatures.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE for cryogenic sealing is less about a specific temperature rating and more about a thorough design that accommodates its predictable changes in hardness and size.
Summary Table:
| Property | Behavior at Low Temperatures | Impact on Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Plasticity | Maintained down to near 0 K (-273°C) | Prevents brittle fracture under load |
| Stiffness | Increases significantly | Reduces ability to adapt to movement |
| Thermal Contraction | High (greater than metal glands) | Can cause loss of sealing force |
| Tensile Elongation | Reduced | Not a primary concern for compressed O-rings |
Need a reliable seal for your cryogenic application?
PTFE's ability to function at temperatures approaching absolute zero makes it a unique solution for demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. However, success hinges on a design that accounts for its thermal contraction and increased stiffness.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom O-rings and seals. We work with you from prototype to high-volume production to ensure your sealing solution is optimized for performance across your entire temperature range, including extreme cryogenics.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and leverage our expertise in advanced polymer sealing solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a Teflon O-ring and what is its primary function? A Guide to Superior Sealing
- What are PTFE seals and what makes them exceptional? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What benefits do Teflon sheets provide in DTG printing? Achieve Consistent, Professional Prints
- Why are PTFE lined ball valves suitable for the food and pharmaceutical industries? Ensuring Purity and Compliance
- What temperature range can PTFE O-rings withstand? Unlock Extreme Thermal Performance from -200°C to 260°C
- What are the key benefits of PTFE coatings in corrosion resistance? Achieve Unmatched Protection for Your Components
- Why are PTFE fasteners used in applications requiring electrical insulation? Ensure Reliable, Non-Conductive Performance
- What are the characteristics of graphite PTFE gland packings? High-Performance Sealing for Demanding Applications



















