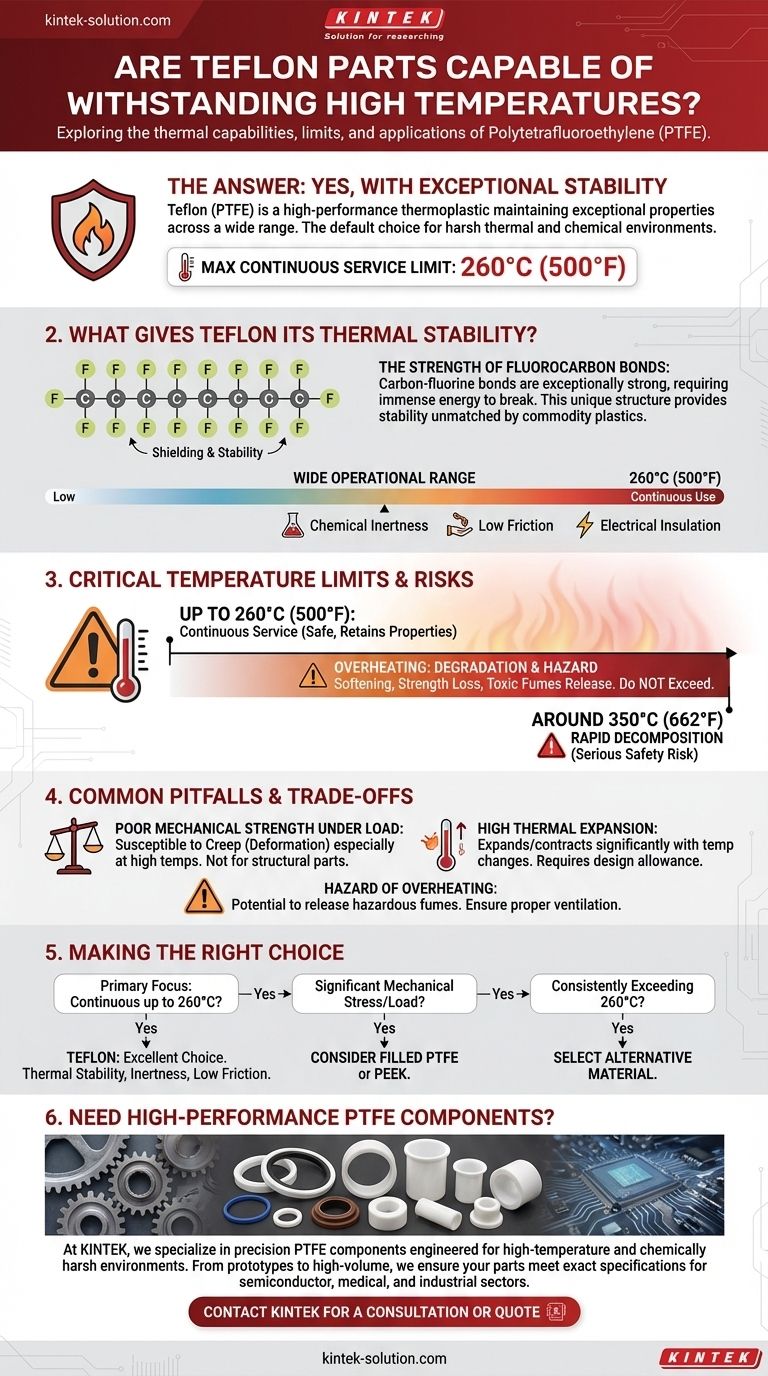
Yes, Teflon parts are renowned for their ability to withstand high temperatures. The material, chemically known as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a high-performance thermoplastic that maintains its exceptional properties across a very wide temperature range. This makes it a default choice for components used in harsh industrial environments where both thermal stability and chemical resistance are required.
While Teflon is an excellent choice for high-temperature applications, its effectiveness is defined by a specific operational ceiling. The critical detail isn't just that it resists heat, but understanding its performance limit of 260°C (500°F) for continuous use.
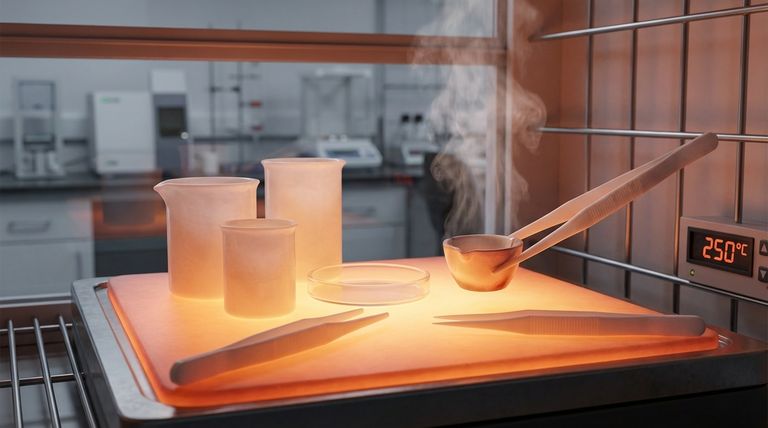

What Gives Teflon Its Thermal Stability?
Teflon's high-temperature performance is not an accident; it's a direct result of its unique molecular structure. This structure gives it stability that commodity plastics cannot match.
The Strength of Fluorocarbon Bonds
Teflon is composed of a long chain of carbon atoms, with each carbon atom completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong, requiring a great deal of thermal energy to break.
A Wide Operational Range
This molecular stability gives pure PTFE an impressive continuous service temperature of up to 260°C (500°F). It can operate in this range for extended periods without significant degradation of its core properties.
Retaining Key Properties at Temperature
Crucially, Teflon doesn't just survive the heat; it continues to perform. Within its operational range, it retains its famous chemical inertness, extremely low coefficient of friction, and excellent electrical insulating properties.
The Critical Temperature Limit and Its Implications
While "high temperature" is a useful descriptor, engineers and designers must work with precise numbers. For Teflon, the 260°C limit is the most important figure to understand.
The 260°C (500°F) Continuous Service Limit
This is the industry-standard maximum temperature for long-term, continuous use. Parts like seals, gaskets, and bushings designed for high-heat equipment are specified to operate at or below this temperature.
The Onset of Degradation
Pushing Teflon beyond this limit initiates material degradation. While it won't melt in a conventional sense, it will begin to soften, lose its mechanical strength, and, most importantly, can start to release toxic fluorocarbon fumes.
Significant Decomposition
At even higher temperatures, around 350°C (662°F), decomposition becomes much more rapid. Using Teflon in applications where it could reach these temperatures is a serious safety and performance risk.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. To use Teflon effectively, you must be aware of its limitations, especially as temperatures increase.
Poor Mechanical Strength Under Load
Virgin Teflon is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to creep, meaning it can slowly deform over time when under a constant load. This effect is amplified at higher temperatures. It is not suitable for high-load structural components.
High Thermal Expansion
Teflon expands and contracts with temperature changes more than many other materials. This high coefficient of thermal expansion must be accounted for in designs with tight tolerances to prevent parts from seizing or failing.
The Hazard of Overheating
The potential to release hazardous fumes when overheated cannot be overstated. Proper ventilation is essential in any application where Teflon could accidentally be exposed to temperatures well above its service limit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if Teflon is the appropriate material for your specific high-temperature needs.
- If your primary focus is continuous operation up to 260°C (500°F): Teflon is an exceptional choice, providing a unique combination of thermal stability, chemical inertness, and low friction.
- If your application involves significant mechanical stress or load: Consider using a filled grade of Teflon (such as glass- or carbon-filled PTFE) to improve strength and creep resistance, or evaluate a different polymer like PEEK.
- If your environment will consistently exceed 260°C (500°F): You must select an alternative material, as standard Teflon will degrade and fail under these conditions.
By respecting its precise thermal limits and mechanical properties, you can reliably engineer Teflon components for demanding high-performance applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE / Teflon) |
| Max Continuous Service Temp | 260°C (500°F) |
| Key Strength | Excellent chemical inertness & thermal stability within its range |
| Critical Limitation | Degrades and releases fumes above 260°C; susceptible to creep under load |
| Ideal For | Seals, liners, labware in semiconductor, medical, and lab environments |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—that are engineered to perform reliably in high-temperature and chemically harsh environments. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production for the semiconductor, medical, or industrial sectors, our expertise ensures your components meet exact thermal and mechanical specifications.
Let's discuss your application requirements and material challenges. Contact our engineering team today to get a quote or request a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Microwave Digestion Vessels for Demanding Applications
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















