In many critical aspects, yes. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) gaskets offer exceptional durability, often surpassing standard PTFE in sealing performance and resistance to creep. However, their durability profile is different; they are softer and more compressible, which makes them less suitable for certain high-pressure applications where the rigidity of standard PTFE is required.
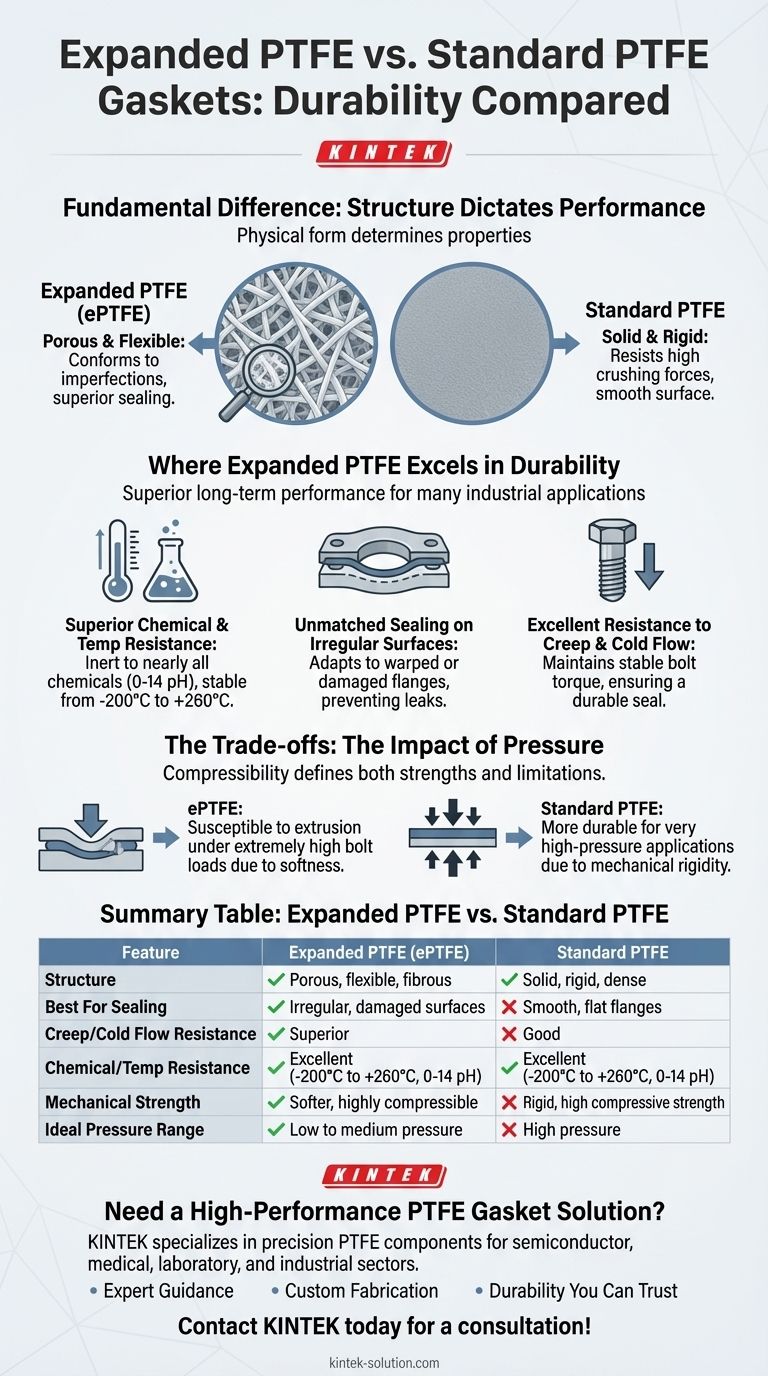
The core difference lies in their structure: Expanded PTFE's porous, flexible nature makes it a superior sealing material for irregular surfaces, while standard PTFE's solid, rigid form gives it an edge in high-pressure environments. Your application's specific mechanical demands will determine which is more "durable" for the job.

The Fundamental Difference: Structure Dictates Performance
To understand their durability, you must first understand their construction. The unique properties of each gasket type stem directly from their physical form.
Standard PTFE: Solid and Rigid
A standard PTFE gasket is machined from a solid billet of material. It is dense, rigid, and has a smooth surface.
This solid construction makes it highly resistant to being crushed under extreme compressive forces.
Expanded PTFE: Porous and Flexible
Expanded PTFE is created through a process that introduces a porous, fibrous structure into the material. It is soft, highly compressible, and flexible.
This flexibility allows it to conform perfectly to surface imperfections, creating a more reliable and durable seal, especially on older or damaged flanges.
Where Expanded PTFE Excels in Durability
For many common industrial applications, the specific durability advantages of expanded PTFE make it the superior choice for long-term performance.
Superior Chemical and Temperature Resistance
Expanded PTFE retains all of the outstanding chemical resistance of pure PTFE. It is inert to nearly all chemicals across the entire 0-14 pH range.
It is only vulnerable to molten alkali metals and elemental fluorine. This, combined with its wide operating temperature range (-200°C to +260°C), ensures long-term stability in aggressive environments.
Unmatched Sealing on Irregular Surfaces
This is the key advantage of ePTFE. Its softness and flexibility allow it to adapt to irregular or warped flange surfaces, compensating for deformation where a rigid gasket would fail.
By creating a tighter, more complete seal, it prevents leaks and extends the service life of the entire flange assembly.
Excellent Resistance to Creep and Cold Flow
Creep, or cold flow, is the tendency of a material to deform under sustained stress, which can lead to a loss of bolt torque and eventual seal failure.
Expanded PTFE exhibits superior resistance to creep, meaning it maintains a stable and consistent bolt tightening force over time, ensuring a durable and reliable seal.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Impact of Pressure
While expanded PTFE has clear advantages, its primary strength—compressibility—also defines its main limitation.
The Role of Softness
The soft, porous structure of ePTFE is what allows it to conform so well to imperfect surfaces.
However, this same softness means it is more susceptible to extrusion or damage under extremely high bolt loads or in high-pressure systems where the gasket has minimal surface area.
Standard PTFE for High-Pressure Environments
For applications involving very high pressures, the mechanical rigidity of solid, standard PTFE is often necessary.
Its solid structure provides greater resistance to being crushed or forced out of the flange, making it the more durable choice when compressive strength is the single most critical factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right gasket requires matching the material's durability profile to the specific demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is sealing older, damaged, or irregular flanges: Expanded PTFE is the more durable and reliable choice due to its superior conformability.
- If your primary focus is long-term seal integrity in chemically aggressive environments: Both are excellent, but ePTFE's superior creep resistance and adaptability provide a more reliable long-term seal.
- If your primary focus is handling extremely high pressures or bolt loads: Standard PTFE's rigidity and compressive strength make it the more durable option for these specific mechanical stresses.
Ultimately, the most durable gasket is the one that is best suited for its specific operating conditions.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Standard PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Porous, flexible, fibrous | Solid, rigid, dense |
| Best For Sealing | Irregular, damaged, or warped flanges | Smooth, flat flanges |
| Creep/Cold Flow Resistance | Superior | Good |
| Chemical/Temp Resistance | Excellent (0-14 pH, -200°C to +260°C) | Excellent (0-14 pH, -200°C to +260°C) |
| Mechanical Strength | Softer, highly compressible | Rigid, high compressive strength |
| Ideal Pressure Range | Low to medium pressure | High pressure |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Gasket Solution?
Choosing the right gasket is critical for the safety and efficiency of your operations. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom ePTFE and standard PTFE gaskets, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Help you select the optimal material for your specific pressure, temperature, and surface conditions.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring a perfect fit and performance.
- Durability You Can Trust: Components built for long-term reliability in aggressive environments.
Let our experts help you achieve a leak-free, durable seal. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications



















