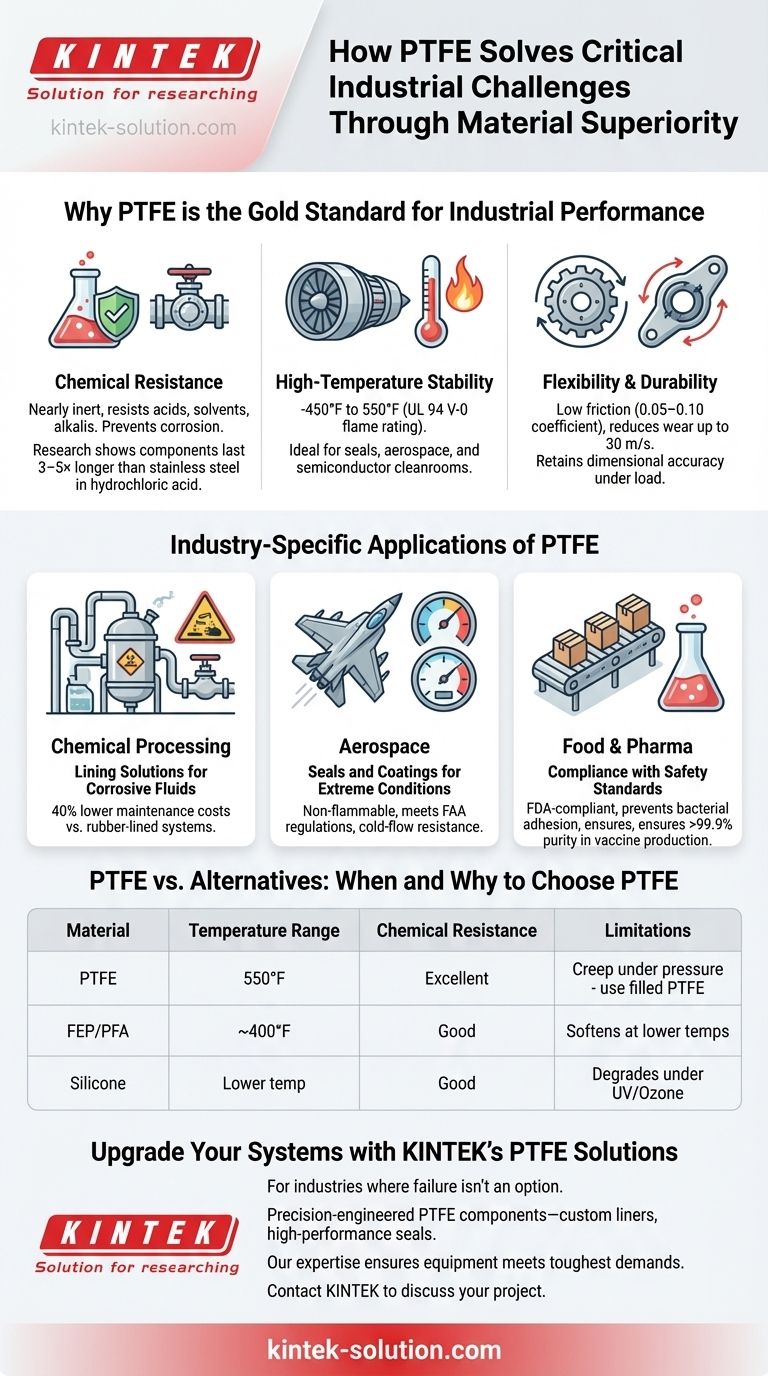
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) stands as the gold standard for industrial performance, offering unmatched chemical resistance, thermal stability, and durability. This article explores why industries from chemical processing to aerospace rely on PTFE to solve their most demanding material challenges—and how to leverage its strengths effectively.
Why PTFE is the Gold Standard for Industrial Performance
PTFE’s unique molecular structure delivers three key advantages that outperform conventional materials:
Chemical Resistance in Aggressive Environments
PTFE is nearly inert, resisting attacks from acids, solvents, and alkalis that degrade metals, rubbers, and even other fluoropolymers like PFA. In chemical processing, PTFE-lined valves and coated fasteners prevent corrosion-induced failures, ensuring safety and reducing downtime. Research shows PTFE components last 3–5× longer than stainless steel in hydrochloric acid exposure.
High-Temperature Stability in Demanding Processes
From cryogenic (-450°F) to extreme heat (550°F), PTFE maintains structural integrity. Aerospace applications leverage this for seals in jet engines, where PTFE’s UL 94 V-0 flame rating ensures safety during thermal cycling. Unlike silicones, PTFE doesn’t off-gas or degrade at high temperatures, making it ideal for semiconductor cleanrooms.
Flexibility and Durability in Mechanical Components
PTFE’s low friction coefficient (0.05–0.10) reduces wear in dynamic parts like bushings, even at speeds up to 30 m/s. Its flexibility accommodates thermal expansion in pipelines, while machined PTFE parts retain dimensional accuracy under load.
Industry-Specific Applications of PTFE
Chemical Processing: Lining Solutions for Corrosive Fluids
PTFE linings in reactors and pipes handle sulfuric acid, chlorine, and other aggressive media. Case studies reveal 40% lower maintenance costs compared to rubber-lined systems, thanks to PTFE’s non-reactivity.
Aerospace: Seals and Coatings for Extreme Conditions
High-PV (pressure-velocity) PTFE grades endure the combined stresses of jet engine seals, outperforming FEP in longevity. Their non-flammability meets FAA regulations, while cold-flow resistance prevents seal failure at altitude.
Food and Pharma: Compliance with Safety Standards
FDA-compliant PTFE coatings on conveyor belts and valves prevent bacterial adhesion and chemical leaching. In vaccine production, PTFE labware ensures >99.9% purity by resisting sterilants like ethylene oxide.
PTFE vs. Alternatives: When and Why to Choose PTFE
Comparative Advantages Over FEP, PFA, and Silicone
- FEP/PFA: While easier to mold, they soften at lower temperatures (~400°F vs. PTFE’s 550°F). PTFE is preferred for long-term chemical immersion.
- Silicone: Lacks PTFE’s non-stick properties and degrades under UV/ozone exposure.
Limitations and Mitigation Strategies
PTFE’s creep tendency under sustained pressure requires design adaptations:
- Use rubber-energized seals in hydraulic systems.
- Opt for filled PTFE (e.g., glass-reinforced) to improve load-bearing capacity.
Upgrade Your Systems with KINTEK’s PTFE Solutions
For industries where failure isn’t an option, KINTEK delivers precision-engineered PTFE components—from custom liners to high-performance seals. Our expertise ensures your equipment meets the toughest operational demands while reducing lifecycle costs. [Contact KINTEK] to discuss your project’s needs today.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
Related Articles
- The Physics of a Perfect Fit: How PTFE Eliminates an Athlete's Hidden Distractions
- Beyond "Non-Stick": Why Your PTFE Components Fail and How to Fix It for Good
- The PTFE Paradox: Why the 'Perfect' Material Fails—And How to Make It Work
- The Unseen Workhorse: Why PTFE Is the Default Choice for Impossible Problems
- Your "Inert" PTFE Component Might Be the Real Source of System Failure




















