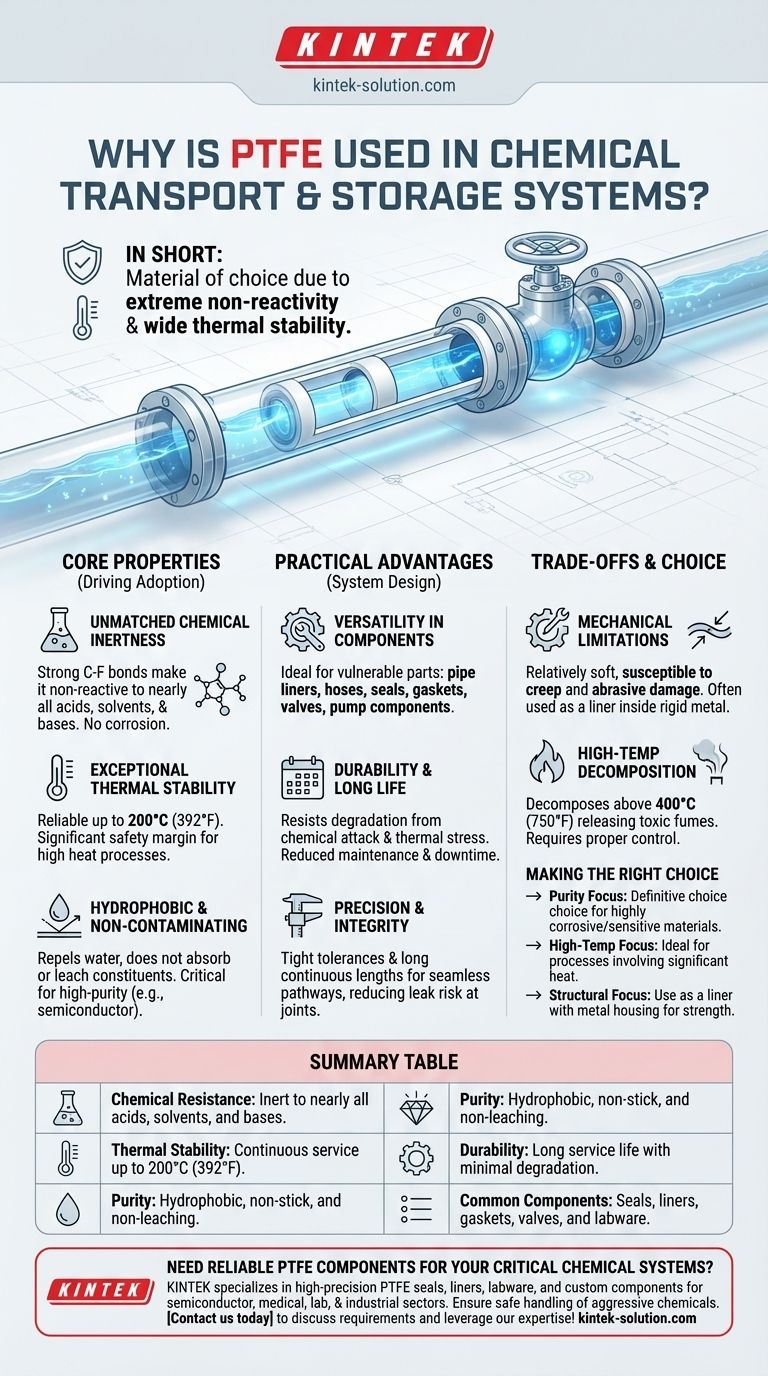
In short, PTFE is the material of choice for chemical transport and storage because of its two defining characteristics: it is almost completely immune to chemical attack and it remains stable across a very wide range of temperatures. This combination of extreme non-reactivity and thermal resistance makes it uniquely reliable for safely handling the most aggressive and hazardous substances.
The core challenge in chemical handling is ensuring system integrity to prevent leaks, degradation, and contamination. PTFE solves this by being one of the most chemically inert and thermally stable polymers available, making it a predictable and exceptionally safe material for critical applications.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE Adoption
The reason PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) has become a standard in chemical processing is not due to a single feature, but a combination of properties that stem directly from its unique molecular structure.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE's structure is composed of a chain of carbon atoms completely sheathed by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and stable.
This molecular shield makes the material non-reactive to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, solvents, and bases. It will not corrode or degrade, even with prolonged exposure to highly aggressive substances.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE performs reliably across a broad temperature spectrum. It remains functional in continuous service at temperatures up to 200°C (392°F).
Its melting point is approximately 327°C (621°F), providing a significant safety margin for processes that involve exothermic reactions or high ambient heat, such as inside engine compartments.
Hydrophobic and Non-Contaminating
The material is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and does not absorb substances. More importantly, it is inert and does not leach its own constituents into the chemicals it contains.
This is critical in high-purity applications, such as in the semiconductor or pharmaceutical industries, where even trace amounts of contamination can ruin a product.
Practical Advantages in System Design
These fundamental properties translate directly into tangible benefits when building and operating chemical handling systems.
Versatility in Components
PTFE's properties make it ideal for the most vulnerable parts of a system. It is commonly fabricated into pipe liners, hoses, seals, gaskets, valves, and pump components.
Using PTFE ensures that the points of contact with the chemical are fully protected, preventing system failure at joints or moving parts.
Durability and Long Service Life
Because PTFE does not degrade from chemical attack or thermal stress within its operating limits, components made from it have a very long and predictable service life.
This resilience reduces the need for frequent inspection and replacement, lowering long-term maintenance costs and minimizing system downtime.
Precision and System Integrity
PTFE can be manufactured to tight tolerances and in very long, continuous lengths for applications like hose liners.
This capability allows for the creation of seamless transport pathways, which significantly reduces the risk of leaks that can occur at joints and connections.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While exceptionally capable, PTFE is not the perfect material for every single application. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to creep, which is slow deformation under sustained pressure, and can be damaged by high-velocity abrasive particles.
For this reason, it is often used as a liner inside a more rigid, structurally strong metal pipe or housing that provides the necessary mechanical support.
High-Temperature Decomposition
While very stable, if PTFE is heated well beyond its operating limits (above 400°C / 750°F), it can decompose and release toxic fumes. Proper temperature control and system design are essential to prevent this scenario.
Cost and Processing
PTFE is a specialty polymer and is generally more expensive than common plastics like PVC or polyethylene. It also requires specialized processing techniques and cannot be melt-processed in the same way as many other thermoplastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and chemical resistance: PTFE is the definitive choice for handling highly corrosive or sensitive materials where contamination is not an option.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature fluid transport: Its wide operating range makes it ideal for processes involving significant heat, far exceeding the capabilities of many other polymers.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under high pressure: Use PTFE as a liner or coating, relying on a metal housing to provide the required mechanical strength.
By understanding both its unparalleled strengths and its specific limitations, you can leverage PTFE to build exceptionally safe and reliable chemical handling systems.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Advantage |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all acids, solvents, and bases |
| Thermal Stability | Continuous service up to 200°C (392°F) |
| Purity | Hydrophobic, non-stick, and non-leaching |
| Durability | Long service life with minimal degradation |
| Common Components | Seals, liners, gaskets, valves, and labware |
Need reliable PTFE components for your critical chemical systems? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure your systems handle aggressive chemicals safely, with custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and leverage our expertise in material science for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How is a PTFE bearing pad installed on prefabricated beams? A Guide to Secure, Low-Friction Installation
- Why is PTFE more expensive than other sealing materials? Superior Performance Justifies the Cost
- How long do PTFE valves typically last? Maximize Valve Lifespan Up to 50 Years
- What are the weight and installation advantages of PTFE expansion bellows over metal bellows? Achieve Easier, Faster Installation.
- What are the benefits of PTFE backup rings? Enhance Seal Life in High-Pressure Systems
- Which machining techniques are suitable for creating rough edges on PTFE? Master CNC Milling for Controlled Textures
- Why is EPDM the preferred choice for pneumatic butterfly valves in water treatment systems? | KINTEK
- What is a PTFE sliding elastomeric bearing? A Guide to Managing Large Structural Movements



















