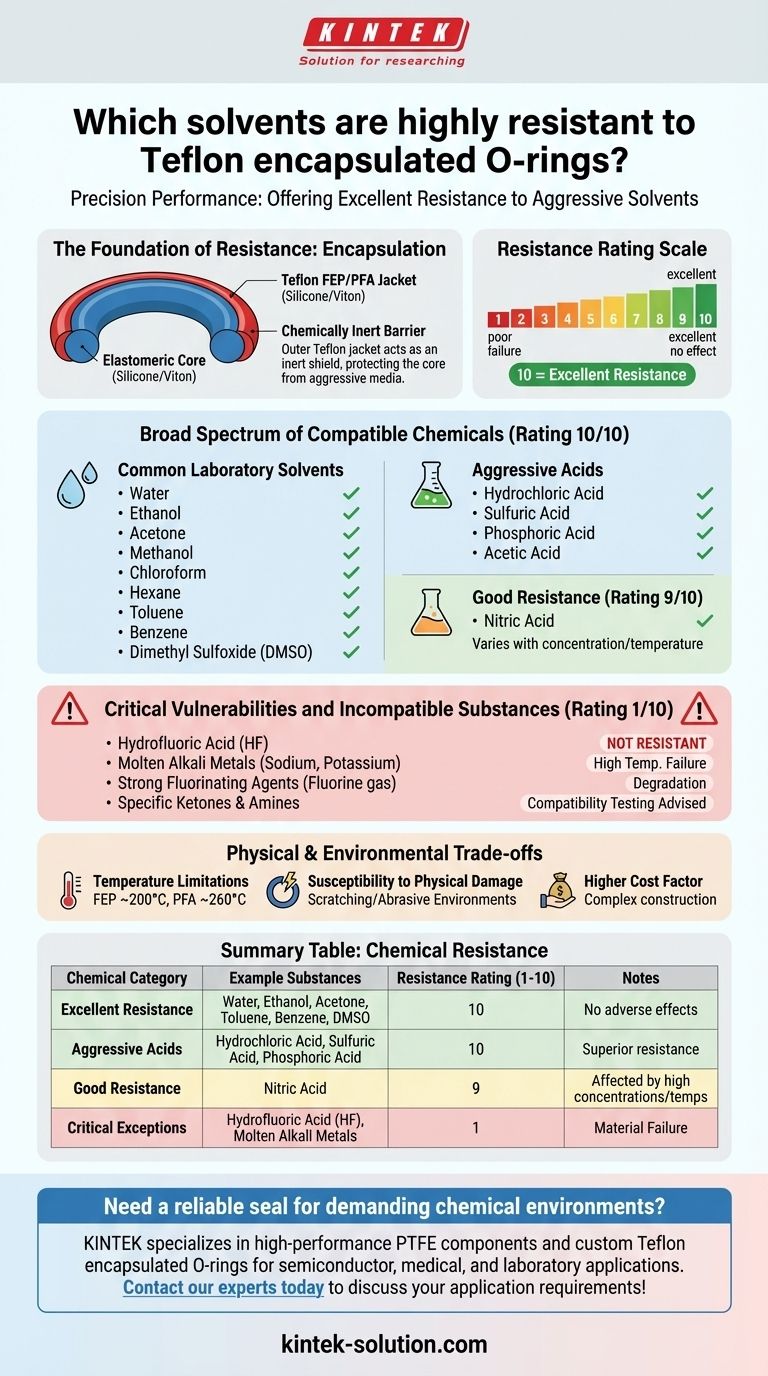
To be precise, Teflon encapsulated O-rings offer excellent resistance (rated 10 out of 10) to a wide array of common and aggressive solvents. This list includes water, ethanol, acetone, methanol, chloroform, hexane, toluene, benzene, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Their robust performance extends to many aggressive acids as well.
While Teflon encapsulation provides a formidable barrier against most solvents and acids, its true value is realized by understanding its few, but critical, exceptions—most notably hydrofluoric acid, molten alkali metals, and susceptibility to physical damage.

The Foundation of Resistance: Encapsulation
A Chemically Inert Barrier
Teflon encapsulated O-rings consist of an elastomeric core (like silicone or Viton) seamlessly wrapped in a thin, durable jacket of Teflon FEP or PFA.
This outer Teflon jacket is the source of the seal's extraordinary chemical resistance. It acts as an inert shield, protecting the inner core from contact with aggressive media.
The Resistance Rating Scale
Chemical compatibility for these seals is typically measured on a scale from 1 to 10.
A rating of 10 indicates excellent resistance with no adverse effects, while a rating of 1 signifies poor resistance and material failure.
Broad Spectrum of Compatible Chemicals
Common Laboratory Solvents
Teflon encapsulated O-rings are an ideal choice for applications involving a wide range of organic and inorganic solvents.
They consistently achieve a resistance rating of 10 against water, ethanol, acetone, methanol, chloroform, hexane, toluene, benzene, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Aggressive Acids and Bases
Their robust nature extends to highly corrosive acids.
These O-rings show excellent resistance (rated 10) to hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, and acetic acid. They also have good resistance (rated 9) to nitric acid, though performance can be affected by very high concentrations and temperatures. They are generally resistant to most bases.
Critical Vulnerabilities and Incompatible Substances
Hydrofluoric Acid (HF)
This is the most significant chemical exception. Teflon encapsulated O-rings are not resistant to hydrofluoric acid, receiving a resistance rating of 1, especially in concentrated solutions.
Molten Alkali Metals
At high temperatures, molten alkali metals such as sodium and potassium will attack the Teflon jacket and cause the seal to fail.
Strong Fluorinating Agents
Extremely powerful fluorinating agents, such as elemental fluorine gas at high temperatures and pressures, can also degrade the Teflon encapsulation.
Specific Ketones and Amines
While resistant to acetone (a ketone), the performance of these O-rings may be degraded by exposure to certain other specific ketones and amines. Compatibility testing is advised if these are present in your application.
Understanding the Physical and Environmental Trade-offs
Temperature Limitations
The operational temperature range is dictated by the Teflon jacket. For FEP encapsulation, the limit is generally around 200°C (392°F), while PFA can handle temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
Susceptibility to Physical Damage
The Teflon jacket, while chemically inert, is relatively soft. It is prone to scratching and damage in abrasive environments or during installation. Any compromise to the jacket exposes the vulnerable inner core.
Higher Cost Factor
Due to their complex two-part construction, encapsulated O-rings are typically more expensive than standard elastomeric or solid Teflon O-rings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires matching its capabilities to your specific operational environment.
- If your primary focus is general solvent and acid resistance: Teflon encapsulated O-rings are an excellent and reliable choice for a vast range of chemicals.
- If your application involves hydrofluoric acid, molten alkali metals, or elemental fluorine: You must seek an alternative sealing material specifically designed for these substances.
- If your system contains abrasive particles or requires high-pressure dynamic sealing: Carefully evaluate the risk of physical damage to the Teflon jacket and consider more robust alternatives.
Ultimately, a successful application depends on understanding both the exceptional strengths and the precise limitations of your chosen material.
Summary Table:
| Chemical Category | Example Substances | Resistance Rating (1-10) |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent Resistance | Water, Ethanol, Acetone, Toluene, Benzene, DMSO | 10 |
| Aggressive Acids | Hydrochloric Acid, Sulfuric Acid, Phosphoric Acid | 10 |
| Good Resistance | Nitric Acid (varies with concentration/temperature) | 9 |
| Critical Exceptions | Hydrofluoric Acid (HF), Molten Alkali Metals | 1 |
Need a reliable seal for demanding chemical environments?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom Teflon encapsulated O-rings. Our seals are designed for superior chemical resistance in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. We prioritize precision and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Ensure your system's integrity with seals built for chemical resistance. Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















