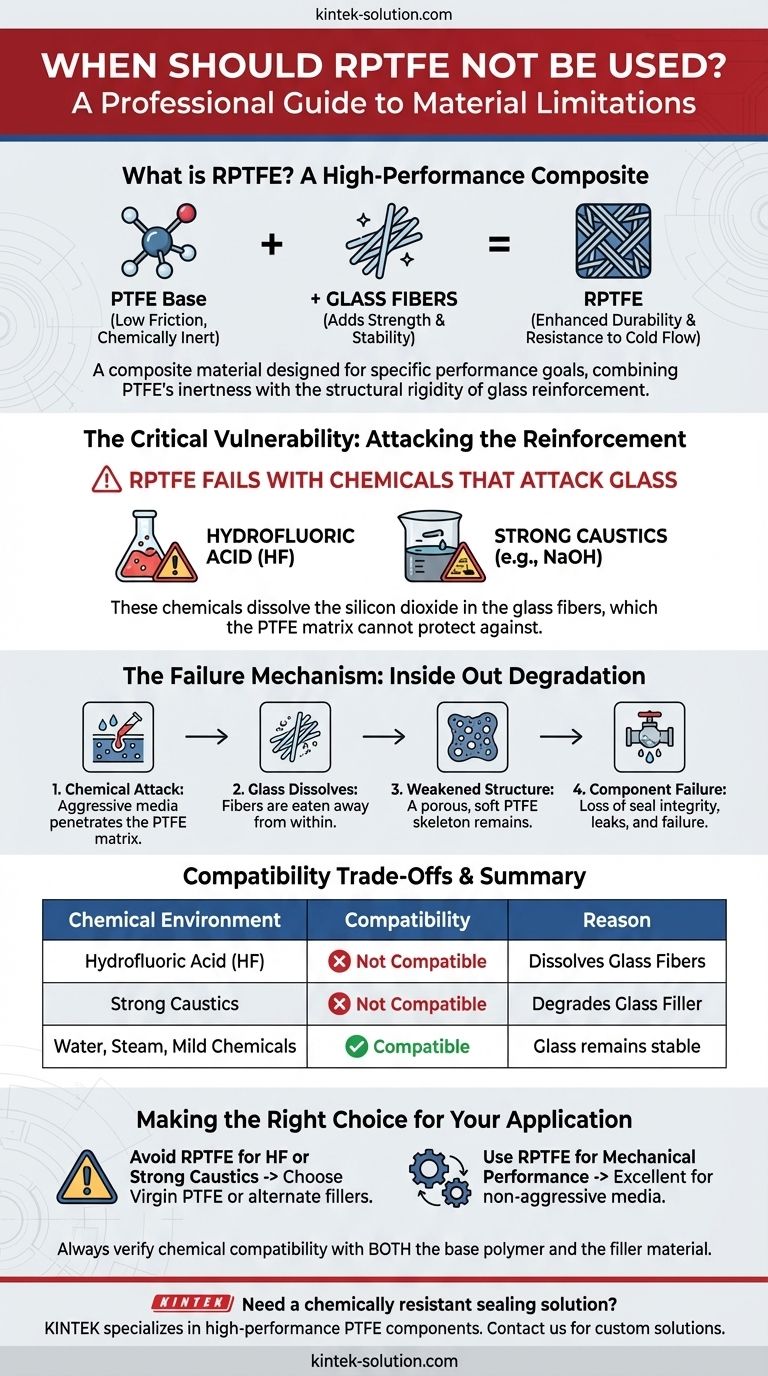
RPTFE should not be used in any application where the working fluid contains chemicals that attack glass. The most common examples of these are hydrofluoric acid and strong caustic solutions, which will degrade the glass fiber reinforcement within the material and lead to component failure.
The "R" in RPTFE stands for "Reinforced," which is typically achieved by adding glass fibers to a standard PTFE base. While this reinforcement dramatically improves mechanical properties, it also introduces the chemical vulnerabilities of glass, creating a critical limitation that does not exist in pure, un-filled PTFE.

What is RPTFE? The Role of Reinforcement
To understand the limitations of RPTFE, you first need to understand its composition as a composite material. It is not a single substance, but a combination designed to achieve specific performance goals.
The Base Material: PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is known for its exceptional chemical inertness and extremely low friction. You may know it by the brand name Teflon®.
However, on its own, PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under mechanical load and temperature, it is highly susceptible to deformation and "cold flow," where the material slowly creeps out of its intended shape.
The Reinforcement: Adding Glass Fibers
To combat the softness of PTFE, fillers are added. In RPTFE, the filler is typically a percentage (often 15%) of milled glass fibers.
These fibers act like rebar in concrete, dramatically increasing the material's rigidity, compressive strength, and resistance to cold flow. This makes RPTFE far more durable for demanding applications like valve seats and seals.
The Result: A High-Performance Composite
The final material, RPTFE, combines the benefits of its constituent parts: the low friction and chemical resistance of PTFE with the strength and stability of glass. This composite structure is key to its performance—and its limitations.
The Point of Failure: When Glass Is Attacked
The fundamental weakness of RPTFE is not the PTFE base, but its glass reinforcement. While the PTFE matrix protects the glass fibers from many chemicals, it cannot protect them from media that are aggressive to glass itself.
The Specific Chemical Weakness
The primary culprits are hydrofluoric acid (HF) and strong caustics (e.g., concentrated sodium hydroxide). These chemicals will dissolve the silicon dioxide that forms the basis of glass.
The Failure Mechanism
When exposed to these chemicals, the media works its way into the material and begins to dissolve the glass fibers embedded within the PTFE matrix.
The structural reinforcement is effectively eaten away from the inside out, leaving behind a porous and weakened PTFE structure.
The Consequence: Compromised Integrity
Once the glass reinforcement is gone, the material loses its enhanced mechanical properties. It reverts to behaving like soft, un-filled PTFE and will quickly fail under pressure.
This results in a loss of sealing integrity, leading to dangerous leaks and complete failure of the component, such as a valve seat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material always involves balancing its strengths and weaknesses. RPTFE is no exception.
The Benefit: Enhanced Mechanical Properties
The reason for using RPTFE is its superior strength, stability, and wear resistance compared to virgin PTFE. For thousands of applications involving water, steam, hydrocarbons, and mild chemicals, it is a more robust and reliable choice.
The Limitation: Targeted Chemical Vulnerability
The trade-off for that enhanced strength is a narrower window of chemical resistance. The glass filler introduces a specific vulnerability that pure PTFE does not have. You gain mechanical performance by sacrificing universal chemical compatibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Always verify the chemical compatibility of your service media against the component materials. When dealing with reinforced polymers, this means checking compatibility with both the base polymer and the filler material.
- If your primary focus is handling hydrofluoric acid or strong caustics: You must avoid RPTFE. Specify virgin PTFE or a polymer with a more suitable, chemically-resistant filler.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance under pressure and temperature: RPTFE is an excellent and cost-effective choice, provided your media is not aggressive to glass.
Ultimately, understanding the role of the filler material is the key to correctly specifying any reinforced polymer.
Summary Table:
| Chemical Environment | RPTFE Compatibility | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) | ❌ Not Compatible | Attacks and dissolves the glass fiber reinforcement. |
| Strong Caustic Solutions | ❌ Not Compatible | Degrades the glass filler, compromising structural integrity. |
| Water, Steam, Hydrocarbons, Mild Chemicals | ✅ Compatible | Glass reinforcement remains stable, providing superior mechanical performance. |
Need a chemically resistant sealing solution for demanding applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom seals, liners, and labware. Whether your application requires the universal chemical resistance of virgin PTFE or the enhanced mechanical strength of a reinforced composite, our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get the right material for your specific needs.
Contact us today to discuss your application requirements and let our precision production capabilities deliver a reliable solution. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















