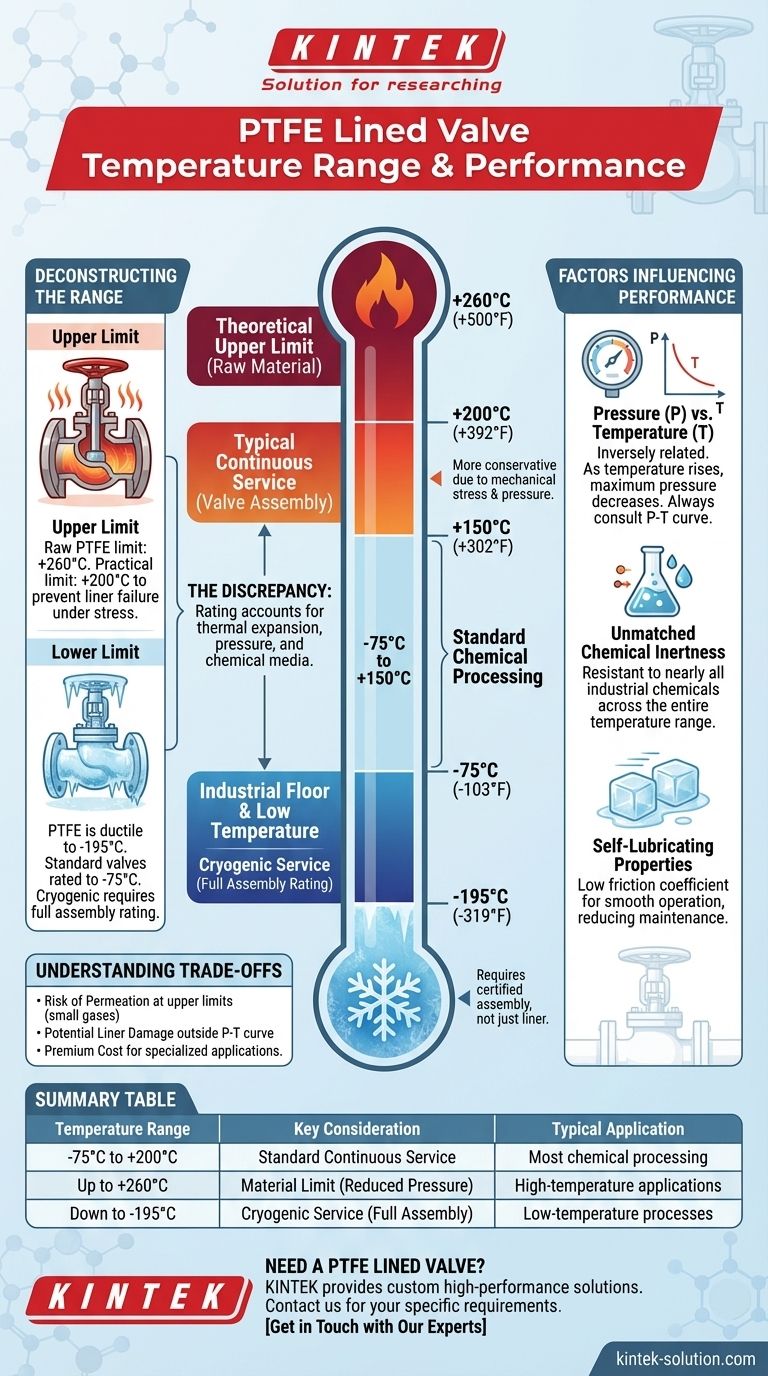
To be precise, a PTFE lined valve can generally operate within a temperature range of approximately -75°C to +260°C (-103°F to +500°F). However, the effective service temperature for a specific valve is often more conservative, typically rated between -195°C and 200°C (-319°F to +392°F), depending on the valve's design, pressure, and the specific media being handled.
The core principle to understand is that while the raw material (PTFE) has a broad theoretical temperature limit, the practical, safe operating range of a finished valve assembly is determined by the manufacturer based on real-world conditions like pressure and mechanical stress.

Deconstructing the Temperature Range
To select the right component, it's critical to understand why different temperature ratings exist and what they mean for your application. The discrepancy isn't an error; it reflects the difference between material science and mechanical engineering.
The Upper Temperature Limit
The widely cited upper limit for pure, unstressed PTFE is +260°C (500°F). This is the point where the material itself begins to lose significant structural integrity.
However, a valve liner is under constant mechanical stress and pressure. For this reason, most manufacturers will specify a more conservative continuous service temperature, often around +200°C (392°F), to ensure a long service life and prevent liner failure or permeation.
The Lower Temperature Limit
PTFE maintains its properties exceptionally well at low temperatures, remaining ductile even in cryogenic conditions down to -195°C (-319°F) and below.
Valves intended for standard chemical processing are often rated to a more common industrial floor of -75°C (-103°F). If your application involves true cryogenic service, you must ensure the entire valve assembly, including the metal body and other components, is designed for such extremes.
Why the Discrepancy Exists
The final temperature rating on a valve's data sheet is not just for the PTFE liner. It represents the performance of the entire engineered system.
This rating accounts for the differential thermal expansion between the metal valve body and the PTFE liner, the pressure rating of the valve, and the specific chemical media it will encounter.
Beyond Temperature: Factors Influencing Performance
Temperature is the primary variable, but it does not act in isolation. To ensure reliability, you must consider these interconnected factors.
The Role of Pressure
Pressure and temperature are inversely related. As the operating temperature of a valve increases, its maximum allowable working pressure decreases.
Always consult the manufacturer's pressure-temperature (P-T) curve for the specific valve model you are considering. This chart is the definitive guide to safe operation.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
A key reason for selecting PTFE is its remarkable resistance to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This inertness is maintained across its entire operating temperature range.
This property makes PTFE lined valves a default choice for handling corrosive media in industries like chemical dosing and processing.
Self-Lubricating Properties
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, comparable to wet ice on wet ice. This inherent self-lubrication ensures smooth valve operation without the need for external lubricants, reducing maintenance and preventing contamination of the process media.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly capable, PTFE lined valves are not without limitations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Risk of Permeation
As PTFE approaches its upper temperature limits, it can become slightly more permeable to very small molecule gases, like hydrogen or helium. For most liquid applications, this is not a concern.
Potential for Liner Damage
Operating the valve outside its specified pressure-temperature curve can lead to liner damage. Excessive heat can cause the liner to soften and deform, while extreme thermal cycling can stress the bond between the liner and the valve body.
Cost Considerations
PTFE lined valves are a premium product due to the material and manufacturing process. Their cost is justified in applications where chemical resistance and temperature stability are non-negotiable requirements for safety and process purity.
Selecting the Right Valve for Your Process
Use the following guidelines to match a valve's capabilities to your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is standard chemical processing (up to 150°C): A valve with a standard 200°C upper limit provides a significant safety margin and is a reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature service (above 180°C): You must scrutinize the manufacturer's P-T curve. The valve's pressure rating will be significantly reduced at these temperatures.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic or low-temperature service: Confirm that the entire valve assembly, not just the liner, is certified for your target temperature to avoid brittleness and failure of the metal body or seals.
Ultimately, your most reliable guide is always the manufacturer's technical data sheet for the specific valve model you intend to use.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Consideration | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| -75°C to +200°C | Standard Continuous Service | Most chemical processing |
| Up to +260°C | Material Limit (Reduced Pressure) | High-temperature applications |
| Down to -195°C | Cryogenic Service (Full Assembly Rating) | Low-temperature or cryogenic processes |
Need a PTFE Lined Valve for Your Demanding Application?
Selecting the right valve is critical for the safety and efficiency of your process. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom-fabricated valves, seals, and liners for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We ensure our valves are engineered for your specific temperature, pressure, and chemical requirements, providing unmatched corrosion resistance and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your application requirements and get a custom solution that guarantees performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Can PTFE be molded into complex shapes? No, Here's the Machining Solution
- Why are PTFE flange gaskets suitable for chemical processing industries? Unlock Superior Safety & Reliability
- Why are PTFE lined check valves ideal for commercial environments? Ensure System Integrity in Corrosive Applications
- What are the best applications for expanded PTFE (ePTFE) gaskets? Solve Sealing Challenges with Low Force
- What support is available for selecting the right PTFE valve design and size? Get Expert Guidance for Your Application
- Why is PTFE preferred in CNC machining for product design? Unlock High-Performance Components
- What are the key considerations for selecting PTFE material for high performance butterfly valves? Ensure Long-Term Reliability
- What factors should be considered when choosing a PTFE gasket material? Ensure a Perfect Seal for Your Application



















