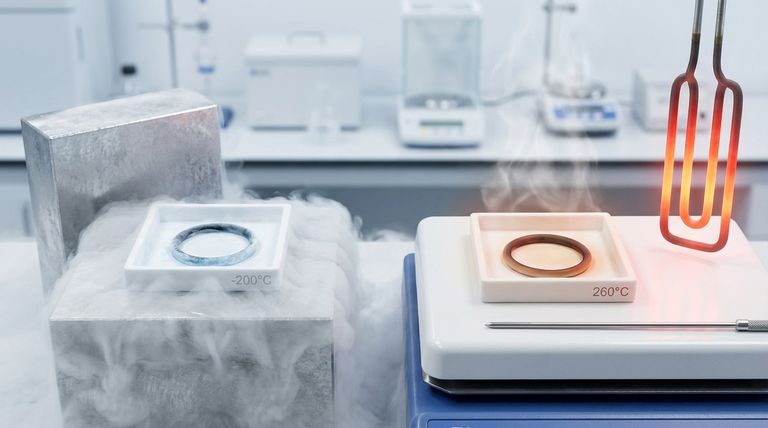
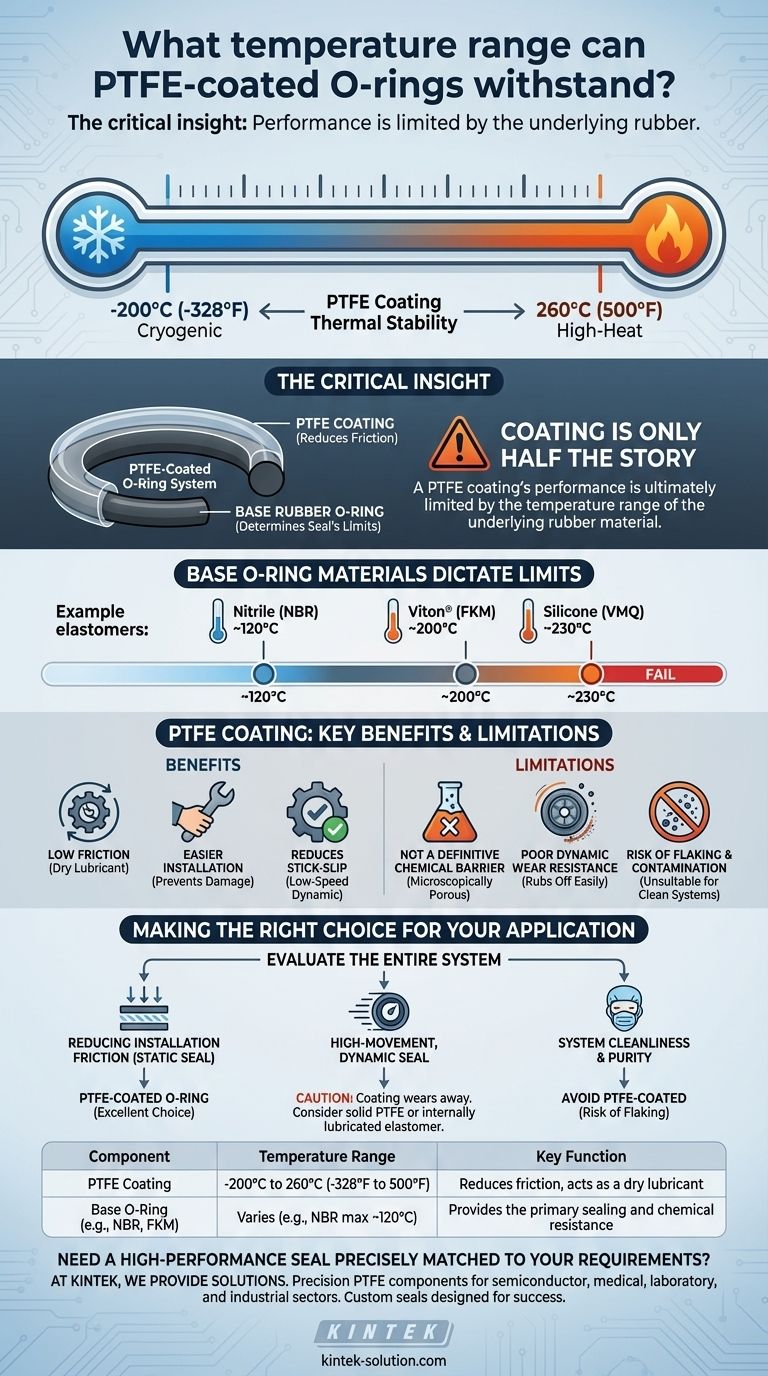
In short, a PTFE coating can technically withstand an exceptionally wide temperature range, from approximately -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). This thermal stability allows it to function in both cryogenic conditions and high-heat environments. However, this number only tells part of the story.
The critical insight is that a PTFE-coated O-ring's performance is ultimately limited by the temperature range of the underlying rubber material. The coating primarily serves to reduce friction, not to enhance the seal's fundamental temperature or chemical resistance.

The Exceptional Thermal Range of PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for its thermal stability. Understanding its capabilities is the first step in evaluating its use as a coating for O-rings.
High-Temperature Stability
The upper limit for a PTFE coating is generally accepted as 260°C (500°F). This allows it to be used in demanding high-heat processes found in the aerospace, automotive, and industrial sectors, such as in steam pipelines or engine components.
Cryogenic Performance
On the low end, PTFE maintains its integrity down to -200°C (-328°F). This makes it a viable option for cryogenic applications where many other materials would become brittle and fail.
Why the Coating is Only Half the Story
Thinking of the PTFE coating as a simple temperature upgrade for any O-ring is a common and costly mistake. The coating and the O-ring work as a system, and the weaker component dictates the system's limits.
The Role of the Base O-Ring
A PTFE coating is applied to a standard elastomer O-ring, such as Nitrile (NBR), Viton® (FKM), or Silicone (VMQ). Each of these materials has its own distinct temperature range that is almost always narrower than that of the PTFE coating itself.
For example, a standard NBR O-ring typically fails above 120°C. Applying a PTFE coating does not change this fact; the NBR will still degrade at that temperature, causing the seal to fail regardless of the coating's stability.
Coating as a Friction Reducer
The most significant benefit of a PTFE coating is its low coefficient of friction. This acts as a dry lubricant, making installation easier, preventing damage during assembly, and reducing stick-slip in low-speed dynamic applications.
Not a Definitive Chemical Barrier
The thin PTFE coating is microscopically porous. It does not provide significant additional chemical resistance. The base O-ring material must be selected to be fully compatible with the chemicals and fluids in your application.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While beneficial in the right context, PTFE-coated O-rings come with critical trade-offs that you must consider to avoid seal failure or system contamination.
Poor Dynamic Wear Resistance
In applications with frequent or high-speed movement, the PTFE coating can rub off easily. It is often best considered a one-time lubricant for installation in static seals rather than a durable surface for dynamic sealing.
Risk of Flaking and Contamination
The coating can flake off over time, especially under mechanical stress. These microscopic PTFE particles can contaminate clean systems, making them entirely unsuitable for applications in the medical, food and beverage, or semiconductor industries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct seal, you must evaluate the entire system, not just a single material property.
- If your primary focus is reducing installation friction in a static seal: A PTFE-coated O-ring is an excellent choice, as long as the base elastomer is correctly specified for your temperature and chemical environment.
- If your primary focus is a high-movement, dynamic seal: Be cautious. The coating will likely wear away, so consider a solid PTFE O-ring or an internally lubricated elastomer instead.
- If your primary focus is system cleanliness and purity: You should avoid PTFE-coated O-rings due to the inherent risk of particle flaking and contamination.
Ultimately, choosing the right seal requires matching the properties of the complete component to the demands of your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Temperature Range | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE Coating | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Reduces friction, acts as a dry lubricant |
| Base O-Ring (e.g., NBR, FKM) | Varies (e.g., NBR max ~120°C) | Provides the primary sealing and chemical resistance |
Need a high-performance seal that's precisely matched to your application's temperature, chemical, and dynamic requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom seals and O-rings, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We don't just supply parts—we provide solutions. Our expertise ensures you get a seal that delivers optimal performance, longevity, and reliability, whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and get a seal designed for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications



















