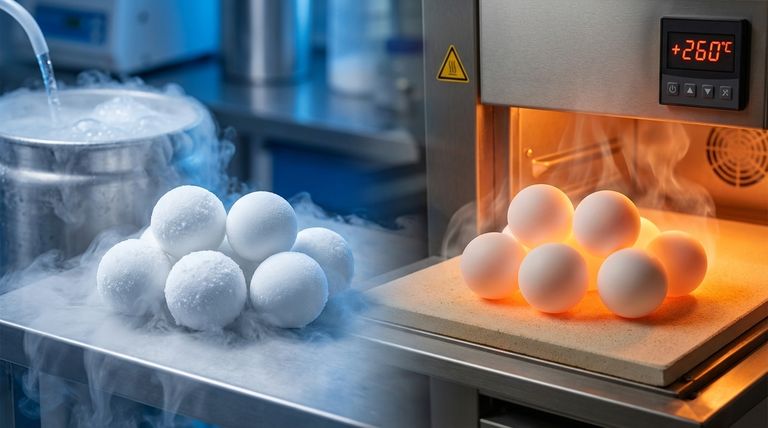
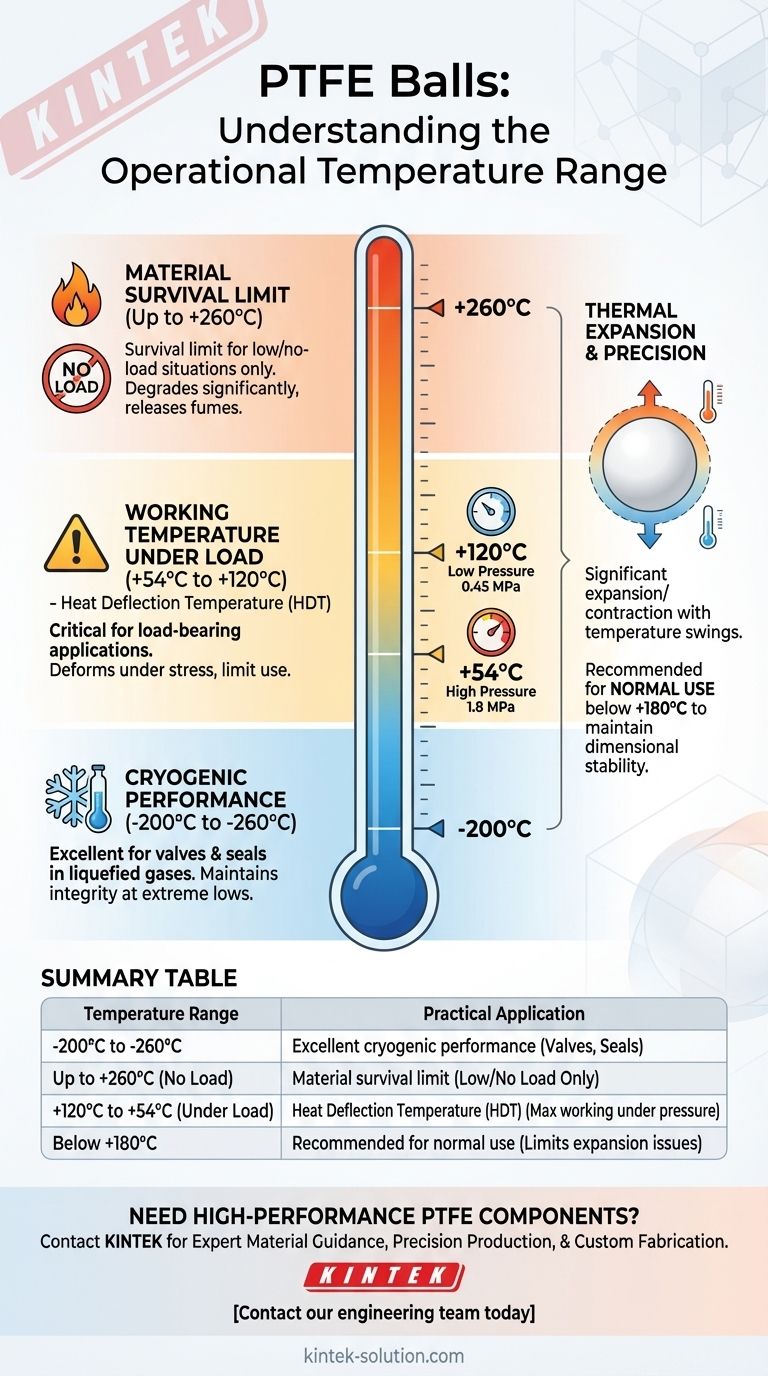
In short, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) balls can operate within a very wide temperature range. They maintain their fundamental properties from cryogenic lows of -200°C (-328°F) up to high-temperature peaks of +260°C (+500°F). This makes them suitable for an extreme variety of applications where other polymers would fail.
The key takeaway is not the wide temperature range itself, but understanding how PTFE's mechanical properties change within that range. While it can survive at +260°C, its ability to withstand pressure and maintain its shape degrades at much lower temperatures, a critical distinction for any engineering application.

The Full Operational Temperature Spectrum
PTFE is renowned for its thermal stability, but the "safe" operating temperature depends heavily on the mechanical stresses involved in your specific application.
Cryogenic Performance (The Low End)
PTFE maintains its integrity and properties even at extremely low temperatures. Its lower working limit is consistently cited around -200°C to -260°C (-328°F to -436°F).
This makes it an excellent choice for components used in cryogenic systems, such as valves and seals for liquid nitrogen or other liquefied gases.
High-Temperature Performance (The High End)
The widely accepted upper limit for PTFE is +260°C (+500°F). Above this temperature, the material begins to degrade significantly, releasing potentially hazardous fumes.
However, this number represents the material's survival limit, not necessarily its practical upper working limit in a real-world system.
Why "Working Temperature" is a More Critical Metric
The maximum temperature rating of +260°C is only relevant for applications with little to no mechanical load. For most uses, two other factors are far more important: heat deflection and thermal expansion.
The Impact of Load: Heat Deflection Temperature
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) is the temperature at which a material begins to deform under a specific load. For PTFE, this temperature is much lower than its melting point.
The data shows a heat-deflection temperature of 120°C (248°F) under a low pressure of 0.45 MPa. This drops dramatically to just 54°C (129°F) under a higher pressure of 1.8 MPa.
This means if your PTFE ball is under mechanical stress—for example, in a loaded check valve—it will start to soften and deform long before it reaches its 260°C limit.
The Problem of Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a very high coefficient of thermal expansion. It expands and contracts significantly as temperatures change.
This is why some sources recommend keeping temperature swings below 180°C for "normal use."
Large temperature fluctuations can cause a PTFE ball to change in size, potentially compromising the precision of your assembly or causing it to jam.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing PTFE for a temperature-sensitive application requires balancing its benefits against its physical limitations.
Performance vs. Pressure at High Temperatures
Using PTFE balls near their +260°C limit is only feasible in very low-load or no-load situations.
If the ball must act as a load-bearing surface or seal, you must design for its heat deflection temperature, not its maximum survival temperature.
Dimensional Stability and Tolerances
The high thermal expansion of PTFE means that its dimensional tolerance is temperature-dependent. A ball that is perfectly sized at room temperature may be too large or too small at its operating temperature.
Your design must account for this expansion to maintain proper clearance and function across the entire expected temperature range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select PTFE correctly, you must analyze your specific operational demands.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic or low-load applications: PTFE is an excellent choice, performing reliably across its entire documented range from -200°C to +260°C.
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature application under mechanical load: You must use the heat deflection temperature as your guide, limiting continuous use to temperatures well below 120°C and potentially as low as 54°C depending on the pressure.
- If your primary focus is high precision with variable temperatures: Your design must incorporate allowances for PTFE's significant thermal expansion to ensure consistent performance.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between temperature, pressure, and expansion is the key to successfully deploying PTFE components in any demanding environment.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Consideration | Practical Application |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to -260°C | Excellent cryogenic performance | Valves and seals for liquid gases |
| Up to +260°C (No Load) | Material survival limit | Low or no-load situations only |
| +120°C to +54°C (Under Load) | Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) | Maximum working temperature for loaded applications |
| Below +180°C | Recommended for normal use | Limits issues from high thermal expansion |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Environments?
Understanding the precise thermal limits of PTFE is critical for your project's success and safety. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—that meet the exacting demands of the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We help you navigate these complexities by providing:
- Expert Material Guidance: Ensure your PTFE balls and other components are specified correctly for your specific temperature, pressure, and precision requirements.
- Precision Production: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we manufacture components with the accuracy needed for reliable performance across your entire operating range.
- Custom Fabrication: We tailor solutions to overcome challenges like thermal expansion, ensuring dimensional stability and long-term reliability.
Don't let temperature limitations compromise your design. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your application and get a quote for precision PTFE components you can trust.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- In which industries are PTFE-lined piping systems commonly used? Ensure Safety and Purity in Harsh Environments
- What is the primary difference between PTFE and Graphite packing materials? A Guide to Selecting the Right Seal
- In which industries are PTFE heat press sheets commonly used? Essential for Textile Printing & Custom Apparel
- Why is PTFE used in anti-corrosion applications? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Harsh Environments
- What types of PTFE machined parts are commonly produced? Essential Components for Demanding Industries
- What automotive components are made using PTFE machining? Enhance Performance in Extreme Conditions
- Can PTFE butterfly valves be used for all types of fluids? Maximize Chemical Resistance and Purity
- What are the key technical features of PTFE tri clamp gaskets? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















