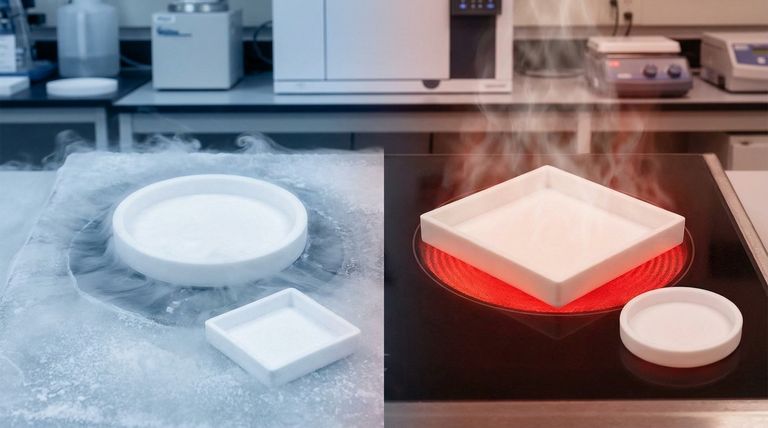
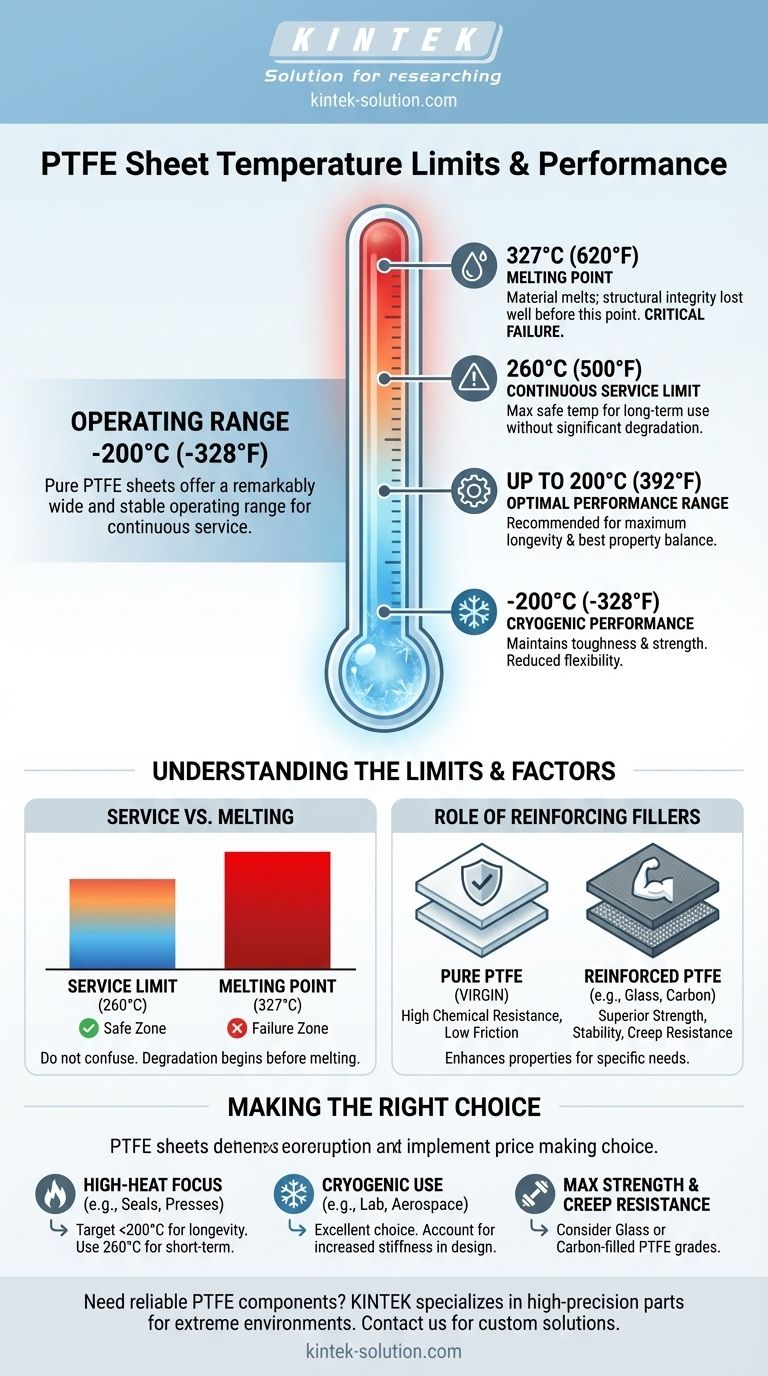
In short, pure PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) sheets have a remarkably wide and stable operating temperature range. They are designed for continuous service at temperatures from approximately -200°C (-328°F) up to +260°C (500°F). This resilience at both cryogenic and high-heat extremes makes it a uniquely versatile material.
The key to successfully using PTFE is to understand the difference between its continuous service temperature and its melting point. While it doesn't melt until 327°C (620°F), its mechanical properties begin to degrade well below that point, making 260°C the safe and practical upper limit for most applications.

Defining the Temperature Limits of PTFE
To specify PTFE correctly, you must look beyond a single number and understand the different thresholds that define its performance. Each one tells a different story about the material's capabilities.
The Continuous Service Temperature
The most important figure for any engineer or designer is the continuous service temperature. For PTFE, this is universally cited as 260°C (500°F).
This is the maximum temperature at which the material can operate for extended periods without significant degradation of its core properties. Applications like heat press sheets and industrial seals rely on this specific, reliable limit.
Exceptional Cryogenic Performance
PTFE performs just as impressively at the opposite end of the thermal spectrum. It maintains high strength, toughness, and its self-lubricating properties at temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F).
While some sources note its flexibility is best above -79°C (-110°F), it does not become brittle in the way many other polymers do, making it suitable for cryogenic components.
Melting Point vs. Service Temperature: A Critical Distinction
A common point of failure is confusing a material's service temperature with its melting point. The melting point of PTFE is approximately 327°C (620°F).
However, operating PTFE near this temperature is a critical error. Long before it melts, the material will lose its structural integrity, dimensional stability, and other mechanical properties. The 260°C service limit exists to keep you safely in the zone where the material performs as expected.
Factors That Influence Thermal Performance
The 260°C limit is not an absolute cliff but the beginning of a performance decline. True expert application requires understanding the nuances of how PTFE behaves within its range.
The Concept of "Optimal Performance"
While PTFE can withstand 260°C, its best balance of properties is often found at lower temperatures.
For demanding applications, many manufacturers recommend a continuous operating temperature closer to 200°C (392°F). This more conservative range ensures maximum longevity and retention of its non-stick and low-friction characteristics.
The Role of Reinforcing Fillers
Pure, or "virgin," PTFE can be enhanced by adding fillers. Materials like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze are mixed into the PTFE matrix to create a composite.
Glass-filled PTFE, for example, exhibits higher compressive strength and greater thermal stability than pure PTFE. These reinforced grades can handle higher loads at elevated temperatures where pure PTFE might begin to creep or deform.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting PTFE is not just about its strengths but also about being aware of its limitations, especially at thermal extremes.
Degradation at High Temperatures
Operating PTFE continuously near its 260°C limit will accelerate its aging process. Over time, it can become less flexible and its mechanical strength will decrease. Performance is not a simple on/off switch; it is a gradual decline.
Stiffness at Cryogenic Temperatures
While PTFE remains remarkably tough at cryogenic temperatures, its flexibility is reduced. For applications requiring a seal to remain pliable at -200°C, you must account for this increased stiffness in your design.
Pure PTFE vs. Reinforced Grades
The primary trade-off involves choosing between pure PTFE and a filled grade. Pure PTFE offers the highest chemical resistance and the lowest coefficient of friction. However, reinforced grades provide superior mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to wear, especially at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material decision should be guided by the primary goal of your specific design.
- If your primary focus is high-heat applications (e.g., heat presses, industrial seals): Target a working temperature below 200°C for longevity, using the 260°C limit only for short-term exposure.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic use (e.g., lab equipment, aerospace components): PTFE is an excellent choice, but account for its reduced flexibility at the lowest extremes in your mechanical design.
- If you need maximum mechanical strength and creep resistance at high temperatures: Consider a glass-filled or carbon-filled grade of PTFE, as it offers superior stability under load.
By understanding these operational nuances, you can confidently specify PTFE for its unmatched thermal stability in your project.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Point | Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Service (Upper Limit) | 260°C (500°F) | Maximum safe temperature for long-term use without significant degradation. |
| Cryogenic Performance (Lower Limit) | -200°C (-328°F) | Maintains toughness and strength at extreme low temperatures. |
| Melting Point | 327°C (620°F) | The material melts, but structural integrity is lost well before this point. |
| Optimal Performance Range | Up to 200°C (392°F) | Recommended range for maximum longevity and best balance of properties. |
Need a PTFE component that reliably performs in extreme temperatures?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength.
Whether you require a standard part or a custom-fabricated solution from prototype to high-volume production, our expertise ensures your application performs safely and efficiently from cryogenic conditions to high-heat environments.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries



















