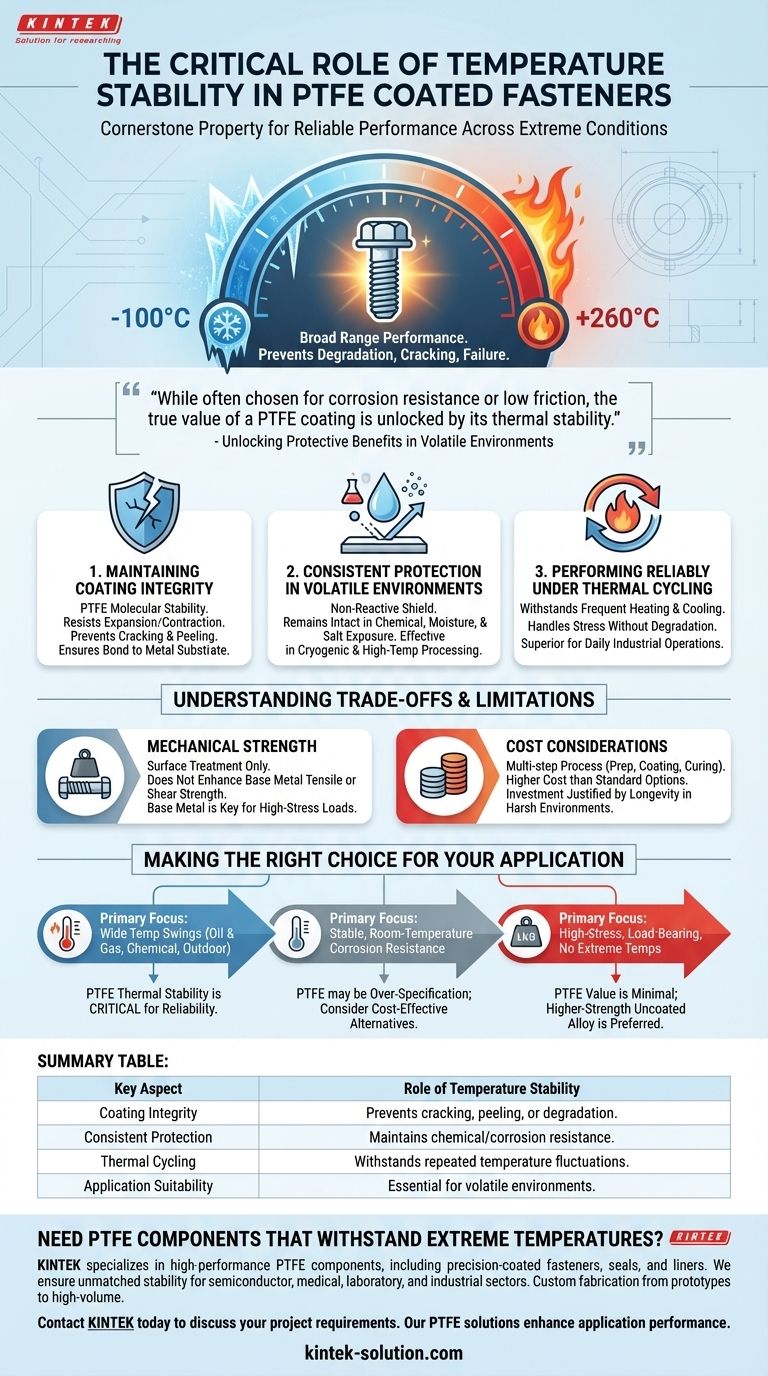
In short, temperature stability is a cornerstone property that allows PTFE coated fasteners to perform reliably across an extremely broad range of temperatures. This stability ensures the coating does not degrade, crack, or fail when exposed to high heat, deep cold, or rapid thermal cycling. It is the quality that preserves all of PTFE's other protective benefits in demanding real-world conditions.
While often chosen for its corrosion resistance or low friction, the true value of a PTFE coating is unlocked by its thermal stability. This property ensures the fastener's other protective features remain intact and functional, even in the most volatile operating environments.

Why Thermal Stability is a Critical Performance Factor
A fastener's primary role is to maintain structural integrity. A coating's primary role is to protect that fastener. If the coating fails due to temperature, the fastener becomes vulnerable.
Maintaining Coating Integrity
Extreme temperature changes cause materials to expand and contract. Lesser coatings can become brittle in the cold or soft in the heat, leading to cracking and peeling.
PTFE's molecular structure is inherently stable, allowing it to resist these changes. This ensures the protective layer remains firmly bonded to the fastener's metal substrate without flaking off.
Enabling Consistent Protection in Volatile Environments
A fastener might be exposed to corrosive chemicals, moisture, and salts. The PTFE coating acts as a non-reactive shield against these agents.
However, this chemical and corrosion resistance is only effective if the coating itself is physically present and intact. Thermal stability guarantees the shield stays in place, whether the application is in a sub-zero cryogenics facility or a high-temperature processing plant.
Performing Reliably Under Thermal Cycling
Many industrial applications involve frequent temperature fluctuations—machinery heating up during operation and cooling down when idle, for example.
This constant cycling places immense stress on a coating. PTFE's ability to handle this cycle without degradation is what makes it a superior choice for equipment and infrastructure that must perform reliably day after day.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its thermal performance is exceptional, a PTFE coating is a specialized solution with specific limitations. It is not a universal upgrade for every application.
Mechanical Strength
The PTFE coating is a surface treatment; it does not enhance the underlying fastener's tensile or shear strength. In high-stress or extreme load-bearing applications, the mechanical properties of the base metal are the primary consideration.
Cost Considerations
The multi-step manufacturing process—which involves surface preparation, precise coating application, and high-temperature curing—makes PTFE coated fasteners more expensive than standard galvanized or uncoated alternatives. This investment is justified by performance and longevity in harsh environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if the thermal stability of PTFE coated fasteners is necessary for your project, consider your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is consistent performance in environments with wide temperature swings (e.g., oil & gas, chemical processing, outdoor infrastructure): The thermal stability of PTFE is a critical feature that ensures long-term reliability and prevents premature failure.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance in a stable, room-temperature environment: While beneficial, the thermal stability of PTFE may be an over-specification, and other coating options could be more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is high-stress, load-bearing applications without extreme temperatures or corrosive elements: The value of the PTFE coating is minimal, and a higher-strength, uncoated alloy fastener is likely the more appropriate choice.
Ultimately, understanding the role of temperature stability allows you to select a fastener that provides reliable protection, not just under ideal conditions, but within the harsh realities of its intended environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Role of Temperature Stability |
|---|---|
| Coating Integrity | Prevents cracking, peeling, or degradation from thermal expansion/contraction. |
| Consistent Protection | Maintains chemical/corrosion resistance by keeping the PTFE shield intact. |
| Thermal Cycling | Withstands repeated temperature fluctuations without performance loss. |
| Application Suitability | Essential for volatile environments (e.g., chemical processing, oil & gas). |
Need PTFE Components That Withstand Extreme Temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including precision-coated fasteners, seals, and liners. Our expertise ensures your parts deliver unmatched thermal stability and reliability, even in the most demanding conditions of the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision to meet your exact specifications.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our PTFE solutions can enhance your application's performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries



















