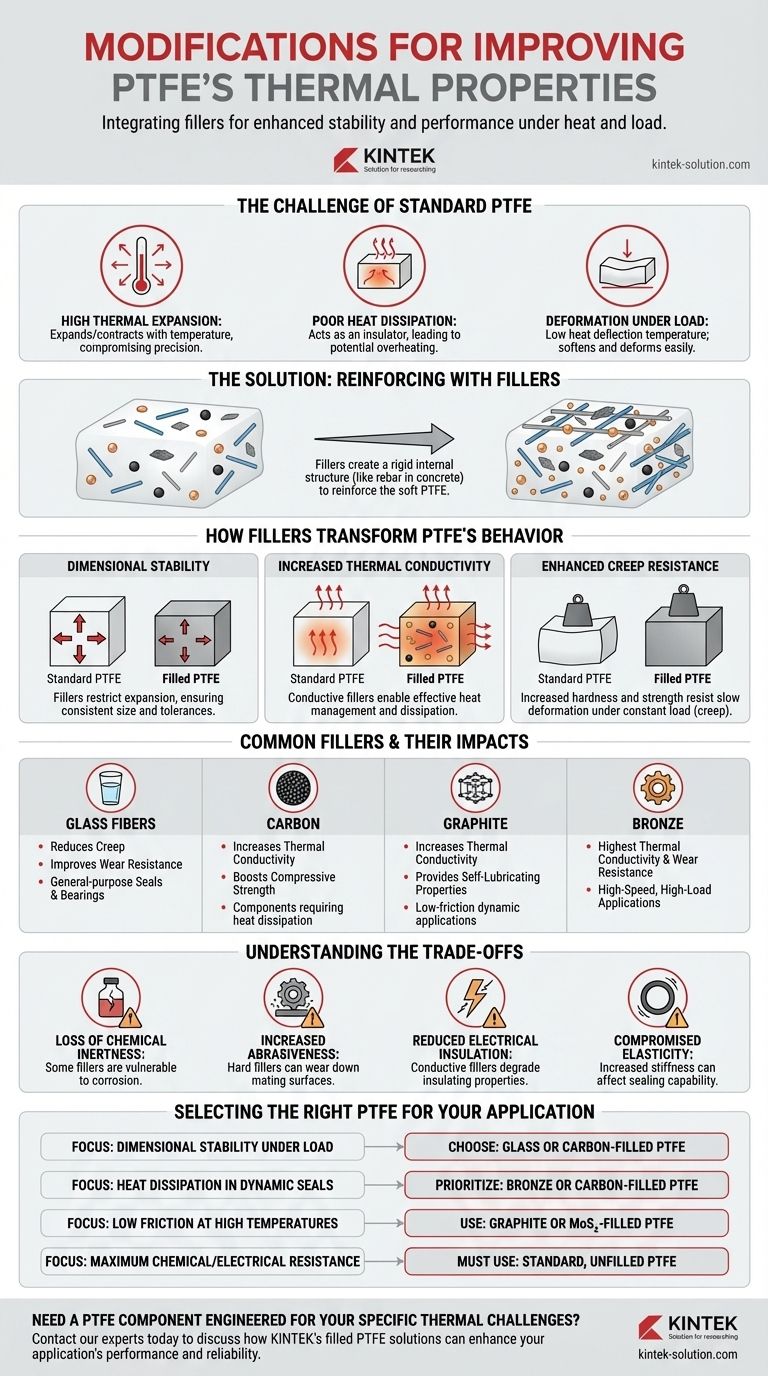
To improve its thermal properties, standard Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is modified by adding fillers. These reinforcing agents, such as glass fibers, carbon, graphite, or bronze, are blended into the PTFE matrix to enhance its performance, particularly its dimensional stability and resistance to deformation under heat and load.
While standard PTFE boasts an exceptionally wide and stable operating temperature range, its practical application is often limited by a high rate of thermal expansion and a tendency to deform under load. Fillers are introduced not to increase its temperature ceiling, but to control these behaviors and make the material more mechanically robust within its existing thermal window.

The Inherent Thermal Profile of Standard PTFE
To understand why modifications are necessary, we must first appreciate the distinct thermal strengths and weaknesses of pure, unfilled PTFE.
A Remarkable Operating Temperature Range
Standard PTFE is one of the most thermally stable polymers available. It maintains its properties and structural integrity across a vast temperature spectrum, typically from -260°C (-436°F) up to +260°C (+500°F).
The Hidden Weakness: Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a very high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes, which can compromise tight tolerances in precision components like seals and bearings.
Poor Heat Dissipation
As a natural thermal insulator, pure PTFE has low thermal conductivity (around 0.25 W/m·K). It does not dissipate heat effectively, which can lead to heat buildup in high-speed or high-friction applications, potentially causing premature failure.
Deformation Under Load
The most critical limitation is PTFE's low heat deflection temperature, which can be as low as 54°C (129°F) under significant pressure. This means the material will begin to soften and deform under load at temperatures far below its maximum service limit.
How Fillers Fundamentally Change PTFE's Behavior
Adding fillers is analogous to adding rebar to concrete. The filler creates a rigid internal structure that reinforces the softer PTFE polymer, directly addressing its inherent thermal weaknesses.
Improving Dimensional Stability
Fillers have a much lower thermal expansion rate than PTFE. By integrating them into the polymer, they physically restrict the material's ability to expand, dramatically improving its dimensional stability across temperature changes.
Increasing Thermal Conductivity
Fillers like carbon, graphite, and especially bronze are thermally conductive. They create pathways for heat to escape, transforming the PTFE composite from an insulator into a material that can effectively manage and dissipate heat.
Enhancing Creep Resistance
Fillers significantly increase the hardness and compressive strength of PTFE. This reinforcement drastically improves its resistance to creep—the tendency to slowly deform under a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures.
Common Fillers and Their Specific Impacts
Different fillers are chosen to target specific performance improvements.
Glass Fibers
This is a common, general-purpose filler that significantly reduces creep and improves wear resistance. It provides a good balance of enhanced mechanical and thermal properties.
Carbon
Carbon increases compressive strength and hardness while also boosting thermal conductivity. It provides excellent wear resistance, particularly in applications involving water.
Graphite
Like carbon, graphite improves thermal conductivity. Its primary benefit, however, is providing self-lubricating properties, which lowers the coefficient of friction and reduces heat generation in dynamic applications.
Bronze
Bronze offers the highest thermal conductivity and wear resistance of all common fillers. It is ideal for high-speed, high-load applications where heat dissipation is the top priority.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Modifying PTFE is not without its compromises. Introducing fillers fundamentally alters the material's original properties.
Loss of Chemical Inertness
Pure PTFE is famously inert to nearly all chemicals. However, fillers like bronze can be attacked by corrosive agents, reducing the composite's overall chemical resistance.
Increased Abrasiveness
Hard fillers, particularly glass fibers, can be abrasive to softer mating surfaces. This must be considered when designing components like seals that run against a metal shaft.
Reduced Electrical Insulation
While pure PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator, adding conductive fillers like carbon or bronze will significantly degrade this property.
Compromised Elasticity
Fillers make PTFE more rigid and less flexible. For applications like O-rings that rely on elasticity to form a proper seal, this increased stiffness can be a significant drawback.
Selecting the Right PTFE for Your Application
The choice of filled or unfilled PTFE depends entirely on the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability under load: Choose a glass-filled or carbon-filled PTFE to minimize thermal expansion and creep.
- If your primary focus is heat dissipation in dynamic seals: Prioritize bronze or carbon-filled PTFE for their superior thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is low friction at high temperatures: Graphite or Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂) filled PTFE will provide the best self-lubricating properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical or electrical resistance: You must use standard, unfilled PTFE and design your system to accommodate its thermal limitations.
Understanding these modifications allows you to leverage PTFE not just for its temperature resistance, but for its engineered performance under specific thermal and mechanical challenges.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Thermal/Mechanical Improvements | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fibers | Reduces creep, improves wear resistance | General-purpose seals, bearings |
| Carbon/Graphite | Increases thermal conductivity, wear resistance | Components requiring heat dissipation |
| Bronze | Highest thermal conductivity & wear resistance | High-speed, high-load applications |
Need a PTFE Component Engineered for Your Specific Thermal Challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, our precision production and custom fabrication expertise ensure your parts meet exact thermal and mechanical requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our filled PTFE solutions can enhance your application's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE rotary shaft lip seals suitable for aerospace applications? Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What are the properties of PTFE encapsulated O-rings? Superior Sealing for Harsh Environments
- Why did PTFE seals fall out of favor in the 1950s and 1960s? A Lesson in Material Misunderstanding
- What makes PTFE O-Rings superior to those made of other materials? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are some specific applications of Teflon lip seals in industrial machinery? Engineered for Extreme Conditions
- How does the chemical resistance of PTFE bushes benefit their applications? Ensure Longevity in Corrosive Environments
- What are the advantages of PTFE O-rings compared to elastomeric O-rings? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the common uses of Teflon in mechanical engineering? Solve Friction, Sealing & Corrosion Challenges



















