In hydraulic and pneumatic systems, the most common sealing materials are elastomers and polymers selected to match specific operational demands. While materials like Nitrile and Polyurethane are workhorses for standard applications, advanced fluoropolymers such as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are specified for severe sealing conditions involving extreme temperatures or aggressive chemicals.
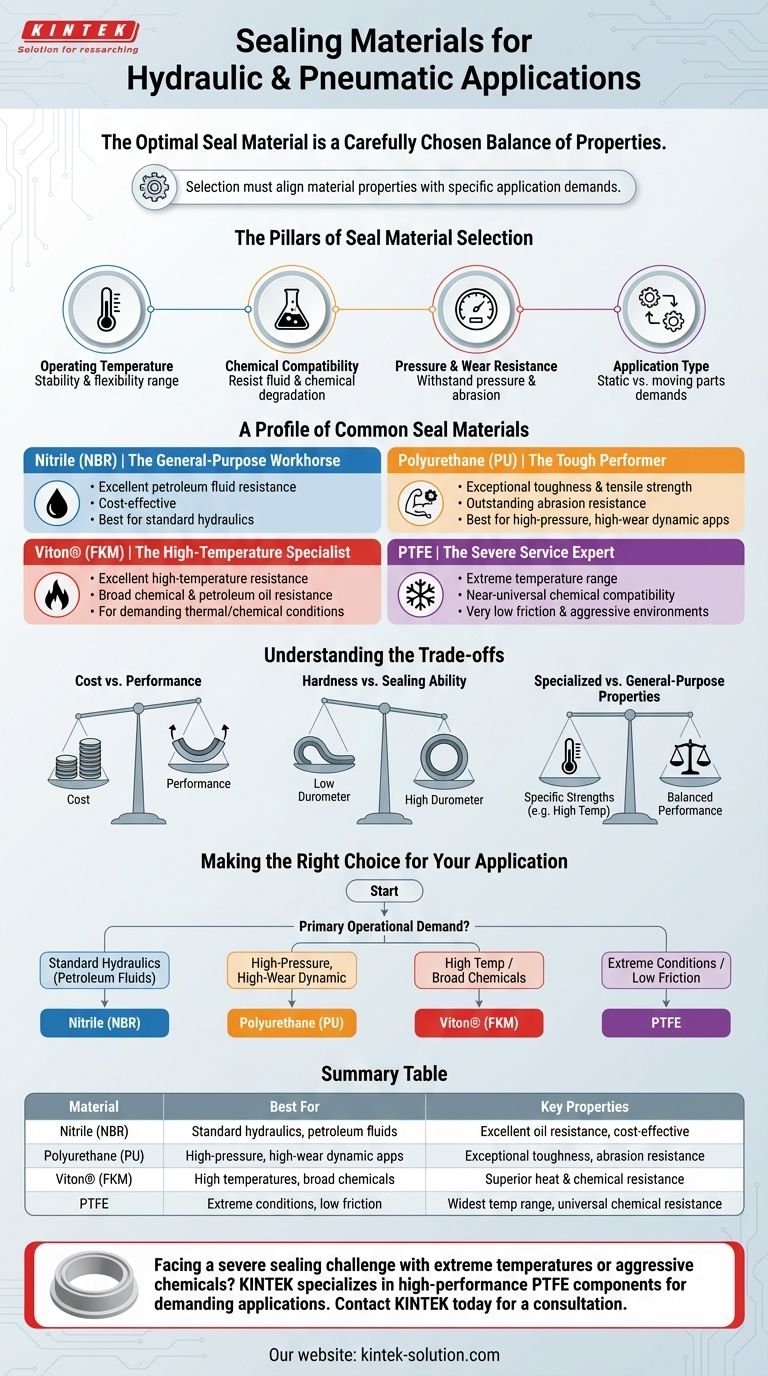
The optimal seal material is not a single "best" option, but rather a carefully chosen balance. Your selection must align the material's specific properties—such as temperature range, chemical resistance, and wear characteristics—with the precise demands of your application.
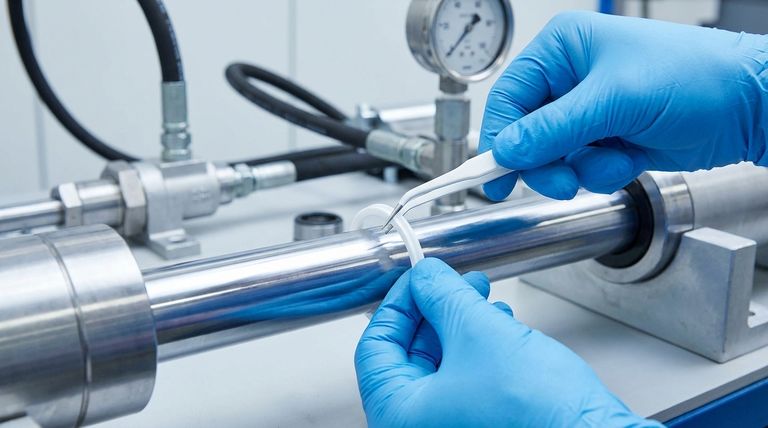

The Pillars of Seal Material Selection
Choosing the right material requires evaluating the environment it will operate in. Four key factors dominate this decision-making process, ensuring the seal maintains its integrity and prevents leaks or contamination.
Operating Temperature
A material's ability to remain stable and flexible across a system's temperature range is critical. Materials can become brittle at low temperatures or degrade and swell at high temperatures, leading to seal failure.
Chemical Compatibility
The seal must resist degradation from the hydraulic fluid, gas, or any external chemicals it might encounter. Incompatibility can cause the material to soften, harden, or swell, compromising its sealing ability.
Pressure and Wear Resistance
The material must be strong enough to withstand system pressure without extruding into gaps. For dynamic applications with moving parts, high abrasion and wear resistance are essential for a long service life.
Application Type (Static vs. Dynamic)
The demands on a seal differ greatly between static applications (sealing non-moving parts) and dynamic ones (sealing moving parts like pistons or rods). Dynamic seals require materials with lower friction and higher durability.
A Profile of Common Seal Materials
While hundreds of material variations exist, a few core types cover the vast majority of hydraulic and pneumatic applications.
Nitrile (NBR): The General-Purpose Workhorse
Nitrile, also known as Buna-N, is the most widely used seal material due to its excellent resistance to petroleum-based hydraulic fluids and its low cost. It offers a great balance of properties for standard industrial applications.
Polyurethane (PU): The Tough Performer
Polyurethane is known for its exceptional toughness, high tensile strength, and outstanding abrasion resistance. This makes it a top choice for high-pressure, high-wear dynamic hydraulic applications.
Viton® (FKM): The High-Temperature Specialist
FKM, a fluoroelastomer commonly known by the brand name Viton®, provides excellent resistance to high temperatures, petroleum oils, and a wide range of chemicals. It is used in demanding applications where Nitrile would quickly fail.
PTFE: The Severe Service Expert
As a fluoropolymer, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is specified for the most severe sealing conditions. Its key advantages are an extremely wide temperature range, near-universal chemical compatibility, and a very low coefficient of friction, making it ideal for aggressive media or low-friction dynamic seals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every material choice involves a compromise. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for selecting a reliable and cost-effective solution.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between a material's performance capabilities and its cost. NBR is highly economical for standard use, while high-performance materials like FKM and PTFE come at a significant price premium justified by their ability to handle extreme conditions.
Hardness vs. Sealing Ability
Softer materials (lower durometer) conform better to surfaces and can provide a better seal in low-pressure applications. However, they are more prone to being forced out, or "extruded," under high pressure. Harder materials resist extrusion but may require finer surface finishes to seal effectively.
Specialized vs. General-Purpose Properties
A material that excels in one area, such as high-temperature resistance, may have poor performance in another, like low-temperature flexibility. There is no single material that excels in all categories, reinforcing the need to match the material to the specific application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your system's primary operational demand as the starting point for your material selection.
- If your primary focus is standard hydraulics with petroleum-based fluids: Nitrile (NBR) offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure, high-wear dynamic applications: Polyurethane (PU) provides the necessary toughness and abrasion resistance.
- If your primary focus is high temperatures or broad chemical exposure: Viton® (FKM) is the reliable choice for resisting thermal and chemical degradation.
- If your primary focus is extreme conditions or very low friction: PTFE is the premier material for the most severe service environments.
Ultimately, a well-chosen seal is the foundation of a reliable and efficient fluid power system.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrile (NBR) | Standard hydraulics, petroleum fluids | Excellent oil resistance, cost-effective |
| Polyurethane (PU) | High-pressure, high-wear dynamic apps | Exceptional toughness, abrasion resistance |
| Viton® (FKM) | High temperatures, broad chemicals | Superior heat & chemical resistance |
| PTFE | Extreme conditions, low friction | Widest temp range, universal chemical resistance |
Facing a severe sealing challenge with extreme temperatures or aggressive chemicals?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the most demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication capabilities, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensure you get a sealing solution engineered for reliability and longevity.
Let our experts help you select or custom-design the perfect seal for your system. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between PTFE and Teflon for gasket design? Select the Right Fluoropolymer for Your Sealing Needs
- What is the primary filler used in PTFE-based materials and why? A Guide to Choosing the Right Reinforcement
- How do composite bellows compare to PTFE bellows? Choose the Right Bellow for Your Application
- How does temperature tolerance benefit PTFE reducing flanges? Ensure Reliable Performance from Cryogenic to High Heat
- What is the cost-benefit analysis of using Teflon gland packing? Maximize ROI with Low-Cost Seals
- What makes PTFE rotary shaft seals suitable for low friction or dry running applications? Unlock High-Speed, Dry-Running Performance
- In which industries are PTFE mill-type envelope gaskets applied? Ensure Leak-Free Sealing in Demanding Environments
- What are the steps to create a custom Teflon sheet for a heat press? Boost Your Production Efficiency & Quality



















