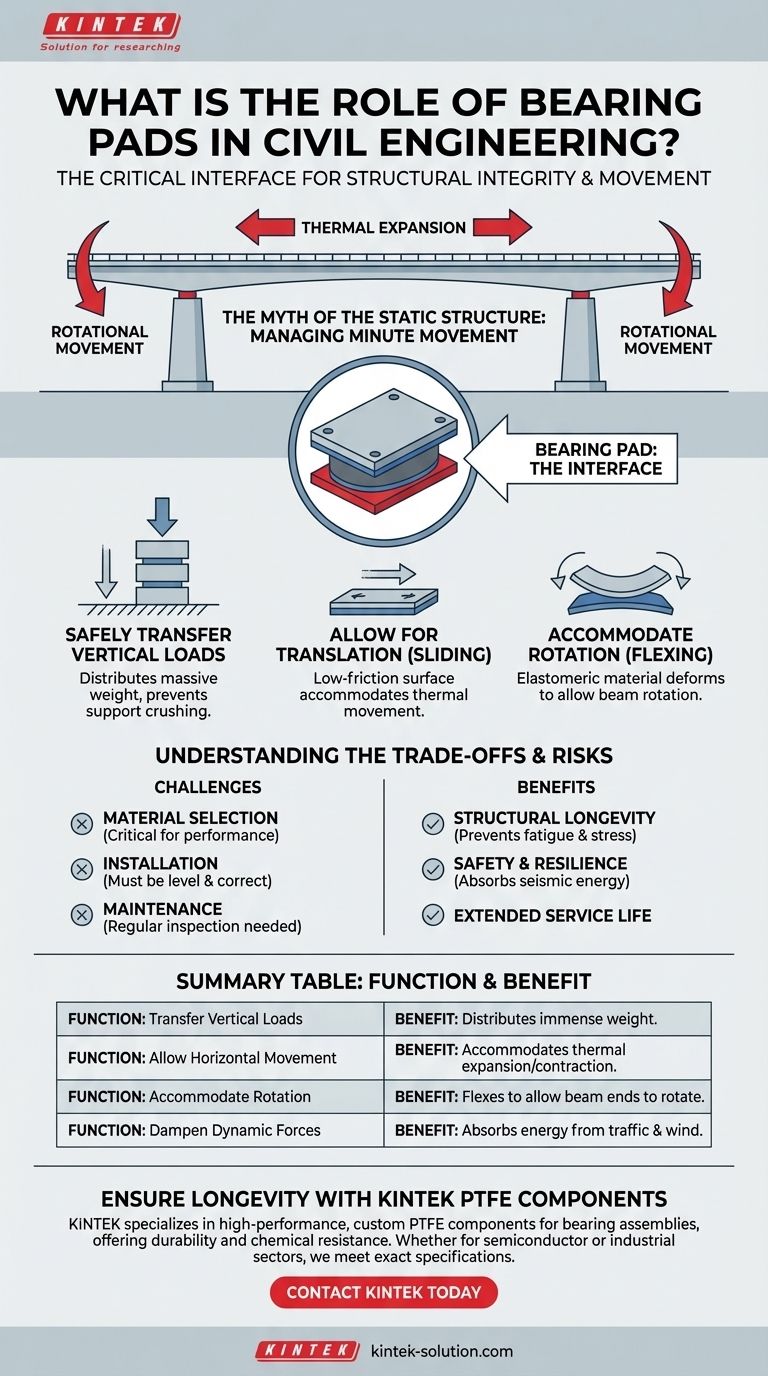
In essence, a bearing pad acts as a critical interface in a structure, designed to safely transfer immense vertical loads from a beam or girder to its supporting element while simultaneously allowing for small, controlled movements. These pads prevent the buildup of destructive stresses that would otherwise damage the structure.
The core function of a bearing pad is to solve a fundamental paradox in structural engineering: allowing massive, seemingly rigid structures to safely move, flex, and shift in response to environmental forces without compromising their strength or integrity.

The Myth of the Static Structure
To understand the role of bearing pads, we must first accept that large civil structures like bridges and buildings are not static. They are in a constant state of minute movement, and these movements must be managed.
Thermal Expansion and Contraction
Materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. Over the span of a long bridge girder, a change in ambient temperature can cause its length to change by several inches.
Without a bearing pad, this expansion and contraction would be restrained, inducing enormous internal stresses that could crack concrete or buckle steel.
Rotational Movements
When a horizontal beam is placed under a load (like traffic on a bridge), it deflects or sags slightly in the middle. This sag causes the ends of the beam to rotate by a very small angle.
A rigid connection would resist this rotation, creating high stress concentrations at the support point. The bearing pad flexes to accommodate this rotation.
Other Dynamic Forces
Structures are also subjected to movements from live loads (traffic), wind, shrinkage of concrete over time, and seismic activity. A bearing pad helps absorb and dampen the energy from these forces.
How Bearing Pads Accomplish Their Task
A bearing pad is an engineering solution that performs two seemingly contradictory functions simultaneously: providing firm support while allowing for flexibility.
Safely Transferring Vertical Loads
The primary job of the pad is to bear the massive weight of the superstructure (the bridge deck or building floor). It distributes this concentrated load over a wider area on the substructure (the pier or column) to prevent crushing the concrete.
Allowing for Translation (Sliding)
To handle thermal expansion and contraction, the bearing pad provides a surface with low friction. This allows the beam to slide horizontally back and forth without building up stress. Some pads use layers of elastomer and steel, while others use materials like PTFE (Teflon) for this purpose.
Accommodating Rotation (Flexing)
The pad is typically made of an elastomeric material (a type of rubber) that can deform and compress. When a beam end rotates, one side of the pad compresses slightly more than the other, allowing the structure to flex without damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While essential, bearing pads are not a "fit-and-forget" solution. Their selection and installation are critical to the health of the entire structure.
Material Selection is Critical
The specific type of bearing pad—from plain elastomeric pads to complex mechanical pot bearings—must be carefully chosen based on the expected loads and movements. Using the wrong type of pad can lead to premature failure of the pad or damage to the structure it is meant to protect.
Installation and Maintenance Challenges
Improper installation, such as placing the pad on an uneven surface, can create unintended stress points and prevent it from functioning correctly. Furthermore, elastomeric pads can degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and environmental contaminants, requiring regular inspection and eventual replacement.
How This Applies to Structural Design
The choice and implementation of a bearing pad directly relate to the primary goals of the structural design.
- If your primary focus is structural longevity: Bearing pads are essential for preventing the fatigue and stress concentration that lead to cracks and deterioration, significantly extending the service life of the structure.
- If your primary focus is safety and resilience: In seismically active regions, specialized bearing pads act as isolators, absorbing earthquake energy and preventing catastrophic failure of bridge piers and building columns.
Ultimately, this small, often-unseen component is one of the most important pieces in ensuring a large structure can endure the dynamic forces of its environment.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Transfer Vertical Loads | Distributes immense weight to prevent crushing of supports. |
| Allow Horizontal Movement | Accommodates thermal expansion/contraction to prevent stress buildup. |
| Accommodate Rotation | Flexes to allow beam ends to rotate under load without damage. |
| Dampen Dynamic Forces | Absorbs energy from traffic, wind, and seismic activity. |
Ensure the Longevity and Safety of Your Structure with Precision-Engineered PTFE Components
The correct bearing pad material is critical for structural performance. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including low-friction sliding surfaces for bearing assemblies—that offer exceptional durability and chemical resistance.
Whether you're designing for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise in custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders ensures you get a component that meets exact specifications.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance the resilience and service life of your civil engineering projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems



















