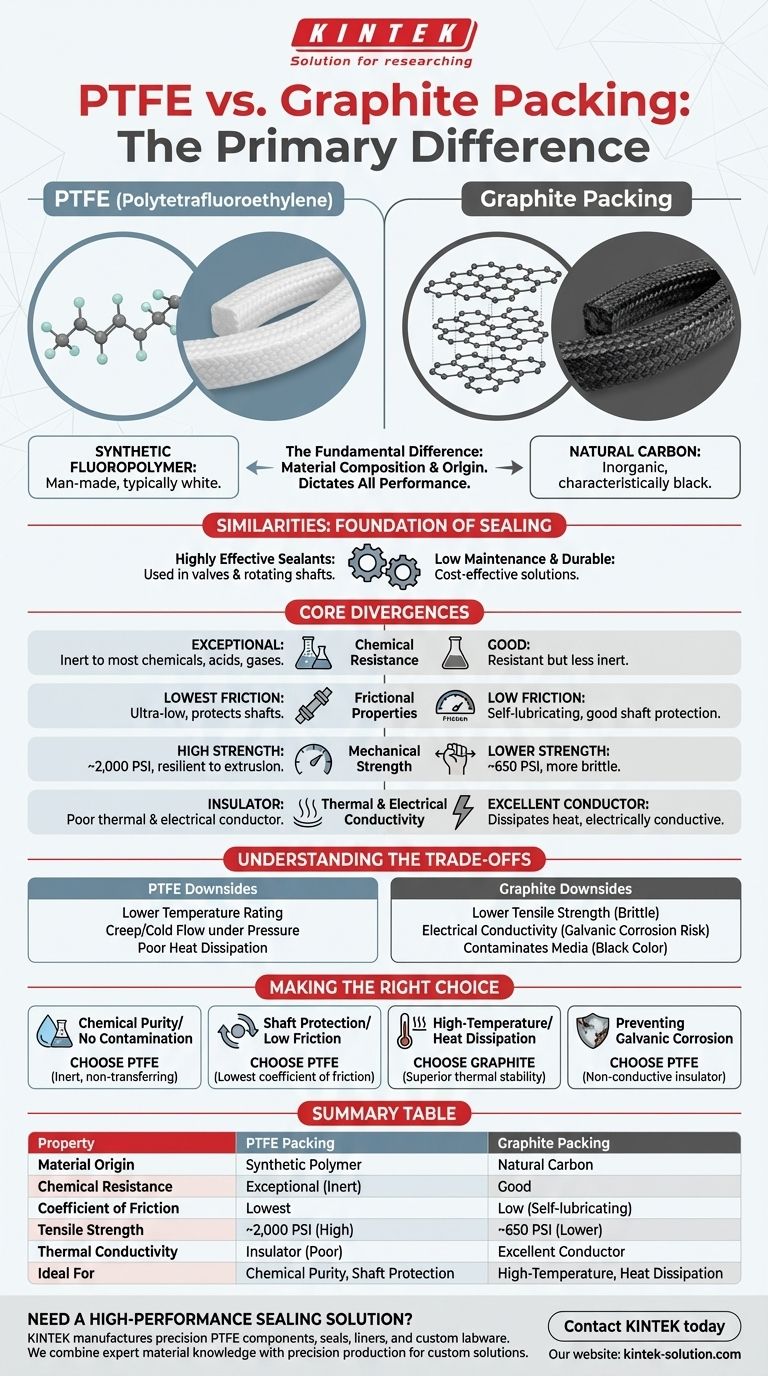
The fundamental difference between PTFE and graphite packing is their material composition and origin. Graphite is a naturally occurring, stable form of pure carbon, whereas PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a synthetic fluoropolymer. This core distinction dictates every other performance characteristic, from chemical resistance and friction to mechanical strength and thermal properties.
The choice between PTFE and graphite packing is not a matter of which is "better," but which is precisely suited for your specific operational environment. Your decision must be driven by the application's demands regarding chemical compatibility, temperature, and potential for shaft wear.

Similarities: The Foundation of Sealing
Before exploring their differences, it's important to recognize why both materials are staples in sealing applications. They share a strong foundational set of properties.
### Common Advantages
Both PTFE and graphite packing are highly effective sealants, often manufactured in a braided style for use in valves and rotating shafts.
They are known for their low maintenance requirements, excellent durability, and long shelf life, making them cost-effective solutions for industrial sealing.
Core Differences: Where They Diverge
The practical differences between these two materials stem directly from graphite being a form of carbon and PTFE being a synthetic polymer.
### Material Composition and Appearance
Graphite packing is derived from a natural, inorganic form of carbon. It is characteristically black.
PTFE is a man-made polymer. It is typically white, which is a critical visual distinction that also signifies it will not transfer color or contaminate media.
### Chemical Resistance
PTFE is exceptionally resistant to nearly all chemicals, acids, corrosive substances, and gases. Its only significant vulnerability is to molten alkali metals.
Graphite offers good chemical resistance but is not as universally inert as PTFE, making PTFE the superior choice for extremely aggressive chemical services.
### Frictional Properties
PTFE possesses the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid material. This ultra-low friction is ideal for protecting shafts from wear and reducing drag in rotating equipment.
Graphite also has a low coefficient of friction and is self-lubricating. This property helps it seal effectively without damaging equipment, though PTFE remains the leader in low-friction performance.
### Mechanical Strength
There is a significant difference in mechanical integrity. PTFE packing demonstrates a much higher tensile strength, rated around 2,000 PSI.
Graphite packing is more brittle and has a lower tensile strength, typically around 650 PSI. This makes PTFE more resilient to extrusion under high pressure.
### Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Graphite is an excellent thermal conductor. This allows it to dissipate heat away from the shaft or valve stem, which is a major advantage in high-temperature or high-speed applications. It is also electrically conductive.
PTFE is a thermal and electrical insulator. It does not conduct heat away, which can be a limitation in certain high-speed applications. Its non-conductive nature, however, is an advantage in preventing galvanic corrosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither material is a perfect solution for all scenarios. Understanding their inherent limitations is key to avoiding misapplication and potential equipment failure.
### The Downsides of PTFE
PTFE's primary limitation is its lower temperature rating compared to graphite. It can also exhibit "creep" or cold flow under sustained pressure. Because it is a thermal insulator, it does not dissipate heat well, which can be problematic for high-speed shafts.
### The Downsides of Graphite
Graphite's lower tensile strength makes it more susceptible to breaking or extruding under pressure. Its electrical conductivity can cause galvanic corrosion with certain valve stem materials. Furthermore, its black color can leach and contaminate the process media, making it unsuitable for food-grade, pharmaceutical, or other high-purity applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection should be a direct response to the specific demands of the equipment and process.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity or media non-contamination: Choose PTFE for its inertness and because it will not transfer color.
- If your primary focus is protecting shafts from wear and minimizing friction: Choose PTFE for its exceptionally low coefficient of friction.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature service or heat dissipation: Choose Graphite for its superior thermal stability and conductivity.
- If your primary focus is preventing galvanic corrosion: Choose PTFE for its non-conductive, insulating properties.
Understanding these core material properties empowers you to select the precise packing material that ensures operational reliability and longevity.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Packing | Graphite Packing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Synthetic Polymer | Natural Carbon |
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional (Inert) | Good |
| Coefficient of Friction | Lowest | Low (Self-lubricating) |
| Tensile Strength | ~2,000 PSI (High) | ~650 PSI (Lower) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Insulator (Poor) | Excellent Conductor |
| Ideal For | Chemical Purity, Shaft Protection | High-Temperature, Heat Dissipation |
Need a High-Performance Sealing Solution?
Selecting the right packing material is critical for the reliability and longevity of your equipment. The choice between PTFE and Graphite depends entirely on your specific operational demands for chemical compatibility, temperature, friction, and pressure.
KINTEK manufactures precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and specialized industrial sectors. We combine expert material knowledge with precision production to deliver custom solutions, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring optimal performance for your application.
Let our experts help you choose the perfect seal. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements and get a solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the installation advantages of PTFE lined butterfly valves? Simplify Setup & Save on Costs
- How is PTFE applied in electronics and semiconductor manufacturing? Ensure Purity and Performance
- What are the aerospace and defense applications of PTFE? Essential for Extreme Reliability
- Why is PTFE considered a benchmark for low-friction materials? Unmatched Performance for Smooth Motion
- How can PTFE be processed into parts? A Guide to Molding and Machining for High-Performance Components
- Why are PTFE gaskets used in the petrochemical industry? For Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How does the PTFE sliding pad function smoothly? An Inside Look at Low-Friction Engineering
- Why are PTFE heat press sheets essential for custom printing? Achieve Flawless, Professional Results



















