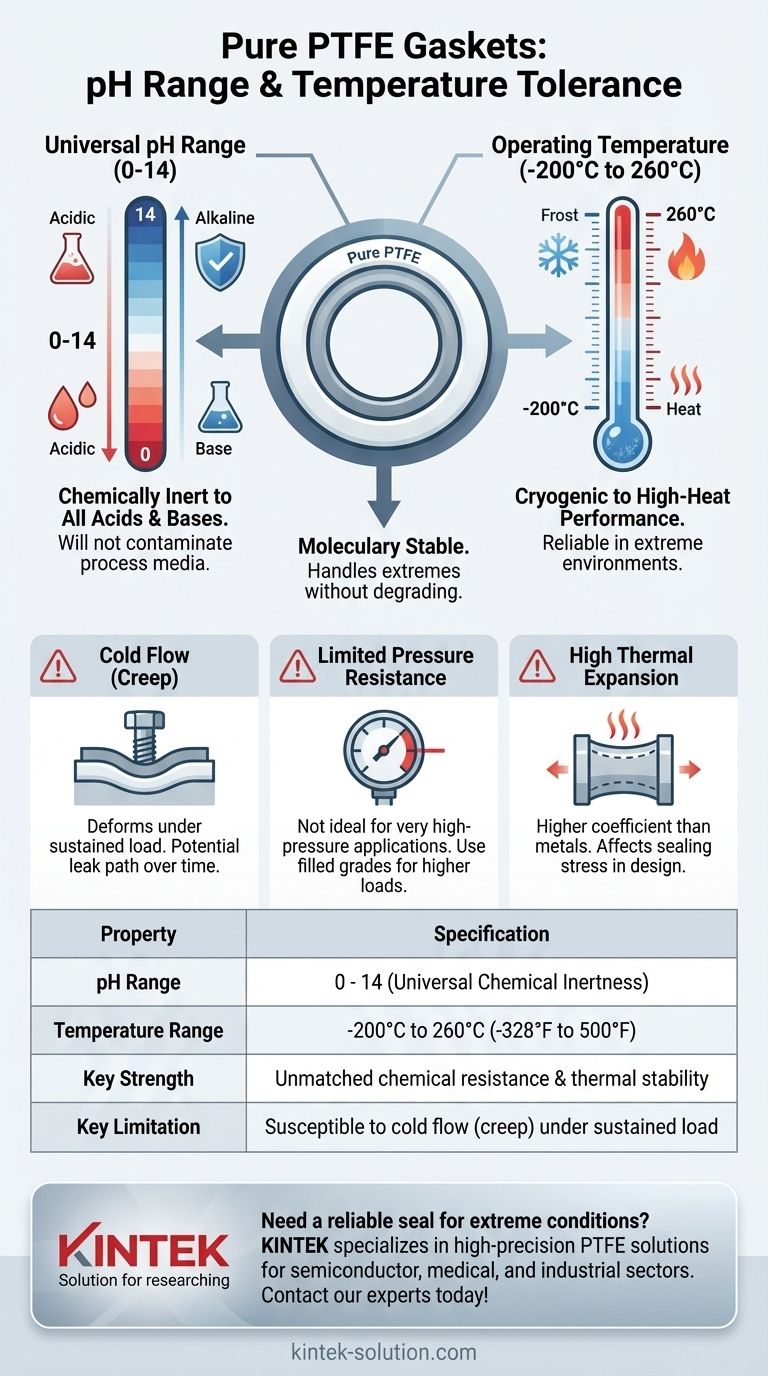
To put it directly, pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets are renowned for their exceptional chemical and thermal resilience. They have a universal pH range of 0-14, making them inert to virtually all acids and bases. Their effective operating temperature range is from approximately -200°C (-328°F) to 260°C (500°F), allowing them to function in both cryogenic and high-heat environments.
The true value of a PTFE gasket isn't just its impressive specifications, but its consistent, reliable performance across this entire spectrum. Its molecular stability is the reason it can handle both highly corrosive chemicals and extreme temperature fluctuations without degrading.

Unpacking the Chemical Resistance (pH 0-14)
What a Universal pH Range Means
A pH range of 0-14 signifies that pure PTFE is chemically inert. It will not react with, corrode, or break down when exposed to the most aggressive acids or the most caustic alkaline solutions.
This makes it a default choice in industries where fluid purity and equipment longevity are critical, as the gasket material will not contaminate the process media.
The Source of Its Inertness
PTFE's incredible resistance stems from its molecular structure. It is composed of a chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by fluorine atoms.
The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry, creating a non-reactive surface that chemicals cannot easily attack.
Understanding the Temperature Tolerance
High-Temperature Stability (Up to 260°C)
PTFE gaskets maintain excellent mechanical strength and sealing capability up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F).
This allows them to be used in high-temperature processes like chemical processing and metallurgy without losing their structural integrity or becoming brittle.
Cryogenic Performance (Down to -200°C)
Unlike many materials that become fragile and crack at low temperatures, PTFE retains its flexibility and sealing properties even in extreme cold.
This makes it a reliable choice for cryogenic applications, such as sealing flanges in systems that handle liquified gases like nitrogen.
Key Performance Trade-offs of Pure PTFE
While its chemical and thermal properties are outstanding, it's critical to understand the mechanical limitations of pure, unmodified PTFE.
The Challenge of Cold Flow (Creep)
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material that can "creep" or "cold flow" over time. Under the sustained compressive load of a bolted flange, the gasket material can slowly deform and move out of the seal area.
This can lead to a loss of bolt torque and, eventually, a potential leak path, especially in applications with high pressure or frequent temperature cycles.
Limited Pressure Resistance
Because of its softness and tendency to creep, pure PTFE is not ideal for very high-pressure applications. Modified or filled PTFE grades were developed specifically to overcome this limitation.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than the metals typically used for flanges. This means it expands and contracts more with temperature changes, which can impact the sealing stress and must be considered during joint design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the right material, you must match its properties to the primary demand of your system.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical inertness: Pure PTFE is an industry-standard choice, effectively sealing against the full 0-14 pH spectrum.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: PTFE provides reliable, continuous service up to 260°C (500°F), making it ideal for many industrial processes.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: PTFE maintains its integrity and flexibility at temperatures as low as -200°C, making it suitable for liquified gas applications.
- If your system involves high pressure or thermal cycling: Investigate filled PTFE grades (e.g., glass-filled or carbon-filled), which are specifically engineered to resist cold flow and improve mechanical stability.
Understanding both the exceptional strengths and the inherent limitations of pure PTFE is the key to leveraging it effectively for the most demanding sealing challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| pH Range | 0 - 14 (Universal Chemical Inertness) |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Key Strength | Unmatched chemical resistance and thermal stability |
| Key Limitation | Susceptible to cold flow (creep) under sustained load |
Need a reliable seal for extreme conditions? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals, gaskets, liners, and custom labware. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a sealing solution perfectly matched to your application's demands in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Let's solve your toughest sealing challenge together. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry



















