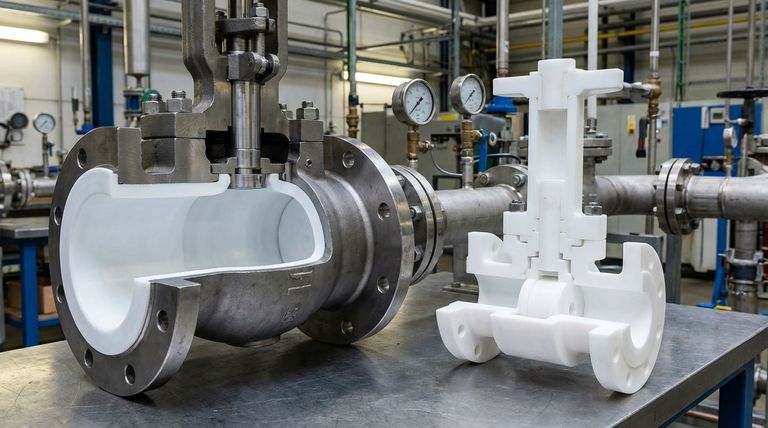
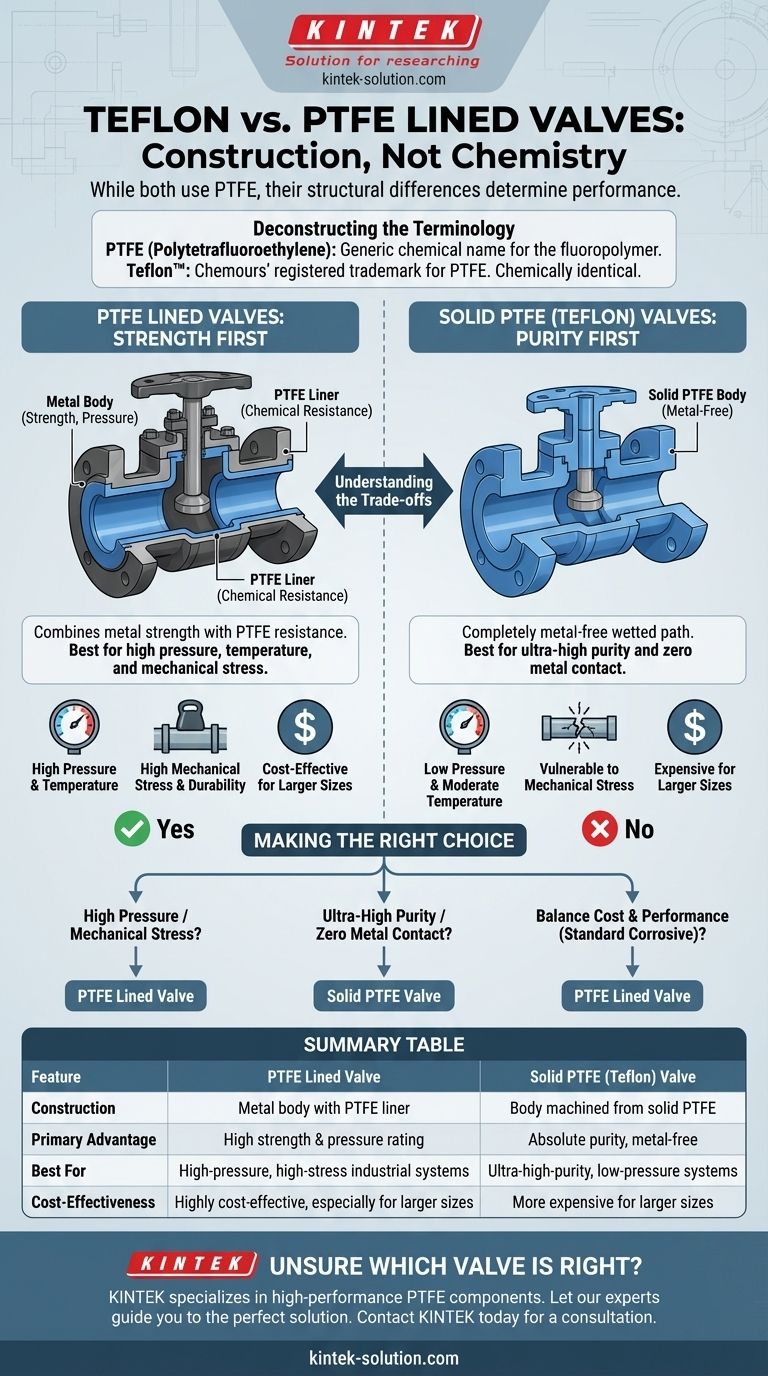
At its core, the difference between a "Teflon valve" and a "PTFE lined valve" comes down to construction, not chemistry. While both utilize the same chemically resistant material (PTFE, which Teflon is a brand name for), a PTFE lined valve has a structural metal body, whereas a "Teflon valve" is a broader term that can refer to a valve made mostly or entirely from solid PTFE.
The critical distinction is structural integrity versus total material purity. A PTFE lined valve combines the strength of metal with the chemical resistance of PTFE, while a solid PTFE valve offers a completely metal-free wetted path.

Deconstructing the Terminology: Teflon vs. PTFE
Before comparing the valves, it's crucial to clarify the names. This is a common source of confusion.
What is PTFE?
PTFE stands for Polytetrafluoroethylene. It is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical inertness and non-stick, low-friction surface.
What is Teflon?
Teflon™ is simply the registered trademark or brand name for PTFE, owned by the Chemours company. For all practical purposes in this context, the material properties of Teflon and generic PTFE are identical.
The Core Difference: Construction and Application
The real choice is not between materials, but between two fundamentally different valve designs that use the same material for chemical protection. Your decision depends entirely on the mechanical demands of your system.
PTFE Lined Valves: Strength First
A PTFE lined valve features a robust outer body, typically made of ductile iron, carbon steel, or stainless steel.
The interior surfaces of this metal body—the parts that come into contact with the fluid—are protected by a thick, seamless liner of PTFE that is mechanically locked into place.
This design delivers the best of both worlds: the immense strength, pressure rating, and rigidity of a metal valve, combined with the near-universal chemical resistance of PTFE.
Solid PTFE or "Teflon" Valves: Purity First
The term "Teflon valve" is often used to describe a valve where the body itself is machined from a solid block of PTFE, or has significant components made of solid PTFE.
These valves are used in applications where a metal body is undesirable, such as in ultra-high-purity systems or when handling specific chemicals that could react even with trace metals.
Their primary limitation is mechanical strength. They have significantly lower pressure and temperature ratings compared to lined valves and are more susceptible to pipeline stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong construction can lead to premature failure or unnecessary expense. The decision hinges on the following factors.
Pressure and Temperature Handling
A PTFE lined valve's metal body allows it to handle high system pressures and temperatures, similar to a standard metal valve.
A solid PTFE valve is limited by the physical properties of the plastic itself, making it suitable only for lower-pressure and moderate-temperature applications.
Mechanical Stress and Durability
Industrial pipelines exert significant stress from weight, vibration, and thermal expansion. The metal body of a lined valve provides the rigidity needed to withstand these forces without failing.
Solid PTFE valves are far more vulnerable to mechanical stress and must be installed and supported with extreme care to prevent cracking or deformation.
Cost Considerations
For smaller valve sizes, the costs can be comparable. However, as valve size increases, solid PTFE valves often become prohibitively expensive due to the large volume of raw PTFE material required.
PTFE lined valves typically offer a more cost-effective solution for larger pipe diameters while providing superior mechanical performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve is a matter of matching the valve's construction to the demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is high pressure or high mechanical stress: Choose a PTFE lined valve for its superior structural integrity and safety.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity or zero metal contact: A solid PTFE valve is the appropriate choice, provided the pressure and temperature are within its limits.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and performance for standard corrosive services: A PTFE lined valve is almost always the most practical, durable, and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, your choice depends on whether your application requires the absolute purity of a solid polymer or the structural robustness of metal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Lined Valve | Solid PTFE (Teflon) Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Metal body with PTFE interior liner | Body machined from solid PTFE |
| Primary Advantage | High strength & pressure rating | Absolute purity, metal-free |
| Best For | High-pressure, high-stress industrial systems | Ultra-high-purity, low-pressure systems |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Highly cost-effective, especially for larger sizes | More expensive for larger sizes |
Unsure which valve is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom valves, seals, and liners for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We can help you navigate the choice between PTFE lined and solid PTFE valves to ensure optimal performance, durability, and cost-efficiency for your specific needs.
Let our experts guide you to the perfect solution. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries



















