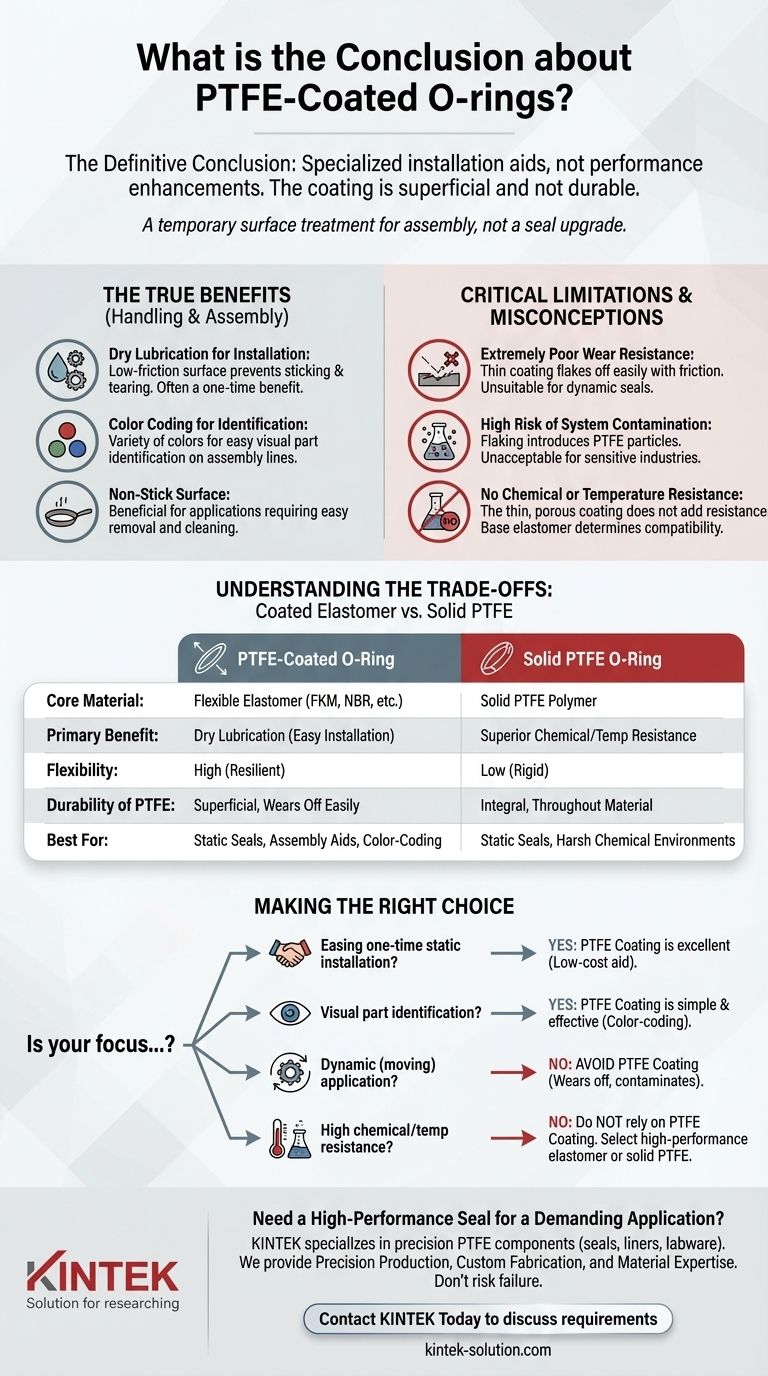
The definitive conclusion is that PTFE-coated O-rings are specialized components for very specific, limited applications. They serve primarily as an inexpensive installation aid due to their dry lubrication and as a means for color-coding parts, but the coating is superficial and not durable.
A PTFE coating should be viewed as a temporary surface treatment, not a fundamental enhancement of the O-ring's performance. The properties of the underlying elastomer (like FKM, NBR, or EPDM) remain the primary factor in determining the seal's suitability for an application.
The True Benefits of a PTFE Coating
The advantages offered by a PTFE coating are almost exclusively related to handling and assembly, not in-service performance.
Dry Lubrication for Installation
The primary benefit is the low-friction surface the coating provides. This "dry lubricant" helps prevent the O-ring from sticking, twisting, or tearing during automated or manual assembly.
However, this lubricating effect is often a one-time benefit. The coating can easily wear off during installation or shortly after.
Color Coding for Identification
PTFE coatings can be produced in a wide variety of colors. This allows for easy visual identification of O-rings by size or material compound on a busy assembly line, reducing the risk of using the incorrect part.
Non-Stick Surface
The coating creates a non-stick surface, which can be beneficial in applications where easy removal and cleaning are required.
Critical Limitations and Misconceptions
Understanding the limitations of a PTFE coating is crucial to avoid seal failure and system damage. Many perceived benefits are common misconceptions.
Extremely Poor Wear Resistance
The coating is exceptionally thin and does not bond strongly to the elastomer. It will flake or rub off easily in dynamic applications where there is any friction or movement.
For this reason, PTFE-coated O-rings are almost always unsuitable for rotating or reciprocating seals.
High Risk of System Contamination
As the coating flakes off, it introduces small particles of PTFE into the system. This contamination is unacceptable in many industries, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and food processing.
The Coating Adds No Chemical or Temperature Resistance
This is the most critical misconception. While the material PTFE itself is highly resistant, the thin, porous coating applied to an O-ring does not provide any meaningful chemical barrier.
The chemical and temperature resistance of the seal is determined entirely by the base elastomer material. You must select a core material (like FKM or FFKM) that is already compatible with your system's media and temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Coated Elastomer vs. Solid PTFE
It is vital not to confuse a PTFE-coated O-ring with a solid PTFE O-ring. They are fundamentally different components with opposing characteristics.
Flexibility and Sealing Force
A PTFE-coated O-ring is an elastomer at its core, meaning it is flexible, resilient, and generates the compression force needed to create a robust seal.
A solid PTFE O-ring is rigid and has a very high compression set. It does not rebound well after being compressed, making it a poor choice for most standard O-ring applications that require a reliable, long-term seal.
Durability and Performance
The performance of a PTFE-coated O-ring is defined by its core material. The coating is a superficial, non-durable layer.
A solid PTFE O-ring offers exceptional chemical and temperature resistance through its entire body, but its lack of flexibility is a major design constraint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use this guide to determine if a PTFE-coated O-ring is appropriate.
- If your primary focus is easing a difficult, one-time static installation: A PTFE coating is an excellent, low-cost choice to prevent twisting and tearing during assembly.
- If your primary focus is visual part identification on an assembly line: The color-coding capabilities of PTFE coatings are a simple and effective solution.
- If you need a seal for a dynamic (moving) application: Avoid PTFE-coated O-rings entirely, as the coating will wear off and cause contamination.
- If you require high chemical or temperature resistance: Do not rely on a PTFE coating for protection. Select a high-performance elastomer like FKM, FFKM, or a solid PTFE seal if the design allows for its rigidity.
Ultimately, a PTFE coating is a surface treatment for assembly, not a performance upgrade for the seal itself.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE-Coated O-Ring | Solid PTFE O-Ring |
|---|---|---|
| Core Material | Flexible Elastomer (FKM, NBR, etc.) | Solid PTFE Polymer |
| Primary Benefit | Dry Lubrication for Easy Installation | Superior Chemical/Temperature Resistance |
| Flexibility | High (Resilient) | Low (Rigid) |
| Durability of PTFE | Superficial, Wears Off Easily | Integral, Throughout the Material |
| Best For | Static Seals, Assembly Aids, Color-Coding | Static Seals in Harsh Chemical Environments |
Need a High-Performance Seal for a Demanding Application?
PTFE-coated O-rings serve a specific purpose, but many applications require a more robust, custom-engineered solution. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We understand that the right seal is critical to your system's performance and longevity. Whether you need a custom elastomer seal, a solid PTFE component, or expert guidance to select the best material, we provide:
- Precision Production: Ensuring exact specifications for reliable performance.
- Custom Fabrication: From initial prototypes to high-volume orders.
- Material Expertise: Helping you choose the optimal solution for chemical compatibility, temperature, and pressure.
Don't let an inadequate seal risk contamination or failure. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution engineered for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PTFE sheet lining in chemical tanks? Achieve Ultimate Corrosion Protection
- Why are PTFE lined ball valves suitable for the food and pharmaceutical industries? Ensuring Purity and Compliance
- What are the advantages of PTFE ball valves? Superior Chemical Resistance & Low-Torque Operation
- What are the three main factors to consider when selecting ball valve seat materials? Ensure System Reliability
- What materials are used for jacket profiles and springs in PTFE seals? A Guide to Material Selection
- What are the key properties of PTFE gaskets that make them effective sealing solutions? Unmatched Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- What is a PTFE lined butterfly valve and how does it work? Control Corrosive & Pure Fluids Safely
- What are some custom grades of PTFE and their compositions? Engineered for Wear, Strength, and Lubricity



















