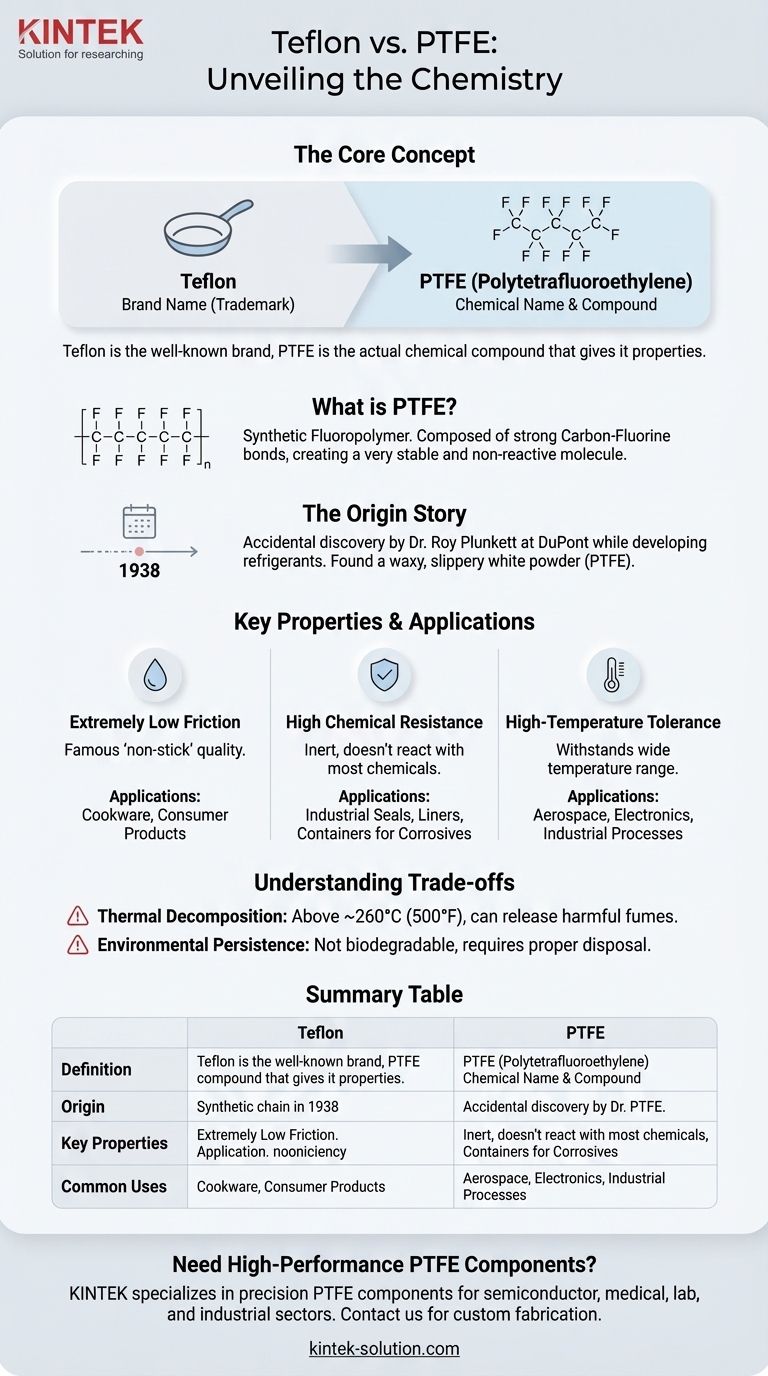
The chemical name for Teflon is Polytetrafluoroethylene, and its common abbreviation is PTFE. While "Teflon" is the well-known brand name, PTFE is the actual chemical compound that gives the material its unique properties. This distinction is crucial for understanding its applications in both consumer and industrial contexts.
The core takeaway is that "Teflon" is not a chemical name itself, but a registered trademark for the chemical Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Understanding this helps clarify that many products use PTFE, even if they aren't branded as Teflon.

From Chemical Compound to Household Name
The relationship between PTFE and Teflon is similar to that between "facial tissue" and "Kleenex." One is the generic chemical or product, and the other is a specific, well-known brand.
What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)?
PTFE is a synthetic fluoropolymer, which is a type of plastic. It is composed of a long chain of carbon atoms, with each carbon atom bonded to two fluorine atoms.
This strong carbon-fluorine bond is the source of many of PTFE's most valuable characteristics. It creates a very stable and non-reactive molecule.
The Origin of the "Teflon" Brand
Teflon was the result of an accidental discovery in 1938 by a scientist named Dr. Roy Plunkett at DuPont. He was working on developing a new refrigerant gas.
He found that a pressurized bottle of the gas appeared empty but still had weight. Upon cutting it open, he discovered a waxy, incredibly slippery white powder inside, which was the newly created PTFE.
DuPont patented the substance and registered the Teflon trademark. The brand is now owned by a spin-off company, Chemours.
Key Properties of PTFE
The unique molecular structure of Polytetrafluoroethylene gives it a powerful combination of useful properties that make it essential in many industries.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This is what creates its famous "non-stick" quality, making it ideal for cookware.
High Chemical Resistance
The strong carbon-fluorine bonds make PTFE inert, meaning it does not react with most chemicals. This allows it to be used in pipes and containers for corrosive substances.
High-Temperature Tolerance
PTFE can withstand a wide range of temperatures without degrading, making it suitable for applications in aerospace, electronics, and demanding industrial processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is incredibly useful, it's important to be aware of its limitations and the associated concerns.
Thermal Decomposition
When heated above approximately 500°F (260°C), PTFE can begin to break down and release potentially harmful fumes. This is the primary concern cited regarding non-stick cookware used at very high heat.
Environmental Persistence
Like many plastics, PTFE is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for a very long time. Proper disposal and recycling are critical considerations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the terminology helps you identify the right material for a specific application, whether you are a consumer or an engineer.
- If your primary focus is consumer products: You are likely looking for the Teflon brand or other branded non-stick coatings, but the underlying technology is almost always PTFE.
- If your primary focus is industrial or engineering applications: You should refer to the material by its chemical name, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), to ensure you are specifying the exact material properties required.
Ultimately, knowing that Teflon is simply a brand name for PTFE empowers you to look beyond marketing and focus on the fundamental properties of the material itself.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Teflon | PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Brand Name (Trademark) | Chemical Name (Polytetrafluoroethylene) |
| Origin | Discovered by DuPont in 1938 | Synthetic Fluoropolymer |
| Key Properties | Non-stick, Low Friction | Chemically Inert, High-Temperature Resistance |
| Common Uses | Non-stick Cookware | Industrial Seals, Liners, Labware |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our custom fabrication ensures durability, chemical resistance, and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your PTFE requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE compare to Polycarbonate (PC) in impact resistance and thermal properties? A Guide to Material Selection
- How does PTFE perform in chemical-heavy environments? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications
- How does Teflon demonstrate superior chemical resistance? Unlocking Its Molecular Fortress
- What family of substances does PTFE belong to? Understanding PFAS & Fluoropolymer Safety
- Why is it dangerous to overheat Teflon cookware? Avoid Toxic Fumes & Protect Your Family
- Why is PTFE compliance with USDA and FDA standards important? Ensure Safety in Food, Pharma & Medical
- What certifications does the manufacturer of PTFE products have? Ensure Quality with ISO 9001 Certification
- What are some common household uses of Teflon? Discover the Material Science in Your Home



















