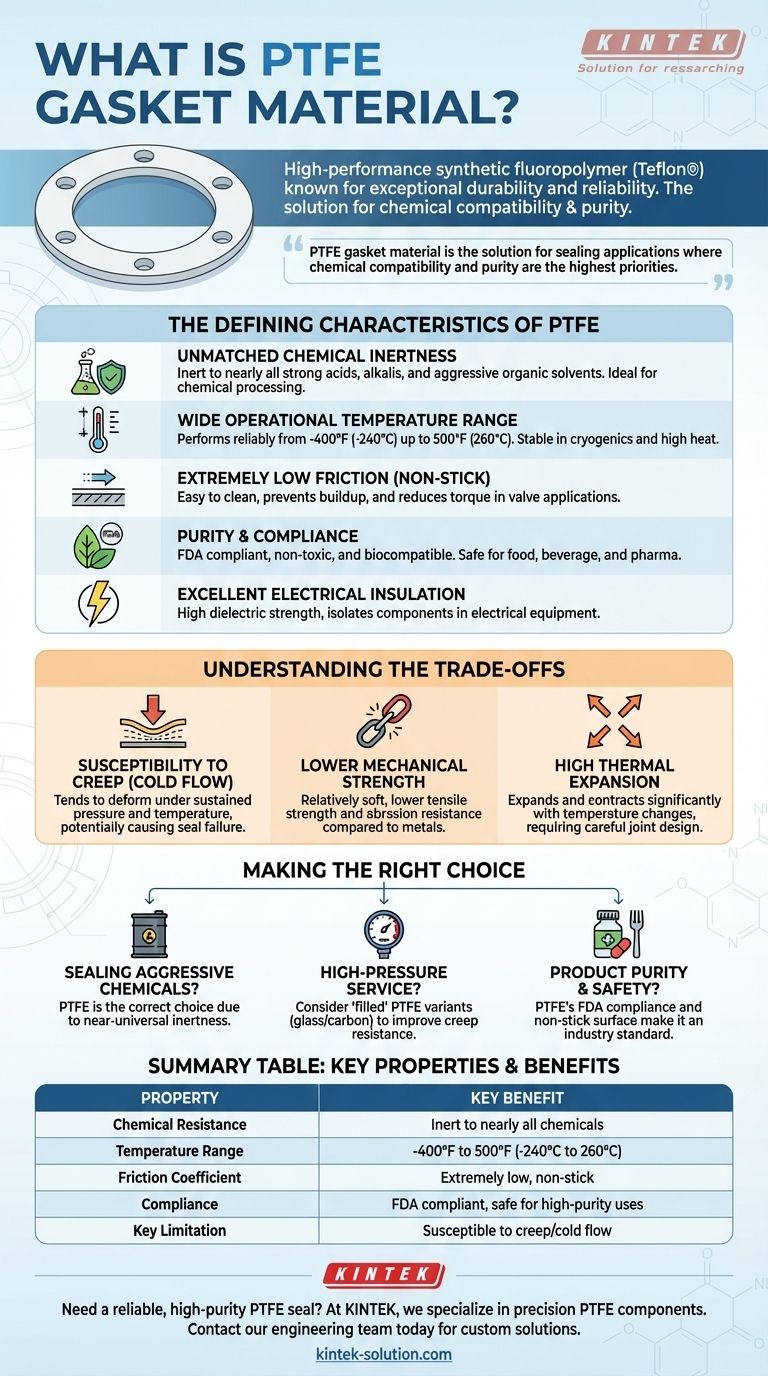
In essence, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer used to create exceptionally durable and reliable gaskets. Often known by the trade name Teflon®, its primary value comes from an unparalleled resistance to virtually all industrial chemicals and its ability to function across an extremely wide temperature range. This unique combination of properties makes it a default choice for the most demanding sealing applications.
PTFE gasket material is the solution for sealing applications where chemical compatibility and purity are the highest priorities. However, understanding its mechanical limitations, such as its tendency to deform under pressure, is critical for ensuring a long-lasting seal.

The Defining Characteristics of PTFE
PTFE's reputation is built on a specific set of high-performance characteristics. These properties work in concert to provide a reliable seal in environments where other materials would quickly fail.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The standout feature of PTFE is its outstanding chemical resistance. It is inert to nearly all chemicals, including strong acids, alkalis, and aggressive organic solvents.
This makes it an ideal choice for equipment in chemical processing plants, laboratories, and any application involving corrosive substances.
Wide Operational Temperature Range
PTFE performs reliably across a vast spectrum of temperatures. It maintains its integrity and sealing capability in conditions ranging from cryogenic lows of -400°F (-240°C) up to high heat of 500°F (260°C).
This stability ensures a consistent seal despite significant thermal cycling or extreme operating environments.
Extremely Low Friction (Non-Stick Surface)
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This creates a non-stick surface that is easy to clean and prevents material buildup.
In applications like valves, this low-friction property can also reduce the torque required for operation.
Purity and Compliance
PTFE is inherently non-toxic and can comply with strict regulatory standards. It meets FDA requirements, making it safe for direct contact with food, beverages, and pharmaceuticals.
Its biocompatibility and the fact that it has virtually no extractables ensure that it will not contaminate the process media.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
As a material with high dielectric strength, PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. This property makes it valuable for creating gaskets that must isolate components in electrical enclosures or equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, pure PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its mechanical limitations, which are critical for proper application.
Susceptibility to Creep and Cold Flow
The most significant limitation of virgin PTFE is its tendency toward creep, or cold flow. Under sustained pressure and temperature, the material can slowly deform and flow out of the seal.
This can lead to a loss of bolt torque and, eventually, a failed seal. This is especially true in high-pressure applications or on flanges with uneven surfaces.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metallic or many fiber-based gasket materials, PTFE is relatively soft. While this aids in conformability on irregular flanges, it also means it has lower tensile strength and resistance to abrasion.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes more than many other materials. This high coefficient of thermal expansion must be accounted for in the design of the joint to prevent stress and potential leaks during thermal cycling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket material requires matching its properties to the primary demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals: PTFE is almost certainly the correct choice due to its near-universal chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure service: You should consider "filled" PTFE variants, which incorporate materials like glass or carbon to drastically improve resistance to creep and cold flow.
- If your primary focus is product purity and safety: PTFE's compliance with FDA regulations and its non-toxic, non-stick surface make it an industry standard for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical processing.
Ultimately, understanding both the exceptional strengths and the inherent weaknesses of PTFE is the key to engineering a safe and reliable seal.
Summary Table:
| Property | Characteristic | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all chemicals | Ideal for corrosive environments |
| Temperature Range | -400°F to 500°F (-240°C to 260°C) | Stable in extreme heat or cryogenics |
| Friction Coefficient | Extremely low | Non-stick, easy to clean, reduces torque |
| Compliance | FDA compliant, non-toxic | Safe for food, pharma, and high-purity uses |
| Key Limitation | Susceptible to creep/cold flow | Requires design consideration for pressure |
Need a reliable, high-purity PTFE seal for your critical application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and specialized industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures a solution that combines chemical resistance, thermal stability, and compliance with your strictest standards.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your specific requirements and receive a custom solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















