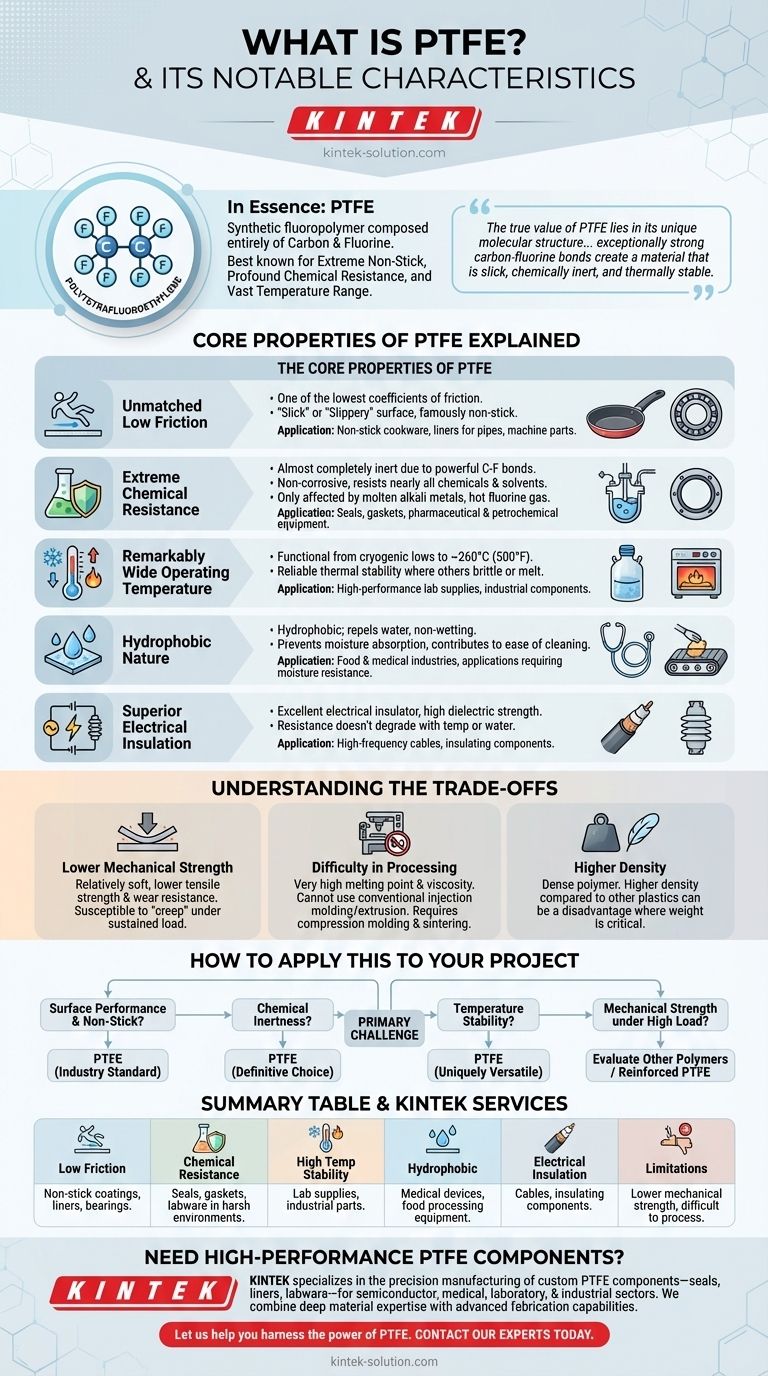
In essence, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer composed entirely of carbon and fluorine. It is best known for its extreme non-stick properties, profound chemical resistance, and ability to withstand a vast range of temperatures, making it a critical material in demanding industrial, laboratory, and consumer applications.
The true value of PTFE lies in its unique molecular structure. The exceptionally strong carbon-fluorine bonds create a material that is simultaneously slick, chemically inert, and thermally stable, a combination of properties rarely found in other polymers.

The Core Properties of PTFE Explained
To understand why PTFE is so widely used, we must look at the practical implications of its primary characteristics. These properties are not isolated; they work together to create an incredibly versatile material.
Unmatched Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This gives it a "slick" or "slippery" surface that is famously non-stick.
This characteristic is the reason it is used as a coating on non-stick cookware and as a liner for pipes and machine parts, where it reduces wear and allows for the smooth handling of materials.
Extreme Chemical Resistance
The powerful bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms make PTFE almost completely inert. It is non-corrosive and resists nearly all chemicals and solvents.
Only highly reactive substances like molten alkali metals or hot fluorine gas can affect it. This makes it indispensable for seals, gaskets, and equipment in the pharmaceutical and petrochemical industries.
A Remarkably Wide Operating Temperature
PTFE remains functional and stable across an extraordinary temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows up to a service temperature of approximately 260°C (500°F).
This thermal stability allows it to perform reliably in environments where most other plastics would become brittle or melt, making it ideal for high-performance lab supplies and industrial components.
Hydrophobic Nature
PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and is non-wetting. This property prevents moisture absorption and contributes to its ease of cleaning.
Because liquids bead up on its surface, it is highly effective in applications requiring moisture resistance or pristine, easily sanitized surfaces, such as in the food and medical industries.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. Its resistance to electricity does not degrade with temperature or exposure to water, making it a reliable choice for high-frequency cables and insulating components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. To use PTFE effectively, it's critical to understand its limitations. Being objective about these trade-offs is key to successful engineering and design.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE is relatively soft and has lower tensile strength and wear resistance. It can be susceptible to "creep," a slow deformation that occurs under a sustained load.
Difficulty in Processing
Due to its very high melting point and high melt viscosity, PTFE cannot be processed using conventional methods like injection molding or extrusion. It typically requires specialized techniques like compression molding and sintering.
Higher Density
PTFE is a dense polymer. In applications where weight is a critical factor, its higher density compared to other plastics can be a significant disadvantage.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the right material depends entirely on the primary challenge you need to solve. Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE is the optimal choice for your needs.
- If your primary focus is surface performance and non-stick properties: PTFE is the industry standard for creating low-friction, easy-release, and easy-to-clean surfaces.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness: It is the definitive choice for components that will be exposed to aggressive or corrosive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is temperature stability: Its ability to perform reliably in both extreme cold and high-heat environments makes it uniquely versatile.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength under high load: You should evaluate other engineering polymers or consider reinforced grades of PTFE.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's distinct profile of strengths and limitations is the key to leveraging its power in the right context.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Practical Implication | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low Friction | Non-stick, reduces wear | Non-stick coatings, pipe liners, bearings |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to most chemicals | Seals, gaskets, labware in harsh environments |
| High Temp Stability | Stable from cryogenic to 260°C (500°F) | High-performance lab supplies, industrial parts |
| Hydrophobic | Repels water, easy to clean | Medical devices, food processing equipment |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength | High-frequency cables, insulating components |
| Limitations | Lower mechanical strength, difficult to process | Not ideal for high-load applications without reinforcement |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Project?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine deep material expertise with advanced fabrication capabilities to deliver solutions that leverage PTFE's unique properties to solve your specific challenges, from prototyping to high-volume production.
Let us help you harness the power of PTFE. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What temperature range can PTFE withstand? Master Its -200°C to 260°C Operating Window
- What is PTFE and what are its common uses in industrial applications? Discover the Ultimate High-Performance Polymer
- What are the properties and applications of carbon-filled PTFE? Enhance Performance in Demanding Environments
- In what applications is PTFE commonly used? Unlock Its Versatility Across Industries
- What impact has PTFE industrial coating had on daily life? Unlocking Modern Convenience & Performance
- What are the cost differences between Nylon and PTFE? A Guide to Smart Material Selection
- What are the general characteristics of PTFE as a material? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the key properties of Teflon (PTFE) that make it suitable for industrial applications?



















