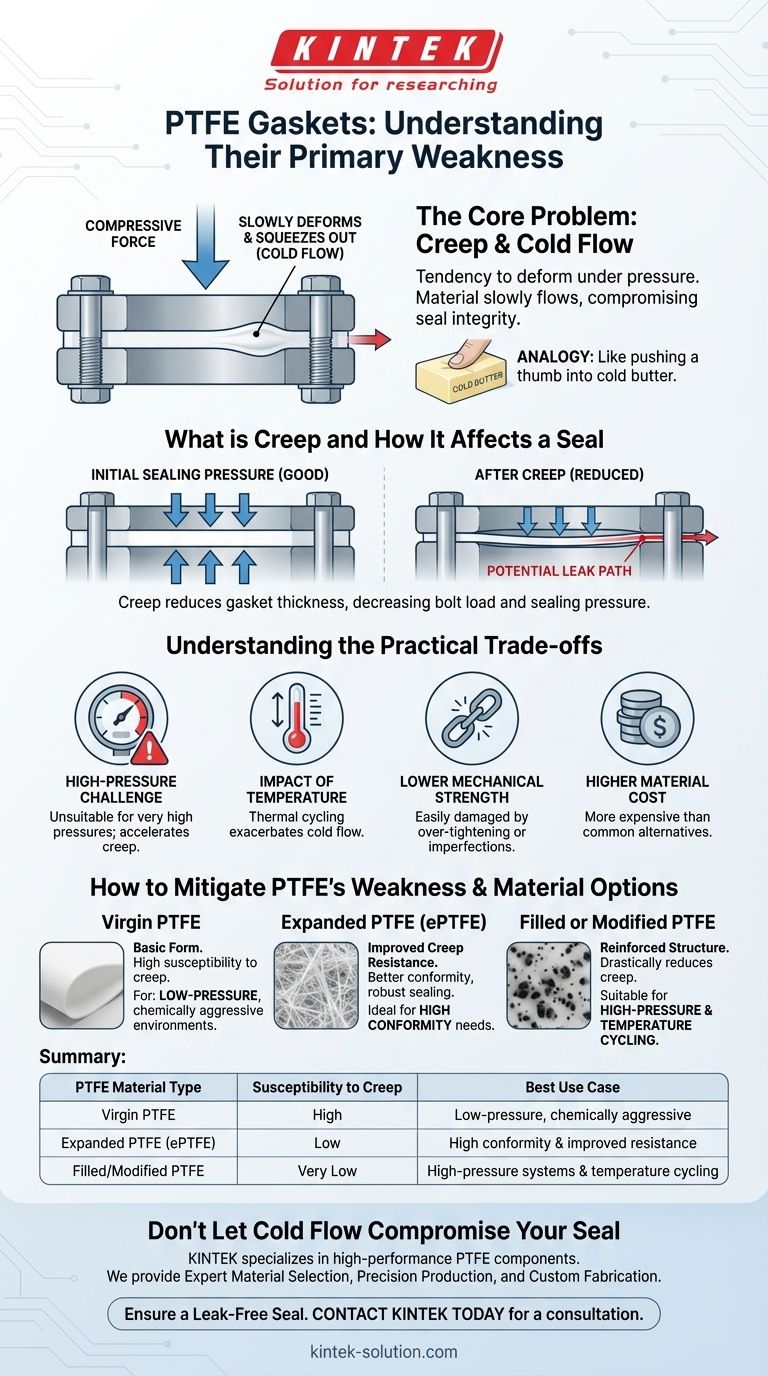
The principal weakness of PTFE gaskets and sheets is their tendency to deform under pressure, a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow. This means that when a compressive force is applied—such as tightening the bolts on a flange—the material can slowly "flow" or squeeze out from its intended shape over time, potentially compromising the integrity of the seal.
While PTFE offers world-class chemical and thermal resistance, its inherent softness is its critical trade-off. This softness leads to "cold flow," where the gasket material slowly deforms under pressure, which can reduce sealing force and lead to potential leaks in demanding applications.

The Core Problem: Creep and Cold Flow Explained
The defining limitation of standard PTFE is directly linked to its physical structure. While this structure provides incredible chemical inertness, it also makes the material susceptible to deformation under mechanical stress.
What is Creep and Cold Flow?
Creep, or cold flow, is the slow, continuous deformation of a solid material under a constant, long-term mechanical load.
Imagine slowly pushing your thumb into a block of cold butter. Even with steady pressure, your thumb will gradually sink deeper. This is analogous to how a PTFE gasket behaves under the constant pressure of a bolted flange.
How This Affects a Gasket Seal
A gasket's function is to maintain a constant sealing pressure between two surfaces. It must be resilient enough to push back against the compressive force of the flanges.
When a PTFE gasket creeps, it effectively becomes thinner in the compressed area. This reduction in thickness lessens the gasket's "push back," decreasing the bolt load and the overall sealing pressure, creating a potential path for leaks.
Why PTFE is Susceptible
Standard, or "virgin," PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. Its molecular structure allows for this gradual movement when subjected to a compressive load, especially at ambient or elevated temperatures. This is a fundamental property of the material itself.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
This tendency to deform creates several practical considerations you must account for when designing a system or choosing a gasket material.
The High-Pressure Challenge
Because of cold flow, standard PTFE gaskets are often unsuitable for very high-pressure applications. The immense compressive force required to contain high pressures will accelerate the rate of creep, increasing the risk of seal failure.
The Impact of Temperature
While PTFE has an excellent operational temperature range (from -100°C to over 240°C), it is not ideal for applications with large, rapid temperature fluctuations. Thermal cycling causes flanges to expand and contract, which can alter bolt loads and exacerbate the cold flow problem.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metallic or even some composite gasket materials, PTFE has lower overall mechanical strength. It can be more easily damaged by over-tightening or imperfections on flange surfaces.
Higher Material Cost
Another practical consideration is cost. Due to the complex manufacturing process of the PTFE polymer, these gaskets are typically more expensive than common rubber or non-asbestos alternatives.
How to Mitigate PTFE's Weakness
Engineers have developed several variations of PTFE to overcome the inherent weakness of cold flow, allowing the material to be used in more demanding services.
Virgin PTFE
This is the most basic form and the most susceptible to creep. It is best suited for low-pressure applications where its chemical purity and inertness are the primary requirements.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
During manufacturing, PTFE can be expanded to create a strong, fibrous structure. This ePTFE material has dramatically improved creep resistance and is much better at conforming to irregular surfaces, making it a far more robust sealing solution.
Filled or Modified PTFE
Adding filler materials—such as glass, silica, or carbon—to the PTFE matrix significantly enhances its mechanical properties. These fillers act as a reinforcing structure, drastically reducing the gasket's tendency to creep and cold flow, making it suitable for higher pressures and temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket material requires balancing performance needs with material limitations.
- If your primary focus is containing aggressive chemicals in a low-pressure, stable system: Standard virgin PTFE is often a sufficient and effective choice.
- If your application involves high pressure or significant temperature cycling: You must use an enhanced material like expanded (ePTFE) or filled PTFE to prevent seal failure from creep.
- If your application is for general use and cost-sensitive: A traditional rubber or composite gasket may be a more economical choice, provided it meets the chemical and temperature requirements.
Understanding PTFE's tendency to creep is the key to selecting the right variant for your specific conditions, ensuring a reliable and long-lasting seal.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Material Type | Susceptibility to Creep/Cold Flow | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | High | Low-pressure, chemically aggressive environments |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Low | Applications requiring high conformity and improved creep resistance |
| Filled/Modified PTFE | Very Low | High-pressure systems and applications with temperature cycling |
Don't Let Cold Flow Compromise Your Seal
Understanding PTFE's limitations is the first step to selecting the perfect gasket material for your demanding application. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We go beyond standard offerings to provide solutions that mitigate weaknesses like creep:
- Expert Material Selection: We help you choose the right PTFE variant—whether virgin, expanded, or filled—to ensure long-term seal integrity.
- Precision Production: Our components are manufactured to exact specifications for reliable performance under pressure.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we engineer PTFE parts tailored to your specific operational pressures and temperatures.
Ensure a leak-free, reliable seal. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on your PTFE component needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What temperature range can expanded PTFE gaskets withstand? From Cryogenic -200°C to High-Temp 260°C
- What chemical resistance properties does PTFE bellow seal possess? Unmatched Protection Against Corrosive Media
- What are the additional benefits of PTFE in bridge bearing design? Enhance Durability & Lower Maintenance Costs
- What types of PTFE shapes are available? From Stock Forms to Custom Components
- Are Teflon parts capable of withstanding high temperatures? Understanding the 260°C Limit for Performance
- What are the main benefits of PTFE envelope gaskets? Achieve Superior Chemical Resistance and Sealing Integrity
- What is the significance of the low friction coefficient in PTFE processing machines? Enhance Quality and Machine Life
- What future trends are expected in Teflon parts machining? AI, Automation, and Sustainability



















